Abstract
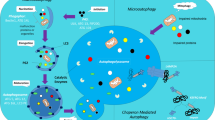
Autophagy is a catabolic pathway for bulk destruction of long-lived proteins and organelles via lysosomes. Basal autophagy represents a reparative, life-sustaining process, but unrestrained autophagic activity promotes cell death. A growing body of evidence suggests that autophagy occurs in advanced atherosclerotic plaques. Vascular smooth muscle cells, macrophages, or endothelial cells treated in vitro with proatherogenic stimuli reveal certain features typical of autophagy, such as LC3 processing, formation of myelin figures, and extensive vacuolization. However, despite the increasing interest in autophagy, its role in atherosclerosis remains poorly understood. Most likely, autophagy safeguards plaque cells against cellular distress, in particular oxidative injury, by degrading the damaged intracellular material. In this way, autophagy is antiapoptotic and contributes to cellular recovery in an adverse environment. Because atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disorder of the arterial intima, pharmacologic approaches have recently been developed to stabilize vulnerable, rupture-prone lesions through selective induction of macrophage autophagic death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2005, 352:1685–1695.
Waxman S, Ishibashi F, Muller JE: Detection and treatment of vulnerable plaques and vulnerable patients. Novel approaches to prevention of coronary events. Circulation 2006, 114:2390–2411.
Clarke MC, Figg N, Maguire JJ, et al.: Apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells induces features of plaque vulnerability in atherosclerosis. Nat Med 2006, 12:1075–1080.
Tabas I: Consequences and therapeutic implications of macrophage apoptosis in atherosclerosis. The importance of lesion stage and phagocytic efficiency. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005, 25:2255–2264.
Kockx MM, Herman AG: Apoptosis in atherosclerosis: beneficial or detrimental? Cardiovasc Res 1999, 45:736–746.
Crisby M, Kallin B, Thyberg J, et al.: Cell death in human atherosclerotic plaques involves both oncosis and apoptosis. Atherosclerosis 1997, 130:17–27.
Yoshimori T: Autophagy: a regulated bulk degradation process inside cells. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 2004, 313:453–458.
Yorimitsu T, Klionsky DJ: Autophagy: Molecular machinery for self-eating. Cell Death Differ 2005, 12:1542–1552.
Levine B, Yuan J: Autophagy in cell death: an innocent convict? J Clin Invest 2005, 115:2679–2688.
Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, et al.: The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature 2004, 432:1032–1036.
Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, et al.: The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med 2007, 13:619–624.
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, et al.: Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 2006, 441:880–884.
Schmid D, Pypaert M, Munz C: Antigen-loading compartments for major histocompatibility complex class II molecules continuously receive input from autophagosomes. Immunity 2007, 26:79–92.
Kunz JB, Schwarz H, Mayer A: Determination of four sequential stages during microautophagy in vitro. J Biol Chem 2004, 279:9987–9996.
Dice JF: Chaperone-mediated autophagy. Autophagy 2007, 3:295–299.
Klionsky DJ, Cuervo AM, Seglen PO: Methods for monitoring autophagy from yeast to human. Autophagy 2007, 3:181–206.
Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Matsui M, et al.: In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol Biol Cell 2004, 15:1101–1111.
Kockx MM, De Meyer GR, Buyssens N, et al.: Cell composition, replication, and apoptosis in atherosclerotic plaques after 6 months of cholesterol withdrawal. Circ Res 1998, 83:378–387.
Martinet W, De Bie M, Schrijvers DM, et al.: 7-ketocholesterol induces protein ubiquitination, myelin figure formation, and light chain 3 processing in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004, 24:2296–2301.
Kockx MM, De Meyer GR, Muhring J, et al.: Apoptosis and related proteins in different stages of human atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation 1998, 97:2307–2315.
Martinet W, Knaapen MW, Kockx MM, De Meyer GR: Autophagy in cardiovascular disease. Trends Mol Med 2007, 13:482–491.
Bach I, Ostendorff HP: Orchestrating nuclear functions: ubiquitin sets the rhythm. Trends Biochem Sci 2003, 28:189–195.
Jia G, Cheng G, Gangahar DM, Agrawal DK: Insulin-like growth factor-1 and TNF-a regulate autophagy through c-jun N-terminal kinase and Akt pathways in human atherosclerotic vascular smooth cells. Immunol Cell Biol 2006, 84:448–454.
Kiffin R, Bandyopadhyay U, Cuervo AM: Oxidative stress and autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal 2006, 8:152–162.
Martinet W, Schrijvers DM, De Meyer GR, et al.: Gene expression profiling of apoptosis-related genes in human atherosclerosis. Upregulation of death-associated protein kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002, 22:2023–2029.
Inbal B, Bialik S, Sabanay I, et al.: DAP kinase and DRP-1 mediate membrane blebbing and the formation of autophagic vesicles during programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 2002, 157:455–468.
Jin Y, Gallagher PJ: Antisense depletion of death-associated protein kinase promotes apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2003, 278:51587–51593.
Bao L, Li Y, Deng SX, et al.: Sitosterol-containing lipoproteins trigger free sterol-induced caspase-independent death in ACAT-competent macrophages. J Biol Chem 2006, 281:33635–33649.
Miettinen TA, Railo M, Lepantalo M, Gylling H: Plant sterols in serum and in atherosclerotic plaques of patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005, 45:1794–1801.
Tabas I, Feinmark SJ, Beatini N: The reactivity of desmosterol and other shellfish-and xanthomatosis-associated sterols in the macrophage sterol esterification reaction. J Clin Invest 1989, 84:1713–1721.
Liu J, Chang CC, Westover EJ, et al.: Investigating the allosterism of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) by using various sterols: in vitro and intact cell studies. Biochem J 2005, 391:389–397.
Yamawaki H, Iwai N: Cytotoxicity of water-soluble fullerene in vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2006, 290:C1495–C1502.
Chau YP, Lin SY, Chen JH, Tai MH: Endostatin induces autophagic cell death in EAhy926 human endothelial cells. Histol Histopathol 2003, 18:715–726.
Nowicki M, Zabirnyk O, Duerrschmidt N, et al.: No upregulation of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 in serum-deprived EA.hy926 endothelial cells under oxLDL exposure, but increase in autophagy. Eur J Cell Biol 2007, 86:605–616.
Schrijvers D, Fret H, Martinet W, Bult H: Statins and oxysterol-induced vascular smooth muscle cell death. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2006, 20:331.
Gozuacik D, Kimchi A: Autophagy as a cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene 2004, 23:2891–2906.
Stoneman V, Braganza D, Figg N, et al.: Monocyte/macrophage suppression in CD11b diphtheria toxin receptor transgenic mice differentially affects atherogenesis and established plaques. Circ Res 2007, 100:884–893.
Yang YP, Liang ZQ, Gu ZL, Qin ZH: Molecular mechanism and regulation of autophagy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005, 26:1421–1434.
Easton JB, Houghton PJ: Therapeutic potential of target of rapamycin inhibitors. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2004, 8:551–564.
Abeliovich H: Regulation of autophagy by the target of rapamycin (Tor) proteins. In Autophagy. Edited by Klionsky DJ. Austin, TX: Landes Bioscience; 2004:60–69.
Verheye S, Martinet W, Kockx MM, et al.: Selective clearance of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by autophagy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007, 49:706–715.
Croons V, Martinet W, Herman AG, et al.: Selective clearance of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007, 320:986–993.
Bjornheden T, Bondjers G: Oxygen consumption in aortic tissue from rabbits with diet-induced atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 1987, 7:238–247.
Lutgens E, de Muinck ED, Kitslaar PJ, et al.: Biphasic pattern of cell turnover characterizes the progression from fatty streaks to ruptured human atherosclerotic plaques. Cardiovasc Res 1999, 41:473–479.
Martinet W, Knaapen MW, De Meyer GR, et al.: Elevated levels of oxidative DNA damage and DNA repair enzymes in human atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation 2002, 106:927–932.
Martin KA, Rzucidlo EM, Merenick BL, et al.: The mTOR/p70 S6K1 pathway regulates vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004, 286:C507–C517.
Martinet W, Verheye S, De Meyer GR: Everolimus-induced mTOR inhibition selectively depletes macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by autophagy. Autophyagy 2007, 3:241–244.
Martinet W, De Meyer GR, Timmermans JP, et al.: Macrophages but not smooth muscle cells undergo benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-DL-Asp(O-methyl)-fluoromethylketone-induced nonapoptotic cell death depending on receptor-interacting protein 1 expression: implications for the stabilization of macrophage-rich atherosclerotic plaques. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006, 317:1356–1364.
Martinet W, Verheye S, De Meyer GR: Selective depletion of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques via macrophage-specific initiation of cell death. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2007, 17:69–75.
Martinet W, Schrijvers DM, Herman AG, De Meyer GR: z-VAD-fmk-induced non-apoptotic cell death of macrophages. Possibilities and limitations for atherosclerotic plaque stabilization. Autophagy 2006, 2:312–314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinet, W., De Meyer, G.R.Y. Autophagy in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 10, 216–223 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-008-0034-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-008-0034-y