Abstract
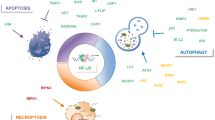
The melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7(mda-7), IL-24, has the specific functions that induce cancer cell apoptosis without doing harm to normal cells. We systematically review the apoptotic signal pathways and their regulatory mechanisms induced by Ad.IL-24 and IL-24 in diverse cancer cells. IL-24 can participate in varied signal transduction pathways, including JAK, p38 MAPK, Wnt/β-catenin, JNK, ER stress and mitochondria-associated signal pathways. And we review five proteins interacting with IL-24, including Bip/GRP78, S1R, PKR, Beclin1 and soluble clusterin, which are relative to the tumor-specific effect of IL-24. It is speculated that ER stress, G-protein pathways and MAPK signal pathways may be the primary upstream effectors which activate the sequential downstream mediators resulting in apoptosis induced by IL-24 in tumor cells. Experimental results also show that IL-24 sensitizes cancer cells and indirectly promotes apoptosis rather than functions as a direct apoptosis inducer itself.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang H, Lin J J, Su Z Z, et al. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression [J]. Oncogene, 1995, 11(12): 2477–2486.
Lee K M, Kang H A, Park M, et al. Interleukin-24 attenuates beta-glycerophosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting apoptosis, the expression of calcification and osteoblastic markers, and the Wnt/betacatenin pathway [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 428(1): 50–55.
Dent P, Yacoub A, Hamed H A, et al. The development of mda-7/IL-24 as a cancer therapeutic [J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 128(2): 375–384.
Eulitt P J, Park M A, Hossein H, et al. Enhancing mda-7/IL-24 therapy in renal carcinoma cells by inhibiting multiple protective signaling pathways using sorafenib and by ad.5/3 gene delivery [J]. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 2014, 10(12): 1290–1305.
Kim J S, Yu S K, Lee M H, et al. Microrna-205 directly regulates the tumor suppressor, interleukin-24, in human KB oral cancer cells [J]. Mol Cells, 2013, 35(1): 17–24.
Dash R, Bhoopathi P, Das S K, et al. Novel mechanism of mda-7/IL-24 cancer-specific apoptosis through sari induction [J]. Cancer Res, 2014, 74(2): 563–574.
Sarkar D, Dent P, Curiel D T, et al. Acquired and innate resistance to the cancer-specific apoptosis-inducing cytokine, mda-7/IL-24: Not insurmountable therapeutic problems [J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2008, 7(1): 109–112.
Hingtgen S, Kasmieh R, Elbayly E, et al. A first-generation multi-functional cytokine for simultaneous optical tracking and tumor therapy [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7): e40234.
Sauane M, Su Z Z, Dash R, et al. Ceramide plays a prominent role in mda-7/IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis [J]. J Cell Physiol, 2010, 222(3): 546–555.
Kreis S, Philippidou D, Margue C, et al. Recombinant interleukin-24 lacks apoptosis-inducing properties in melanoma cells [J]. PLoS One, 2007, 2(12): e1300.
Huang E Y, Madireddi M T, Gopalkrishnan R V, et al. Genomic structure, chromosomal localization and expression profile of a novel melanoma differentiation associated (mda-7) gene with cancer specific growth suppressing and apoptosis inducing properties [J]. Oncogene, 2001, 20(48): 7051–7063.
Wang M, Tan Z, Zhang R, et al. Interleukin 24 (mda-7/ mob-5) signals through two heterodimeric receptors, IL-22r1/IL-20r2 and IL-20r1/IL-20r2 [J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(9): 7341–7347.
Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan R V, Sarkar D, et al. Mda-7/IL-24: Novel cancer growth suppressing and apoptosis inducing cytokine [J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2003, 14(1): 35–51.
Sauane M, Gupta P, Lebedeva I V, et al. N-glycosylation of mda-7/IL-24 is dispensable for tumor cell-specific apoptosis and “bystander” antitumor activity [J]. Cancer Res, 2006, 66(24): 11869–11877.
Gupta P, Walter M R, Su Z Z, et al. BIP/GRP78 is an intracellular target for mda-7/IL-24 induction of cancerspecific apoptosis [J]. Cancer Res, 2006, 66(16): 8182–8191.
Dumoutier L, Leemans C, Lejeune D, et al. Cutting edge: STAT activation by IL-19, IL-20 and mda-7 through IL-20 receptor complexes of two types [J]. J Immunol, 2001, 167(7): 3545–3549.
Zhu H, Yang Z B. Expression pattern of mda-7/IL-24 receptors in liver cancer cell lines [J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2009, 8(4): 402–406.
Yang Y J, Chen D Z, Li L X, et al. Targeted IL-24 gene therapy inhibits cancer recurrence after liver tumor resection by inducing tumor cell apoptosis in nude mice [J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2009, 8(2): 174–178.
Bhutia S K, Das S K, Azab B, et al. Targeting breast cancer-initiating/stem cells with melanoma differentiationassociated gene-7/interleukin-24 [J]. Int J Cancer, 2013, 133(11): 2726–2736.
Park M A, Walker T, Martin A P, et al. Mda-7/IL-24-induced cell killing in malignant renal carcinoma cells occurs by a ceramide/CD95/PERK-dependent mechanism [J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2009, 8(5): 1280–1291.
Yacoub A, Park M A, Gupta P, et al. Caspase-, cathepsin-, and PERK-dependent regulation of mda-7/IL-24-induced cell killing in primary human glioma cells [J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2008, 7(2): 297–313.
Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan R V, Choo H T, et al. Mechanistic aspects of mda-7/IL-24 cancer cell selectivity analysed via a bacterial fusion protein [J]. Oncogene, 2004, 23(46): 7679–7690.
Chada S, Mhashilkar A M, Ramesh R, et al. Bystander activity of ad-mda7: Human mda-7 protein kills melanoma cells via an IL-20 receptor-dependent but stat3-independent mechanism [J]. Mol Ther, 2004, 10(6): 1085–1095.
Parrish-Novak J, Xu W, Brender T, et al. Interleukins 19, 20 and 24 signal through two distinct receptor complexes. Differences in receptor-ligand interactions mediate unique biological functions [J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(49): 47517–47523.
Inoue S, Shanker M, Miyahara R, et al. Mda-7/IL-24-based cancer gene therapy: Translation from the laboratory to the clinic [J]. Curr Gene Ther, 2006, 6(1): 73–91.
Chada S, Bocangel D, Ramesh R, et al. Mda-7/IL-24 kills pancreatic cancer cells by inhibition of the Wnt/PI3K signaling pathways: Identification of IL-20 receptormediated bystander activity against pancreatic cancer [J]. Mol Ther, 2005, 11(5): 724–733.
Sieger K A, Mhashilkar A M, Stewart A, et al. The tumor suppressor activity of mda-7/IL-24 is mediated by intracellular protein expression in nsclc cells [J]. Mol Ther, 2004, 9(3): 355–367.
Sahoo A, Lee C G, Jash A, et al. Stat 6 and c-jun mediate Th2 cell-specific IL-24 gene expression [J]. J Immunol, 2011, 186(7): 4098–4109.
Shefler I, Pasmanik-Chor M, Kidron D, et al. T cell-derived microvesicles induce mast cell production of IL-24: Relevance to inflammatory skin diseases [J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2014, 133(1): 1–3.
Sarkar D, Lebedeva I V, Gupta P, et al. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7 (mda-7)/ IL-24: A “magic bullet” for cancer therapy? [J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2007, 7(5): 577–586.
Weiss R, Sachet M, Zinngrebe J, et al. IL-24 sensitizes tumor cells to TLR3-mediated apoptosis [J]. Cell Death Differ, 2013, 20(6): 823–833.
Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan R V, Lebedeva I, et al. Mda-7/IL-24 induces apoptosis of diverse cancer cell lines through JAK/STAT-independent pathways [J]. J Cell Physiol, 2003, 196(2): 334–345.
Ekmekcioglu S, Ellerhorst J A, Mumm J B, et al. Negative association of melanoma differentiation-associated gene (mda-7) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (INOS) in human melanoma: Mda-7 regulates INOS expression in melanoma cells [J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2003, 2(1): 9–17.
Mamane Y, Heylbroeck C, Genin P, et al. Interferon regulatory factors: The next generation [J]. Gene, 1999, 237(1): 1–14.
Li Y J, Liu G, Li Y, et al. Mda-7/ IL-24 expression inhibits breast cancer through upregulation of growth arrest-specific gene 3 (gas3) and disruption of 1 integrin function [J]. Molecular Cancer Research, 2013, 11(6): 593–603.
Lei Y Y, Wang W J, Mei J H, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction in solid tumors [J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15(20): 8539–8548.
Sarkar D, Su Z Z, Lebedeva I V, et al. Mda-7 (IL-24) mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(15): 10054–10059.
Gopalan B, Litvak A, Sharma S, et al. Activation of the Fas-FasL signaling pathway by mda-7/IL-24 kills human ovarian cancer cells [J]. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(8): 3017–3024.
Sarkar D, Su Z Z, Lebedeva I V, et al. Mda-7 (IL-24): Signaling and functional roles [J]. Biotechniques, 2002, Suppl: 30–39.
Otkjaer K, Holtmann H, Kragstrup T W, et al. The p38 MAPK regulates IL-24 expression by stabilization of the 3’UTR of IL-24 mRNA [J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(1): e8671.
Qian W, Liu J, Tong Y, et al. Enhanced antitumor activity by a selective conditionally replicating adenovirus combining with mda-7/interleukin-24 for B-lymphoblastic leukemia via induction of apoptosis [J]. Leukemia, 2008, 22(2): 361–369.
Gupta P, Su Z Z, Lebedeva I V, et al. Mda-7/IL-24: Multifunctional cancer-specific apoptosis-inducing cytokine [J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2006, 111(3): 596–628.
Pataer A, Vorburger S A, Chada S, et al. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 protein physically associates with the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase PKR [J]. Mol Ther, 2005, 11(5): 717–723.
Yacoub A, Gupta P, Park M A, et al. Regulation of GST-mda-7 toxicity in human glioblastoma cells by ERBB1, ERK1/2, PI3K, and JNK1-3 pathway signaling [J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2008, 7(2): 314–329.
Sauane M, Su Z Z, Dash R, et al. Ceramide plays a prominent role in mda-7/IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis [J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2009, 222(3): 546–555.
Yacoub A, Park M A, Gupta P, et al. Caspase-, cathepsin-, and PERK-dependent regulation of mda-7/IL-24-induced cell killing in primary human glioma cells [J]. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 2008, 7(2): 297–313.
Taha T A, Mullen T D, Obeid L M. A house divided: Ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate in programmed cell death [J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2006, 1758(12): 2027–2036.
Park M A, Hamed H A, Mitchell C, et al. A serotype 5/3 adenovirus expressing mda-7/IL-24 infects renal carcinoma cells and promotes toxicity of agents that increase ROS and ceramide levels [J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2011, 79(3): 368–380.
Lebedeva I V, Su Z Z, Sarkar D, et al. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7, mda-7/interleukin-24, induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by promoting mitochondrial dysfunction and inducing reactive oxygen species [J]. Cancer Res, 2003, 63(23): 8138–8144.
Malhi H, Kaufman R J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease [J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 54(4): 795–809.
Wang M, Kaufman R J. The impact of the endoplasmic reticulum protein-folding environment on cancer development [J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014, 14(9): 581–597.
Malhotra J D, Kaufman R J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: A vicious cycle or a double-edged sword? [J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2007, 9(12): 2277–2293.
Gao H J, Zhu Y M, He W H, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by oxidative stress in decidual cells: A possible mechanism of early pregnancy loss [J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2012, 39(9): 9179–9186.
Corwin W L, Baust J M, Baust J G, et al. The unfolded protein response in human corneal endothelial cells following hypothermic storage: Implications of a novel stress pathway [J]. Cryobiology, 2011, 63(1): 46–55.
Yoshida H, Okada T, Haze K, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced formation of transcription factor complex ERSF including NF-Y (CBF) and activating transcription factors 6alpha and 6beta that activates the mammalian unfolded protein response [J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2001, 21(4): 1239–1248.
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon A D, et al. Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1alphamediated NF-kappab activation and down-regulation of traf2 expression [J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2006, 26(8): 3071–3084.
Do W, Herrera C, Mighty J, et al. Sigma 1 receptor plays a prominent role in IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013, 439(2): 215–220.
Li J, Shi L, Zhang X, et al. Recombinant adenovirus IL-24-Bax promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo [J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2010, 17(11): 771–779.
Dash R, Richards J E, Su Z Z, et al. Mechanism by which MCL-1 regulates cancer-specific apoptosis triggered by mda-7/IL-24, an IL-10-related cytokine [J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(12): 5034–5045.
Collina S, Gaggeri R, Marra A, et al. Sigma receptor modulators: A patent review [J]. Expert Opin Ther Pat, 2013, 23(5): 597–613.
He B, Huang X, Liu X, et al. Cancer targeting gene-virotherapy for pancreatic cancer using oncolytic adenovirus ZD55-IL-24 in immune-competent mice [J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2013, 40(9): 5397–5405.
Panneerselvam J, Munshi A, Ramesh R. Molecular targets and signaling pathways regulated by interleukin(IL)-24 in mediating its antitumor activities [J]. J Mol Signal, 2013, 8(1): 15.
Fels D R, Koumenis C. The PERK/EIF2alpha/ATF4 module of the UPR in hypoxia resistance and tumor growth [J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2006, 5(7): 723–728.
Fritsch R M, Schneider G, Saur D, et al. Translational repression of MCL-1 couples stress-induced EIF2 alpha phosphorylation to mitochondrial apoptosis initiation [J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(31): 22551–22562.
Raven J F, Koromilas A E. PERK and PKR: Old kinases learn new tricks [J]. Cell Cycle, 2008, 7(9): 1146–1150.
Lebedeva I V, Sarkar D, Su Z Z, et al. Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) differentially protect human prostate cancer cells from induction of apoptosis by melanoma differentiation associated gene-7, mda-7/IL-24 [J]. Oncogene, 2003, 22(54): 8758–8773.
Pinton P, Ferrari D, Magalhaes P, et al. Reduced loading of intracellular Ca2+ stores and downregulation of capacitative Ca2+ influx in Bcl-2-overexpressing cells [J]. J Cell Biol, 2000, 148(5): 857–862.
Oakes S A, Scorrano L, Opferman J T, et al. Proapoptotic Bax and Bak regulate the type 1 inositol trisphosphate receptor and calcium leak from the endoplasmic reticulum [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(1): 105–110.
Malhotra J D, Kaufman R J. ER stress and its functional link to mitochondria: Role in cell survival and death [J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2011, 3(9): a004424.
Bhutia S K, Das S K, Azab B, et al. Autophagy switches to apoptosis in prostate cancer cells infected with melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 (mda-7/ IL-24) [J]. Autophagy, 2011, 7(9): 1076–1077.
Lin C H, Shih C H, Tseng C C, et al. CXCl12 induces connective tissue growth factor expression in human lung fibroblasts through the Rac1/ERK, JNK, and AP-1 pathways [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e104746.
Buzas K, Oppenheim J J, Zack Howard O M. Myeloid cells migrate in response to IL-24 [J]. Cytokine, 2011, 55(3): 429–434.
You L, He B, Xu Z, et al. An anti-Wnt-2 monoclonal antibody induces apoptosis in malignant melanoma cells and inhibits tumor growth [J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(15): 5385–5389.
Moretti R M, Montagnani Marelli M, Mai S, et al. Clusterin isoforms differentially affect growth and motility of prostate cells: Possible implications in prostate tumorigenesis [J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67(21): 10325–10333.
Scaltriti M, Brausi M, Amorosi A, et al. Clusterin (SGP-2, ApoJ) expression is downregulated in low-and high-grade human prostate cancer [J]. Int J Cancer, 2004, 108(1): 23–30.
Scaltriti M, Santamaria A, Paciucci R, et al. Intracellular clusterin induces G2-M phase arrest and cell death in PC-3 prostate cancer cells [J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(17): 6174–6182.
Shannan B, Seifert M, Leskov K, et al. Challenge and promise: Roles for clusterin in pathogenesis, progression and therapy of cancer [J]. Cell Death Differ, 2006, 13(1): 12–19.
Trougakos I P, Lourda M, Agiostratidou G, et al. Differential effects of clusterin/apolipoprotein J on cellular growth and survival [J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2005, 38(4): 436–449.
Bhutia S K, Das S K, Kegelman T P, et al. Mda-7/IL-24 differentially regulates soluble and nuclear clusterin in prostate cancer [J]. J Cell Physiol, 2012, 227(5): 1805–1813.
Binet F, Mawambo G, Sitaras N, et al. Neuronal ER stress impedes myeloid-cell-induced vascular regeneration through IRE1alpha degradation of netrin-1[J]. Cell Metab, 2013, 17(3): 353–371.
Pelicano H, Carney D, Huang P. ROS stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications [J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2004, 7(2): 97–110.
Jiang G, Liu Y Q, Wei Z P, et al. Enhanced anti-tumor activity by the combination of a conditionally replicating adenovirus mediated interleukin-24 and dacarbazine against melanoma cells via induction of apoptosis [J]. Cancer Lett, 2010, 294(2): 220–228.
Gupta P, Emdad L, Lebedeva I V, et al. Targeted combinatorial therapy of non-small cell lung carcinoma using a GST-fusion protein of full-length or truncated mda-7/IL-24 with tarceva [J]. J Cell Physiol, 2008, 215(3): 827–836.
Fisher P B. Is mda-7/IL-24 a “magic bullet” for cancer? [J]. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(22): 10128–10138.
Sarkar S, Azab B, Quinn B A, et al. Chemoprevention gene therapy (CGT) of pancreatic cancer using perillyl alcohol and a novel chimeric serotype cancer terminator virus [J]. Curr Mol Med, 2014, 14(1): 125–140.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program) (2012CB518900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31160240, 31260621), the 12th Five Years Key Programs for Science and Technology Development of China (2012ZX10002006), the Hangzhou Normal University Supporting Project (PE13002004042), and the Natural Science Foundation of China of Jiangxi(20114BAB204016)
Biography: LIU Huilin, female, Master candidate, research direction: molecular mechanism of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver senescence, gene therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Chen, J., Jiang, X. et al. Apoptotic signal pathways and regulatory mechanisms of cancer cells induced by IL-24. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 21, 519–530 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-016-1205-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-016-1205-2