Abstract
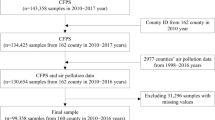
In parallel with the social economic development, the social cost of air pollution is increasing as well. The health depreciation effects and medical cost effects of air pollution are particularly prominent. Based on the traditional health effects of air pollution, this study constructs a health index system from three dimensions: physical health, mental health, and social adaptability. Based on the daily monitoring data of air quality of 122 Chinese cities, and by matching the continuous tracking survey data of the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) in 2015 and 2018, this study constructs a panel model and uses the instrumental variable to empirically investigate the health depreciation effects and medical cost effects of air pollution. It was found that air pollution has a significant health depreciation effect. The effects of AQI (air quality index) on physical health, mental health, and social adaptability were − 0.6682, − 19.0686, and − 0.9816, respectively. Also, air pollution has a significant medical cost effect. The health depreciation and medical cost effects of CO, NO2, and SO2 are more remarkable. Moreover, the number of extreme pollution days has significant and adverse effects on both physical and mental health. Apparently, the number of severe and serious pollution days have higher impacts on social adaptability and medical expenses. In addition, there are significant group heterogeneity and regional heterogeneity in the health depreciation effects and medical cost effects of air pollution.
Highlights
• The impact of air pollution on health is multidimensional.
• The impact of air pollution on the health of different residents is heterogeneous.
• Different pollutants have different health effects and medical cost effects.
• The government should pay attention to the decrease of social adaptability.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available at the following URL/DOI:http://charls.pku.edu.cn/
Notes
http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/i/jyjl/l/202102/20210203038237.shtml. According to the preliminary statistics of GDP in 2020.
Hainan Province, Tibet Autonomous Region, and Ningxia Autonomous Region were not included in the sample.
References
Alderete TL, Habre R, Toledo-Corral CM et al (2017) Longitudinal associations between ambient air pollution with insulin sensitivity, β-Cell function, and adiposity in Los Angeles Latino children. Diabetes 66(7):1789–1796. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-1416
Arceo E, Hanna R, Oliva P (2016) Does the effect of pollution on infant mortality differ between developing and developed countries? Evidence from Mexico City Econ J 126(591):257–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecoj.12273
Barwick PJ, Li S, Rao D, et al. (2018) The morbidity cost of air pollution: evidence from consumer spending in China. Working Paper. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2999068
Berend N (2016) Contribution of air pollution to COPD and small airway dysfunction. Respirology 21(2):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.12644
Bourdrel T, Bind MA, Béjot B et al (2017) Cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 110(11):634–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2017.05.003
Bowatte G, Lodge CJ, Knibbs LD et al (2017) Traffic-related air pollution exposure is associated with allergic sensitization, asthma, and poor lung function in middle age. J Allergy Clin Immunol 139(1):122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.05.008
Cacciottolo M, Wang X, Driscoll I et al (2017) Particulate air pollutants, APOE alleles and their contributions to cognitive impairment in older women and to amyloidogenesis in experimental models. Transl Psychiat 7(1):e1022. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.280
Camarinho R, Garcia PV, Rodrigues AS (2013) Chronic exposure to volcanogenic air pollution as cause of lung injury. Environ Pollut 181(10):24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.05.052
Cao R, Wang Y, Huang J et al (2021) The construction of the air quality health index (AQHI) and a validity comparison based on three different methods. Environ Res 197:110987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110987
Cesur R, Tekin E, Ulker A (2018) Can natural gas save lives? evidence from the deployment of a fuel delivery system in a developing country. J Health Econ 59(5):91–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhealeco.2018.03.001
Chay KY, Michael G (2003) The impact of air pollution on infant mortality: evidence from geographic variation in pollution shocks induced by a recession. Q J Econ 118(3):1121–1167. https://doi.org/10.1162/00335530360698513
Chen Y, Avraham E, Michael G et al (2013) Evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from china’s Huai river policy. P Natl Acad Sci USA 110(32):12936–12941. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2291154
Chen S, Guo C, Huang X (2018) Air pollution, student health, and school absences: evidence from China. J Environ Econ Manag 92(11):465–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2018.10.002
Chen JF, Wu XJ, Tao R (2020) Effects of air pollution on individuals’ direct and spillover behaviors. Adv Psychol Sci 28(08):1293–1306. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01293
Cui EH, Jiang SZ, Jia SB (2016) Research on the impact of environmental pollution, commercial health insurance to health costs: based on the empirical analysis of provincial panel data. Nankai Econ Stud 6:140–150. https://doi.org/10.14116/j.nkes.2016.06.009
Deryugina T, Heutel G, Miller NH et al (2019) The mortality and medical costs of air pollution: evidence from changes in wind direction. Am Econ Rev 109(12):4178–4219. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20180279
Deschenes O, Greenstone M, Shapiro JS (2017) Defensive investments and the demand for air quality: evidence from the NOx budget program. Am Econ Rev 107(10):2958–2989. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20131002
Dong Y (2018) A study on ambient air quality’s effects on public health in China: based on comparative analysis with G20. Popul Econ 19(2):57–68. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-4149.2018.02.006
Douglass JA (2020) How can air quality affect health? Intern Med J 50(11):1403–1404. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.15050
Duflo E, Greenstone M, Hanna R (2008) Indoor air pollution, health and economic well-being. SAPIENS 1(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.5194/sapiens-1-1-2008
Ebenstein A, Fan MY, Greenstone M et al (2017) New evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from China’s Huai river policy. P Natl Acad Sci USA 114(39):10384–10389. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1616784114
Grossman M (1972) On the concept of health capital and the demand for health. J Polit Econ 80(2):223–255. https://doi.org/10.1086/259880
Guan N, Huang XF, Li T (2021) Air quality and health care expenditure --evidence from Chinese middle-aged and elderly samples. China Econ Quart 21(3):775–796. https://doi.org/10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2021.03.02
Huang W, Cao J, Tao Y et al (2012) Seasonal variation of chemical species associated with short-term mortality effects of pm2.5 in xi’an, a central city in china. Am J Epidemiol 175(6):556–566. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwr342
Ito K, Zhang S (2020) Willingness to pay for clean air: evidence from air purifier markets in China. J Polit Econ 128(5):1627–1672. https://doi.org/10.1086/705554
Li L, Lin Y, Xia T et al (2020) Effects of electronic cigarettes on indoor air quality and health. Annu Rev Publ Health 41(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040119-094043
Lin Y, Liu F, Fleisher BM et al (2020) Indoor air quality and health: Empirical evidence from fluoride pollution in China. China Econ Rev 63:101282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2019.03.001
Liu H (2021) Formal and informal care: complementary or substitutes in care for elderly people? Empirical Evidence from China SAGE Open 11(2):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440211016413
Liu H (2021) Research on disability grading based on ICF functional framework: empirical evidence from Zhejiang province. China Front Public Health 9:616180. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.616180
Liu H, Hu T (2021) How does air quality affect residents’ life satisfaction? Evidence based on multiperiod follow-up survey data of 122 cities in China. Environ Sci Pollut R,1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15022-x
Liu C, Chen RJ, Sear F et al (2019) Ambient particulate air pollution and daily mortality in 652 cities. New Engl J Med 381(8):705–715. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1817364
Liu H, Hu T, Wang M (2021) Impact of air pollution on residents’ medical expenses: A study based on the survey data of 122 cities in China. Front Public Health 9:743087. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.743087
Ma JY, Han ZZ, Cai HD (2020) The effect of air quality on life satisfaction: based on the ordered hierarchical spatial autoregressive probit model. Stat Res.37(11),30-43. 10. 19343/j. cnki. 11-1302/c. 2020. 11. 003
Mason T (2019) An evaluation of the air quality health index program on respiratory diseases in Hong Kong: an interrupted time series analysis. Atmos Environ 211:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.05.013
Munzel T, Gori T, Al-Kindi S et al (2018) Effects of gaseous and solid constituents of air pollution on endothelial function. Eur Heart J 39(38):3543–3550. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy481
Olstrup H (2020) An air quality health index (AQHI) with different health outcomes based on the air pollution concentrations in Stockholm during the period of 2015–2017. Atmos 11(2):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020192
Olstrup H, Johansson C, Forsberg B et al (2019) A multi-pollutant air quality health index (AQHI) based on short-term respiratory effects in Stockholm, Sweden. Int J Env Res Pub He 16(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010105
Qin F, Xu M, Qu C (2020) Air pollution exposure and exercise: how to protect health. China Sport Sci 40(2):58–69. https://doi.org/10.16469/j.css.202002007
Schlenker W, Walker WR (2011) Airports, air pollution, and contemporaneous health. Rev Econ Stud 83(2):768–809. https://doi.org/10.1093/restud/rdv043
Schultz ES, Litonjua AA, Erik M (2017) Effects of long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution on lung function in children. Curr Allergy Asthm r 17(6):41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-017-0709-y
Strasert B, Teh SC, Cohan DS (2019) Air quality and health benefits from potential coal power plant closures in Texas. J Air Waste Manage 69(3):333–350
Toledo-Corral CM, Alderete TL, Habre R et al (2018) Effects of air pollution exposure on glucose metabolism in Los Angeles minority children. Pediatr Obes 13(1):54–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijpo.12188
Vlachokostas C, Achillas C, Moussiopoulos N et al (2012) Health effects and social costs of particulate and photochemical urban air pollution: a case study for Thessaloniki. Greece Air Qual Atmos Hlth 5(3):325–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-010-0096-1
Wang YZ, Luo NS (2020) Air pollution, health depreciation and medical costs: research based on the three perspectives of physical health, mental health and social adaptability. Econ Res J.55(12),80–97. https://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/JJYJ202012005.htm
Williams AM, Phaneuf DJ (2019) The morbidity costs of air pollution: evidence from spending on chronic respiratory conditions. Environ Resour Econ 74:571–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-019-00336-9
Xue T, Zhu T, Zheng Y et al (2019) Author correction: declines in mental health associated with air pollution and temperature variability in China. Nat Commun 10(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11660-5
Zhang X, Chen X, Zhang XB (2018) The impact of exposure to air pollution on cognitive performance. P Natl Acad Sci USA 115(37):9193–9197. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1809474115
Zhang JJ, Kan H, Kipen HM (2020) Respiratory health, children’s lung function, and air quality in four Chinese cities: two snapshots in 1993–1996 and 2017–2018. J Thorac Dis 12(10):6311–6314. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd-19-crh-aq-preface
Zhao WX (2020) The effect of air pollution on personal health care expenditure of elderly people: evidence from CHARLS data. Popul Econ 1:75–88. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-4149.2020.00.005
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (71904167) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LQ20G030018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL drafted and revised it critically for important intellectual content and approved the version to be published and carried out language retouching and modification. HL made a substantial contribution to the concept and design of the work, interpretation of data, and drafted the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H. Health depreciation effect and medical cost effect of air pollution: based on multidimensional health perspective. Air Qual Atmos Health 15, 877–892 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-022-01189-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-022-01189-w