Abstract
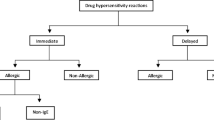
Acute infusion reactions to both chemotherapeutic agents and humanized monoclonal antibodies can occur, which may limit therapeutic options for treatment of malignancies and chronic inflammatory diseases. Many of these acute infusion reactions are consistent with a type I hypersensitivity reaction, including anaphylaxis. If a patient experiences a significant acute infusion reaction, often the recommendation is to discontinue the medication and find an alternative agent. However, the “second-line” agent may be more toxic or inferior. If the reaction is likely a type I or type IV hypersensitivity reaction, one option is to undergo desensitization to the offending drug. Drug desensitization is the process of readministering a needed drug in incremental doses over hours or days until a full therapeutic dose is tolerated. This article will review the current literature on indications and outcomes for drug desensitization in the management of allergy to either chemotherapeutic agents or monoclonal antibodies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Castells MC, Tennant NM, Sloane DE. Hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy: outcomes and safety of rapid desensitization in 413 cases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:574–80.
Markman M, Kennedy A, Webster K, Elson P, Peterson G, Kulp B, et al. Clinical features of hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1141–5.
Markman M, Kennedy A, Webster K, Kulp B, Peterson G, Belinson J. Paclitaxel-associated hypersensitivity reactions: experience of the gynecologic oncology program of the Cleveland Clinic Cancer Center. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:102–5.
Chung CH, O’Neil BH. Infusion reactions to monoclonal antibodies for solid tumors: immunologic mechanisms and risk factors. Oncology. 2009;23:14–7.
Moon DH, Lee JM, Noonan AM, Annunziata CM, Minasian L, Houston N, et al. Deleterious BRCA1/2 mutation is an independent risk factor for carboplatin hypersensitivity reactions. Br J of Cancer. 2013;109:1072–8. This article identified BRCA1/2 mutation carriers to be higher risk for platinum agent hypersensitivity.
Cernadas JR, Brockow K, Romano A, et al. General considerations on rapid desensitization for drug hypersensitivity: a consensus statement. Allergy. 2010;65:1357–66.
Pyle RC, Butterfield JH, Volcheck GW, Podjasek JC, Rank MA, Li JT, et al. Successful outpatient graded administration of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients without HIV and a history of sulfonamide adverse drug reaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2:52–8.
Iwamoto T, Yuta A, Tabata T, et al. Evaluation of basophil CD203c as a predictor of carboplatin-related hypersensitivity reaction in patients with gynecologic cancer. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(9):1487–95. This article suggests that basophil activation test may help predict carboplatin-related anaphylaxis.
Wong JT, Ling M, Patil B, Banerji A, Long A. Oxaliplatin hypersensitivity: evaluation, implications of skin testing, and desensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2:40–5. The first large retrospective series of oxaliplatin hypersensitivity in 48 patients treated with 200 successful desensitizations.
Kim RJ, Peterson G, Kulp B, et al. Skin toxicity associated with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (40 mg/m2) in the treatment of gynecologic cancers. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;97:374–8.
Lotem M, Lyass O, Goldenhersh MA, et al. Skin toxic effects of polyethylene glycol-coated liposomal doxorubicin. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1475–80.
Markman M, Zanotti K, Peterson G, Kulp B, Webster K, Belinson J. Expanded experience with an intradermal skin test to predict for the presence or absence of carboplatin hypersensitivity. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4611–4.
Gomez R, Harter P, Luck HJ, Traut A, Kommoss S, Kandel M, et al. Carboplatin hypersensitivity: does introduction of skin test and desensitization reliably predict and avoid the problem? A prospective single-center study. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009;19:1284–7.
Patil S, Long A, Ling M, et al. A protocol for risk stratification of patients with carboplatin-induced hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:443–7.
Brennan PJ, Rodriguez Bouza T, Hsu F, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to mAbs: 105 desensitizations in 23 patients, from evaluation to treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1259–66.
Matucci A, Pratesi S, Petroni G, et al. Allerogological in vitro and in vivo evaluation of patients with hypersensitivity reactions to infliximab. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013;43:659–64.
Brown SG. Clinical features and severity grading of anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:371–6.
Dizon DS, Sabbatini PJ, Aghajanian C, et al. Analysis of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer or fallopian tube carcinoma retreated with cisplatin after the development after a carboplatin allergy. Gynecol Oncol. 2002;84(3):378–82.
Syrigou E, Nektaria M, Vassias A, et al. Administration of cisplatin in three patients with carboplatin hypersensitivity: is skin testing useful? Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2010;21:333–8.
Hesterberg P, Banerji A, Oren E, et al. Risk stratification for desensitization of patients with carboplatin hypersensitivity: clinical presentation and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;129:1262–7.
Caiado J, Pereira-Santos MC VL, Costa L, Barbosa M, Castells M. Carboplatin, oxaliplatin and cisplatin-specific IgE: cross reactivity and value in the diagnosis of carboplatin and oxaliplatin allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol: In Practice. 2013;1:494–500. Once validated, specific IgE may be useful in risk-stratifying patients.
Madrigal-Burgaleta R, Berges-Gimeno MP, Angel-Pereira D, Ferreiro-Monteagudo R, Ruillen-Ponce C, Pueyo C, et al. Hypersensitivity and desensitization to antineoplastic agents: outcomes of 189 procedures with a new short protocol and novel diagnostic tools assessment. Allergy. 2013;68(7):853–61. A new shorter desensitization protocol.
Piva E, Chieco-Bianchi F, Krajcar V, et al. Adverse reactions in patients with B-cell lymphomas during combined treatment with rituximab: in vitro evaluation of rituximab hypersensitivity by basophil activation test. Am J Hematol. 2012;87(11):E130–1. This article also evaluates basophil activation test as a possible marker for predication of anaphylaxis.
Gastaminza G, de la Borbolla JM, Goikoetxea MJ, Escudero R, Anton J, Espinos J, et al. A new rapid desensitization protocol for chemotherapy agents. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011;21(2):108–12. This article reviews a desensitization protocol that is shorter and a premedication regimen based on radiocontrast allergy.
Chung CH, Mirakhur B, Chan E, et al. Cetuximab-induced anaphylaxis and IgE specific fort galactose-α-1,3-galactose. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1009–17.
Commins SP, James HR, Kelly LA, Pochan SL, Workman LJ, Perzanowski MS, et al. The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-α-1,3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(5):1286-–93.
Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, and the Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Drug Allergy. An updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;105(4):259–73.
Sakaeda T, Kadoyama K, Yabuuchi H, Niijima S, Seki K, Shiraishi Y, et al. Platinum agent-induced hypersensitivity reactions: data mining of the public version of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. AERS Int J Med Sci. 2011;8(4):332–8.
Herrero T, Tornero P, Infante S, Fuentes V, Sanchez NM, de Barrio M, et al. Diagnosis and management of hypersensitivity reactions caused by oxaliplatin. J Investiga Allergol CLin Immunol. 2006;16(5):327–30.
Breslow RG, Caiado J, Castells MC. Acetylsalicyclic acid and montelukast block mast cell mediator-related symptoms during rapid desensitization. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009;102:155–60.
Vultaggio A, Maggi E, Matucci A. Immediate adverse reactions to biologicals: from pathogenic mechanisms to prophylactic management. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;11:262–8.
Ojaimi S, Harnett PR, Fulcher DA. Successful carboplatin desensitization by using omalizumab and paradoxical diminution of total IgE levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2:105–6. This case report presents the added benefit of using omalizumab for drug desensitization.
Sancho-Serra Mdel C, Simarro M, Castells M. Rapid IgE desensitization is antigen specific and impairs early and late mast cell responses targeting FcepsilonRI internalization. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:1004–13.
Morales AR, Shah N, Castells M. Antigen-IgE desensitization in signal transducer and activator of transcription 6-deficient mast cells by suboptimal doses of antigen. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;94:575–80.
Aydogan M, Yologlu N, Gacar G, et al. Successful rapid rituximab desensitization in an adolescent patient with nephrotic syndrome: increase in number of Treg cells after desensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132(2):478–80. This case report also highlights increased in Treg cells after a successful desensitization.
Banerji A, Brennan P, Hesterberg P, et al. Drug desensitizations in the management of allergy and anaphylaxis to chemotherapeutic agents and monoclonal antibodies. In: Castells MC, editor. Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity Reactions. New York: Humana Press; 2011. p. 297–311.
Prieto García A, de la Pineda Losa F. Immunoglobulin E-mediated severe anaphylaxis to paclitaxel. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2010;20(2):170–1.
Castells MC, Matulonis UA. Infusion reactions to systemic chemotherapy. In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA (Accessed on December 10, 2013)
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Karen Hsu Blatman declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Mariana Castells declares that she has received personal fees from Merck, Sanofi, UpToDate, and BWH; grants from NIH Desensitization; and nonfinancial support from AAAAI BOD.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Anaphylaxis and Drug Allergy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu Blatman, K.S., Castells, M.C. Desensitizations for Chemotherapy and Monoclonal Antibodies: Indications and Outcomes. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 14, 453 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-014-0453-5
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-014-0453-5