Abstract
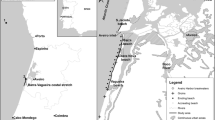
In the winter of 2006/2007 approximately 200,000 m3 of high quality sand from the dredging of the local marina were placed at the ocean-side beaches in the vicinity of a tourism development in Tróia, Portugal. The beach-quality sediment provided a source of “sand of opportunity” which was used to increase the dry-beach width of the highly used coastal stretch. The sediment was placed along approximately 600 m of shoreline and a monitoring program has since being carried out twice a year. High-resolution topographic surveys and sediment analysis are being conducted to evaluate the performance and response of the fill to the local forcing factors and ultimately to evaluate the effectiveness of the fill project. Two years after the nourishment, the sediment has been distributed both cross-shore and alongshore. The pre-nourishment beach slope was attained and the new shoreline has acquired a natural shape. Berm width increased by a maximum of 100 m, and a set of new dune ridges has developed, due to sand accumulation promoted by the settlement of vegetation. In conclusion, 2 years after its completion, the beach nourishment in Tróia can be viewed as a successful project in which the beneficial use of dredged material resulted in: 1) area for increased dune field growth and development, 2) enhancement of potential shorebird nesting areas and habitat, and 3) increased area for recreation purposes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade F, Ferreira MA, Gomes N, Joanaz Melo J, Leitão P, Pint MJ (2005) Strategic environmental assessment in Tróia (Portugal). In: Veloso Gomes F, Taveira Pinto F, Neves L, Sena A, Ferreira O (eds) Proceedings of the First International Conference on Coastal Conservation and Management in the Atlantic and Mediterranean (ICCCM’05), 91–98. Tavira, Portugal, 17–20 April 2005. (Proceedings published as book)
Carapuço AM (2005) Morfodinâmica do vértice noroeste da península de Tróia. MSc Thesis. Universidade do Algarve, 70 p
Carvalho C (1998) GranGraf V 2.0 β, Programa de Tratamento de Dados Granulométricos. F.C.U.L, Lisboa
Davies JL (1964) A morphogenic aproach to the world shorelines. Zeitschrift für Geomorphol 8:127–142
Folk RB, Ward WC (1957) Bazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J Sediment Petrol 27(1):3–26
Gama C (2004) Dinâmica de Sistemas Sedimentares do Litoral Ocidental Português a Sul do Cabo Espichel. PhD Dissertation. Universidade de Évora. 360 p
Hanson H, Brampton A, Capobianco M, Dette H, Hamm L, Laustrup C, Lechuga A, Spanhoff R (2002) Beach nourishment projects, practices, and objectives—a European overview. Coast Eng 47:81–111
Hidromod (2003) Nova Marina de Tróia – Modelação matemática da agitação e da hidrodinâmica de maré. In: Andrade F, Melo J Estudo de impacte ambiental da Marina e Novo Cais dos ferries do Troiaresort (Península de Tróia, Setúbal), pp. 137–157
IMAR (2005) Relatório de Conformidade Ambiental do Projecto de Execução da Marina e novo Cais dos “ferries” do Troiaresort – Anexo III. Submitted to IMOAREIA – Investimentos Turísticos. SGPS, SA, p 146
IMAR (2009) Relatório do Programa de Monitorização Ambiental do projecto da Marina e novo Cais dos “ferries” do Troiaresort. Submitted to IMOAREIA – Investimentos Turísticos. SGPS, SA, p 296
Instituto Hidrográfico (2003) Tabela de Marés 2004. Volume I - Portugal. Instituto Hidrográfico da Marinha. Ministério da Defesa Nacional, Lisboa
IPCC (2007) In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Contribution of working group II to the Fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 976
National Research Council (1995) Beach nourishment and protection. National Academy Press, Washington D.C., p 334
Silveira TM, Kraus NC, Psuty NP, Andrade F (2011) Beach Nourishment on Tróia Peninsula, Portugal. In: Roberts TM, Rosati JD, Wang P (eds) Proceedings, Symposium to Honor Dr. Nicholas C. Kraus. J Coast Res SI59:173–180
Valverde HR, Trembanis AC, Pilkey OH (1999) Summary of beach nourishment episodes on the U.S. east coast barrier islands. J Coast Res 15:1100–1118
Yozzo DJ, Wilber P, Will RJ (2004) Beneficial uses of dredged material for habitat creation, enhancement, and restoration in New York-New Jersey Harbor. J Environ Manag 73:39–52
Acknowledgments
Data were obtained in the framework of the “Environmental monitoring program for the marina and new ferry dock of the Troiaresort”, conducted by the Institute of Marine Research (IMAR) for SONAE turismo. The IMAR team is hereby thanked for their help in the field data gathering over the years.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silveira, T.M., Frazão Santos, C. & Andrade, F. Beneficial use of dredged sand for beach nourishment and coastal landform enhancement—the case study of Tróia, Portugal. J Coast Conserv 17, 825–832 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-013-0283-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-013-0283-y