Abstract
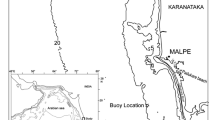
This study is considered as a completion for the carried out previous research on the Egyptian northern coast near Port Said. An evaluation was carried out for the purpose of analyzing satellite measured wave data, or carrying out preliminary evaluations for the study area, in the Nile delta coast near Damitta. The available offshore historical significant wave heights from altimeter measurements are used in this research for the period from 2005 to 2008. In this study waves were transformed from the offshore area to nearshore, sediment transport volumes were evaluated by applying and adjusting some of the practical formulae, which are considered reasonable for this area. The study domain dimensions are 50 km long offshore and 15 km wide alongshore. Wave nearshore transformation is carried out by using the mathematical Simulating WAves Nearshore model (SWAN) based on seasonal/directional bases. Two seasons are considered in the analysis, which are both winter and summer, to represent the mean seasons of the year. The three formulae, which are CERC, van Rijn and Boer and Galvin for sediment transport evaluation are applied in the study area. The reference values were applied for comparison were checked. The obtained rough evaluations were considered acceptable and can be roughly applied for both research and engineering purposes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Aal FM (2002) “Mechanics of sediment transport for alluvial rivers and sandy beaches”. Cairo University-Egypt
Admiralty Publications (2000) “Mediterranean pilot”, NP46. Somerset, UK: Admiralty Publications, Hydrographic Department, pp 15–36
Admiralty Publications (2003) Mina dumyat to bur said (admiralty chart, No. INT-2578), United Kingdom national hydrograph, scale 1: 100,000, 1 sheet
ARGOSS (Advisory and Research Group on Geo Observation Systems and Services) (1995) Waveclimate. (www.waveclimate.com - accessed March, 2006)
ARGOSS (Advisory and Research Group on Geo Observation Systems and Services). The Netherlands (2006) “Validation Report for Online Offshore Wind and Wave Climate, Global database”
Bayram A, Larson M, Hanson H (2007) A new formula for the total longshore sediment transport rate. Coast Eng J 54:700–710
Camenen B, Larroude P (2002) Comparison of sediment transport formulae for the coastal environment. Coast Eng J 48(2):111–132
El-Asmar H (2002) Short term coastal changes along Damietta-Port said Coast Northeast of the Nile Delta, Egypt. J Coast Res 18(3):433–441
El-Asmar H, White K (2002) Changes in coastal sediment transport processes due to construction of New Damietta Harbor, Nile Delta, Egypt. Coast Eng J 46(2):127–138
El Banna MM, Frihy OE (2009) Natural and anthropogenic influences in the northeastern coast of the Nile delta, Egypt. Environ Geol 57(7):1593–1602
Frihy O (2001) The necessity of environmental impact assessment (EIA) in implementing coastal projects: lessons learned from the Egyptian Mediterranean Coast. Ocean Coast Manag 44:489–516
Frihy O, Lawrence D (2004) Evolution of the modern Nile delta promontories: development of accretional features during shoreline retreat. Environ Geol 46(6):914–931
Frihy O, Badr A, Hassan M (2002) Sedimentation processes at the navigation channel of the Damietta Harbour on the Northeastern Nile Delta Coast of Egypt. J Coast Res 18(3):459–469
Frihy OE, Deabes EA, El Gindy AA (2010) Wave climate and Nearshore processes on the Mediterranean Coast of Egypt. J Coast Res 26(1):103–112
Goda Y (1985) “Random seas and design of maritime structures”, advances in ocean engineering, vol 15. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, 323p
Horikawa K (1988) Nearshore dynamics and coastal processes: theory, management, and predictive models. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, 522p
Khalifa MA, El Ganainy MA, Nasr RI (2009) Wave transformation and longshore sediment transport evaluation for the Egyptian northern coast, via extending modern formulae. J Coast Res 25(3):755–767, West Palm Beach (Florida), ISSN 0749-0208
Komar PD (1998) Beach processes and sedimentation, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, 545p
May JP, Tanner WF (1973) The littoral power gradient and shoreline changes. In: Coates DR (ed) Coastal geomorphology. New York State University Press, New York, pp 43–61
Ministry of Transport-Egypt (1996) Climatological Atlas of Egypt
Ris RC, Booij N, Holthuijsen LH, Haagsma IJG (1998) “SWAN User manual”, Cycle II, Delft, The Netherlands: Delft University of Technology
SAILWX (SAILING WEATHER SERVICE, LLC-USA. Sailing Weather Services), 2006. (www.windfinder.com – accessed: July, 2010)
Soulsby RL, Damgaard J (2005) Bed load sediment transport in coastal waters. Coast Eng J 52(8):673–689
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (2002) “Coastal Engineering Manual - Part III: Coastal Sediment Processes”. DC : CERC (Coastal Engineering Research Center), pp 1–113. (www.ce.ufl.edu/~sheppard/eoc6430/Coastal_Engineering_Manual.htm - accessed Oct., 2007)
Van de Graaff J (1999) Coastal sediment transport. Lecture notes, Unesco IHE International Institute for Infrastructural, Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, The Netherlands
Van Rijn LC, Boer S (2006) The effects of grain size and bottom slope on sand transport in the coastal zone. International Conference on Coastal Engineering, (San Diego-USA)
WIKIPEDIA, THE FREE ENCYCLOPEDIA-Nile Delta, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nile_Delta (accessed: August 2009)
Acknowledgements
My deep thanks to my family for the continuous encouragement. Deep gratitude to my professors, who gave the favor of teaching the coastal engineering subjects. Many thanks for this great international scientific journal for support and giving me the chance to publish this post doctor technical communication notes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalifa, M.A. Adoption of recent formulae for sediment transport calculations applied on the Egyptian Nile delta coastal area. J Coast Conserv 16, 37–49 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-011-0166-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-011-0166-z