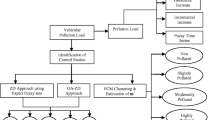
Abstract
Establishing cause–effect relationship between inhaling polluted air due to toxic auto exhaust releases and incidence of pulmonary diseases is not a trivial task. In this endeavor, epidemiological studies with air pollution parametric data have been attempted in the past using statistical technique. Earlier studies of the authors of this paper inferred that the combined belief for respiratory diseases is 0.65 for either simple bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma or allergic rhinitis coupled with conjunctivitis (Yadav et al., Int J Intell Syst 22:9–22, 2013). The sequel demonstrates the application of the computational formalism of fuzzy inference system with a degree of match concept—a level 1 complexity in computing with words for classifying air quality straightway in linguistic term with a linguistic degree of certainty attached to each description. The exhaustive case study relates to classifying air quality in 14 cities with a total of 51 monitoring locations in Maharashtra State, India. It could be stated that straightway describing air quality in linguistic term based on the new formalism is in agreement with the linguistic classification via conventional air quality index method. The study also concludes that the variability in experts’ perception on describing air quality varies from 80 to 98 %.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldauf RW, Lane DD, Marotx GA, Barkman HW, Pierce T (2002) Application of a risk assessment based approach to designing ambient air quality monitoring networks for revaluating non-cancer health impacts. Environ Monit Assess 78:213–227
Deshpande AW, Raje DV (2003) Fuzzy logic applications to environmental management systems: case studies. International conference on Industrial Informatics (INDINO3), Banff, Canada
Khan FI, Sadiq R (2005) Risk based prioritization of air pollution monitoring using fuzzy synthetic evaluation technique. Environ Monit Assess 105(1–3):261–283
Mckone TE, Deshpande AW (2010) Can fuzzy logic bring complex environmental problems into focus? IEEE. 11–17
Mendel JM (2007) Computing with words and its relationships with Fuzzistics’. Inf Sci 177:988–1006
Modak P, Lohani BN (1985) Optimization of ambient air quality monitoring networks. Environ Monit Assess 5:39–53
Pope AC, Burnett RT, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D, Ito K, Thurston GD (2002) Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. J Am Med Assoc 287:1132–1142
Ross TJ (2009) Fuzzy logic with engineering applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, India
Sowlat HM, Gharibi H, Yunesian M, Mahmoudi MT, Lotfi S (2011) A novel, fuzzy-based air quality index (FAQI) for air quality assessment. Atmos Environ 45(12):2050–2059
Yadav JY, Kharat V, Deshpande AW (2011) Fuzzy description of air quality: a case study. 6th International conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology (RSKT), Banff, Canada, Oct. 9–12, 420–427
Yadav JY, Kharat V, Deshpande AW (2013) Evidence theory and fuzzy relational calculus in estimation of health effects due to air pollution. Int J Intell Syst 22(1):9–22
Zadeh L (2001) A new direction in AI—toward a computational theory of perceptions. AI Mag 22(1):73–84
Zadeh LA (2002) From computing with numbers to computing with words-from manipulation of measurements to manipulation of perceptions. Int J Appl Math Comput Sci 12(3):307–324
Zadeh L (2008) Is there a need for fuzzy logic? Inf Sci 178:2751–2779
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prashant Gargav, Suresh Jain, G. Beig, Rakesh Kumar, and Shiva Nagendra for their valuable inputs at every stage of this paper. We are also grateful to anonymous reviewers for a number of thoughtful review comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, J., Kharat, V. & Deshpande, A. Fuzzy description of air quality using fuzzy inference system with degree of match via computing with words: a case study. Air Qual Atmos Health 7, 325–334 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-014-0239-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-014-0239-x