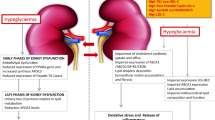
Abstract
Although several factors may mediate the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy, hyperlipidemia is now considered an independent and major determinant of progression of renal disease in diabetes. The following discussion focuses on the experimental evidence that incriminates hyperlipidemia as a pathogenic factor for diabetic nephropathy and the potential mechanisms that may mediate renal injury from hyperlipidemia, as well as the clinical studies involving therapeutic interventions for hyperlipidemia and their impact on progression of diabetic renal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Ayodele OE, Alebiosu CO, Salako BL: Diabetic nephropathy —a review of the natural history, burden, risk factors and treatment. J Natl Med Assoc 2004, 96:1445–1454.
Parving HH, Mauer M, Ritz E: Diabetic nephropathy. In Brenner & Rector’s The Kidney, edn 7. Edited by Brenner BM. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2004:1777–1818.
Moorhead JF, El Nahas M, Chan MK, Varghese Z: Lipid nephrotoxicity in chronic progressive glomerular and tubulo-interstitial disease. Lancet 1982, 1:1309–1311.
Krolewski AS, Warram JHG, Christlies AR: Hypercholesterolemia-A determinant of renal function loss and deaths in IDDM patients with nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 1994, 45:S125-S131.
Ravid M, Neumann L, Lishner M: Plasma lipids and the progression of nephropathy in diabetes mellitus type 2: effect of ACE inhibitors. Kidney Int 1995, 47:907–910.
Gall MA, Hougaard P, Barch-Johnsen K, et al.: Risk factors for development of incipient and overt diabetic nephropathy in patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: prospective observational study. BMJ 1997, 314:783–788.
Klein R, Klein BEK, Moss SE, et al.: The 10-year incidence of renal insufficiency in people with type-1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999, 22:743–751.
Bonnet F, Cooper ME: Potential influence of lipids in diabetic nephropathy: insights from experimental data and clinical studies. Diabetes Metab 2000, 26:254–264.
Hirano T: Lipoprotein abnormalities in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 1999, 71:S22-S24.
Chen HC, Guh JY, Chang JM, et al.: Role of lipid control in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 2005, 67:S60-S62. The authors extensively review the role of lipid in mediating renal injury and the beneficial effects of lipid control in DN.
Trovati M, Cavalot F: Optimization of hypolipidemic and antiplatelet treatment in the diabetic patient with renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004, 15:S12-S20.
Kahri J, Groop PH, Elliott T, et al.: Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein and its relationship to plasma lipoproteins and apolipoprotein A-I containing lipoproteins in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria and clinical nephropathy. Diabetes Care 1994, 17:412–419.
Groop PH, Elliott T, Ekstrand A, et al.: Multiple lipoprotein abnormalities in type I diabetic patients with renal disease. Diabetes 1996, 45:974–979.
Jensen T, Stender S, Deckert T: Abnormalities in plasma concentrations of lipoproteins and fibrinogen in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with increased urinary albumin excretion. Diabetologia 1988, 31:142–145.
Jerums G, Allen TJ, Tsalamandris C, et al.: Relationship of progressively increasing albuminuria to apoprotein[a] and blood pressure in type 2 (non insulin-dependent) and type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1993, 36:1037–1044.
Kasiske BL, O’Donnell MP, Schmitz PG, et al.: The renal injury of diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rats. Kidney Int 1990, 37:880–891.
Misra Luthra K, Misra A, Srivastava LM: Lipoprotein (a): biology and role in atherosclerotic vascular disease. Curr Sci 1999, 76:1553–1560.
Grone HJ, Hohbach J, Grone EF: Modulation of glomerulosclerosis and interstitial fibrosis by native and modi.ed lipoprotein. Kidney Int Suppl 1996, 49:S18-S22.
Chander PN, Gealekman O, Brodsky SV, et al.: Nephropathy in Zucker diabetic fat rat is associated with oxidative and nitrosative stress: prevention by chronic therapy with a peroxynitrite scavenger ebselen. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004, 15:2391–2403.
Takemura T, Yoshioka K, Aya N, et al.: Apolipoproteins and lipoprotein receptors in glomeruli in human kidney diseases. Kidney Int 1993, 43:918–927.
Guijarro C, Kasiske BL, Kim Y, et al.: Early glomerular changes in rats with dietary-induced hypercholesterolemia. Am J Kidney Dis, 1995, 26:152–161.
Pesek-Diamond I, Ding G, Frye J, Diamond JR: Macrophages mediate adverse effects of cholesterol feeding in experimental nephrosis. Am J Physiol 1992, 263:F776-F783.
Cooper ME, Jandeleit-Dahm KAM: Lipids and diabetic renal disease. Curr Diab Rep 2005, 5:445–448.
Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P, Benigni A: Understanding the nature of renal disease progression. Kidney Int 1997, 51:2–15.
Schlondorff D: Cellular mechanisms of lipid injury in the glomerulus. Am J Kidney Dis 1993, 22:72–82.
Krane V, Wanner C: At which stage of chronic kidney disease should dyslipidemia be treated? Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2006, 2:176–177.
Keilani T, Schlueter W, Batlle D: Selected aspects of ACE inhibitor therapy for patients with renal disease: impact on proteinuria, lipids and potassium. J Clin Pharmacol 1995, 35:87–97.
Mulec H, Johnsen SA, Wiklund O, Bjorck S: Cholesterol: a renal risk factor in diabetic nephropathy? Am J Kidney Dis 1993, 22:196–201.
Wilson WF, Myers RH, Larson MG, et al.: Apolipoprotein E alleles, dyslipidemia and coronary artery disease: the Framingham offspring study. JAMA 1994, 272:1666–1671.
Chowdhury TA, Dyer PH, Kumar S, et al.: Association of apolipoprotein epsilon2 allele with diabetic nephropathy in Caucasian subjects with NIDDM. Diabetes 1998, 47:278–280.
Werle E, Fiehn W, Hasslacher C: Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and renal function in German type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1998, 21:994–998.
Onuma T, Laffel LM, Angelico MC, Krolewski AS: Apolipoprotein E genotypes and risk of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 1996, 7:1075–1078.
Hadjadj S, Gallois Y, Bouhanick B, et al.: Lack of contribution of lipid gene polymorphisms to IDDM nephropathy: the GENEDIAB Study [abstract]. Diabetologia 1998, 41(suppl 1):A293.
Eto M, Saito M, Okada M, et al.: Apolipoprotein e genetic polymorphism, remnant lipoproteins, and nephrology in type 2 diabetic patients. Am J Kidney Dis 2002, 40:243–251.
Kimura H, Suzuki Y, Gejyo F, et al.: Apolipoprotein E4 reduces risk of diabetic nephropathy in patients with NIDDM. Am J Kidney Dis 1998, 31:666–673.
Boizel R, Benhamou PY, Corticelli P, et al.: Apo E polymorphism and albuminuria in diabetes mellitus: a role for LDL in the development of nephropathy in NIDDM? Nephrol Dial Transplant 1998, 13:72–75.
Forbes JM, Cooper ME, Old field MD, Thomas MC: Role of advanced glycation end products in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003, 14:S254-S258.
Lassila M, Seah KK, Allen TJ, et al.: Accelerated nephropathy in diabetic apolipoprotein E-knockout mouse: role of advanced glycation end products. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004, 15:2125–2138.
McFarlane SI, Muniyappa R, Francisco R, Sowers JR: Pleiotropic effects of statins: lipid reduction and beyond. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002, 87:1457–1458.
Athyros VG, Papageorgiou AA, Elisaf M, Mikhalidis DP: Statins and renal function in patients with diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Res Opin 2003, 19:615–617.
Inman SR, Stowe NT, Cressman MD, et al.: Lovastatin preserves renal function in experimental diabetes. Am J Med Sci 1999, 317:215–221.
Kim SI, Han DC, Lee HB: Lovastatin inhibits transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression in diabetic rat glomeruli and cultured rat mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000, 11:80–87.
Jandeleit-Dahm K, Cao Z, Cox AJ, et al.: Role of hyperlipidemia in progressive renal disease: focus on diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 1999, 56:S31-S36.
Lee SK, Jin SY, Han DC, et al.: Effects of delayed treatment with enalapril and/or lovastatin on the progression of glomerulosclerosis in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1993, 8:1338–1343.
Park YS, Guijarro C, Kim Y, et al.: Lovastatin reduces glomerular macrophage in flux and expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 mRNA in nephrotic rats. Am J Kidney Dis 1998, 31:190 -194.
Fried LF, Orchard TJ, Kasiske BL: The effect of lipid reduction on renal disease progression. A meta-analysis. Kidney Int 2001, 59:260–269.
Lam KSL, Cheng IKP, Janus ED, et al.: Cholesterollowering therapy may retard the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 1995, 38:604–609.
Tonolo G, Calvia P, Ciccarese M, et al.: Reduction of albuminuria predicts diminished progression in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 1994, 45:S145-S149.
Smulders YM, van Eeden AE, Stehouwer CD, et al.: Can reduction in hypertriglyceridaemia slow progression of microalbuminuria in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus? Eur J Clin Invest 1997, 27:997–1002.
Harris KPG, Wheeler DC, Chong CC: A placebo-controlled trial examining atorvastatin in dyslipidemic patients undergoing CAPD. The Atorvastatin in CAPD Study investigators. Kidney Int 2002, 61:1469–1474.
PDR Drug Interactions. In The PDR Electronic Library Version. Montvale, NJ: Thomson PDR; 2004:6.1.301A-304A.
Weiner DE, Sarnak MJ: Managing dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease. J Gen Intern Med 2004, 19:1045–1052.
The effect of aggressive versus standard lipid lowering by atorvastatin on diabetic dyslipidemia. The Diabetes Atorvastatin Lipid Intervention (DALI) Study Group [no authors listed]. Diabetes Care 2001, 24:1335-1341.
Wanner C, Krane V, Marz W, et al.: Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 2005, 353:238–248.
Owada A, Suda, S, Hata T: Antiproteinuric effect of niceritrol, a nicotinic acid derivative, in chronic renal disease with hyperlipidemia: a randomized trial. Am J Med 2003, 114:347–353.
Stewart KJ: Exercise training and the cardiovascular consequences of type-2 diabetes and hypertension. Plausible mechanisms for improving cardiovascular health. JAMA 2002, 288:1622–1631.
Nakamura T, Kawagoe Y, Ogawa H, et al.: Effect of low-density lipoprotein apheresis on urinary protein and podocyte excretion in patients with nephrotic syndrome due to diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 2005, 45:48–53. The authors describe a relatively new modality of therapy that in.uenced proteinuria and the progression of DN.
Haffner SM; American Diabetes Association: Management of dyslipidemia in adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26(suppl 1):S83-S86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosario, R.F., Prabhakar, S. Lipids and diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep 6, 455–462 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-006-0079-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-006-0079-7