Abstract
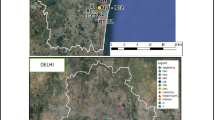
Particulate matter (PM) is one of the most dangerous pollutants in urban environments, and studies have linked it to many adverse health effects. Resuspended road dust makes up a large portion of PM. Therefore, monitoring and estimating the contribution of resuspended dust to PM is vital. In this study, emission rates of fine and coarse PM from different roads of Vellore City in Tamil Nadu, India, is estimated using silt loading protocol adapted by U.S. EPA. Silt load samples are collected from 8 different roads in the study region. The emission rates estimated using silt loading and fleet weight are then used to model the dispersion of PM throughout the study region using AERMOD. Hotspots of high PM concentration are identified at various locations frequented by commuters in the study region. Areas around educational institutions and hospitals in the region show highly elevated levels of PM. This study illustrates that resuspension of road dust can contribute significantly to PM in urban centers. Fine PM concentration exceeding 500 μg/m3 raises concerns about the health of commuters in the study region. This justifies the need for more regulations aiming at reducing the contribution of PM from resuspended road dust to overall urban PM.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abu-Allaban M, Gillies JA, Gertler AW, Clayton R, Proffitt D (2003) Tailpipe, resuspended road dust, and brake-wear emission factors from on-road vehicles. Atmos Environ 37(37):5283–5293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.05.005
Amato F, Cassee FR, Denier van der Gon HAC, Gehrig R, Gustafsson M, Hafner W, Harrison RM, Jozwicka M, Kelly FJ, Moreno T, Prevot ASH, Schaap M, Sunyer J, Querol X (2014) Urban air quality: The challenge of traffic non-exhaust emissions. J Hazard Mater 275:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.053
An Z, Jin Y, Li J, Li W, Wu W (2018) Impact of particulate air pollution on cardiovascular health. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 18(3):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-018-0768-8
Askariyeh MH, Venugopal M, Khreis H, Birt A, Zietsman J (2020) Near-road traffic-related air pollution: resuspended PM2.5 from highways and arterials. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(8):2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17082851
ASTM Standard C136 (2006) Standard test method for sieve analysis of fine and coarse aggregates. ASTM International, West Conshohocken. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0136, http://www.astm.org/cgi-bin/resolver.cgi?C136C136M
Belis CA, Karagulian F, Larsen BR, Hopke PK (2013) Critical review and meta-analysis of ambient particulate matter source apportionment using receptor models in Europe. Atmos Environ 69:94–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.009
Bhuvan (2016) Bhuvan Thematic Data dissemination. https://bhuvan-app1.nrsc.gov.in/thematic/thematic/index.php. Accessed 6 Feb 2021
Carbonell TLM, Sanchez Gacita M, Rivero Oliva J d J, Garea LC, Diaz Rivero N, Meneses Ruiz E (2010) Methodological guide for implementation of the AERMOD system with incomplete local data. Atmos Pollut Res 1(2):102–111. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2010.013
Chen S, Zhang X, Lin J, Huang J, Zhao D, Yuan T, Huang K, Luo Y, Jia Z, Zang Z (2019) Fugitive road dust PM2. 5 emissions and their potential health impacts. Environ Sci Technol 53(14):8455–8465
Councell TB, Duckenfield KU, Landa ER, Callender E (2004) Tire-wear particles as a source of zinc to the environment. Environ Sci Technol 38(15):4206–4214. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034631f
Crisan C (2021) Ccrisan/motioneyeos [Makefile]. https://github.com/ccrisan/motioneyeos (Original work published 2015). Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Denby BR, Kupiainen KJ, Gustafsson M (2018) Review of road dust emissions. In Non-exhaust emissions (pp. 183–203). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811770-5.00009-1
Garry MR, Shock SS, Salatas J, Dau J (2018) Application of a weight of evidence approach to evaluating risks associated with subsistence caribou consumption near a lead/zinc mine. Sci Total Environ 619–620:1340–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.149
Han S, Youn J-S, Jung Y-W (2011) Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 source profiles for resuspended road dust collected using mobile sampling methodology. Atmos Environ 45(20):3343–3351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.04.015
Hans S, Lotte J, Lidia C, Benoit N, Nawrot TS (2015) Long-term exposure to particulate matter air pollution is a risk factor for stroke. Stroke 46(11):3058–3066. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009913
HEI (2010) Traffic-related air pollution: a critical review of the literature on emissions, exposure, and health effects. The Health Effects Institute. https://www.healtheffects.org/publication/traffic-related-air-pollution-critical-review-literature-emissions-exposure-and-health. Accessed 12 Feb 2021
IHME (2016) The cost of air pollution: strengthening the economic cause for action. The World Bank and Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/781521473177013155/pdf/108141-REVISED-Cost-of-PollutionWebCORRECTEDfile.pdf. Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Men C, Liu R, Xu F, Wang Q, Guo L, Shen Z (2018) Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 612:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.123
Mirzaei Aminiyan M, Baalousha M, Mousavi R, Mirzaei Aminiyan F, Hosseini H, Heydariyan A (2018) The ecological risk, source identification, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in road dust: a case study in Rafsanjan, SE Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(14):13382–13395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8539-y
Najmeddin A, Keshavarzi B (2018) Health risk assessment and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with PM10 and road deposited dust in Ahvaz metropolis of Iran. Environ Geochem Health 41:1267–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0209-6
Nath B, Norra S, Chatterjee D, Stüben D (2007) Fingerprinting of land use–related chemical patterns in street sediments from Kolkata, India. Environ Forensic 8(4):313–328. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275920701506516
Nazarpour A, Ghanavati N, Watts MJ (2018) Spatial distribution and human health risk assessment of mercury in street dust resulting from various land-use in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ Geochem Health 40(2):693–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0016-5
Ni L, Chuang C-C, Zuo L (2015) Fine particulate matter in acute exacerbation of COPD. Front Physiol 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00294
NOAA (2020) NOAA/ESRL/GSL - RAOB. https://ruc.noaa.gov/raobs/. Accessed 6 Feb 2021
Pancras JP, Landis MS, Norris GA, Vedantham R, Dvonch JT (2013) Source apportionment of ambient fine particulate matter in Dearborn, Michigan, using hourly resolved PM chemical composition data. Sci Total Environ 448:2–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.083
Shrivastava RK, Neeta S, Geeta G (2013) Air pollution due to road transportation in India: A review on assessment and reduction strategies. J Environ Res Dev 8(1):69
Singh N, Murari V, Kumar M, Barman SC, Banerjee T (2017) Fine particulates over South Asia: Review and meta-analysis of PM2.5 source apportionment through receptor model. Environ Pollut 223:121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.071
Soriano JB, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abera SF, Agrawal A, Ahmed MB, Aichour AN, Aichour I, Aichour MTE, Alam K, Alam N, Alkaabi JM, Al-Maskari F, Alvis-Guzman N, Amberbir A, Amoako YA, Ansha MG, Antó JM, Asayesh H et al (2017) Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir Med 5(9):691–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30293-X
Tartakovsky D, Broday DM, Stern E (2013) Evaluation of AERMOD and CALPUFF for predicting ambient concentrations of total suspended particulate matter (TSP) emissions from a quarry in complex terrain. Environ Pollut 179:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.04.023
Truex TJ, Pierson WR, McKee DE, Shelef M, Baker RE (1980) Effects of barium fuel additive and fuel sulfur level on diesel particulate emissions. Environ Sci Technol 14(9):1121–1124. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60169a018
U.S. EPA (1972) Compilation of air pollutant emission factors. https://www3.epa.gov/ttn/chief/ap42/oldeditions/1st_edition/ap421sted_1972.pdf. Accessed 12 Feb 2021
U.S. EPA (1996a) Air quality criteria for particulate matter. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Research Triangle Park
U.S. EPA (1996b) EPA method 3050b: acid digestion of sediments, sludges, and soils. US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/homeland-security-research/epa-method-3050b-acid-digestion-sediments-sludges-and-soils. Accessed 12 Feb 2021
U.S. EPA (2001) AP-42: compilation of air emission factors [Policies and Guidance]. U.S. EPA. https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-factors-and-quantification/ap-42-compilation-air-emission-factors. Accessed 12 Feb 2021
U.S. GS (2010) Global multi resolution terrain elevation data – 2010. https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-digital-elevation-global-multi-resolution-terrain-elevation. Accessed 6 Feb 2021
Valavanidis A, Vlachogianni T, Fiotakis K, Loridas S (2013) Pulmonary oxidative stress, inflammation and cancer: respirable particulate matter, fibrous dusts and ozone as major causes of lung carcinogenesis through reactive oxygen species mechanisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10(9):3886–3907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10093886
Venkatram A (2000) A critique of empirical emission factor models: a case study of the AP-42 model for estimating PM 10 emissions from paved roads. Atmos Environ 34(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00330-1
Weather Underground (2020) Yerpedu, India weather history | Weather underground. https://www.wunderground.com/history/daily/VOTP/date/2021-2-6. Accessed 6 Feb 2021
Yaroshevsky AA (2006) Abundances of chemical elements in the Earth’s crust. Geochem Int 44(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1134/S001670290601006X
Zanobetti A, Bind M-AC, Schwartz J (2008) Particulate air pollution and survival in a COPD cohort. Environ Health 7(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-7-48
Zhang Y, Cai J, Wang S, He K, Zheng M (2017) Review of receptor-based source apportionment research of fine particulate matter and its challenges in China. Sci Total Environ 586:917–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.071
Zhao P, Feng Y, Zhu T, Wu J (2006) Characterizations of resuspended dust in six cities of North China. Atmos Environ 40(30):5807–5814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.026
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Indian Space Research Organization for providing Bhuvan LULC 50K data. We express our gratitude to National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for providing upper atmosphere radiosonde data. We would like to acknowledge Weather Underground for providing the hourly weather data. We would also extend our sincere thanks to United States Environmental Protection Agency for providing AERMOD and associated co-processors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figure S1:
Vehicle composition during weekdays and weekends (DOCX 20 kb)
Supplementary Table S1:
Correlation coefficient between elements in Silt (DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jose, J., Srimuruganandam, B. Effect of silt loading on particle concentration in the atmosphere from resuspended road dust through particulate matter dispersion modeling. Air Qual Atmos Health 14, 1475–1486 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-021-01034-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-021-01034-6