Abstract
Background
High-mobility group box 2 (HMGB2) is considered as oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), while its clinical implication is still unknown. This study aimed to explore the correlation of HMGB2 with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis in NSCLC patients.
Methods
A total of 133 NSCLC patients who received radical excision were enrolled. HMGB2 expression in the tumor specimens and paired adjacent tissue specimens was determined by immunohistochemical assay (for protein expression) and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay (for gene expression), respectively.
Results
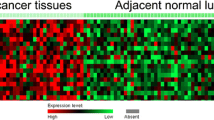
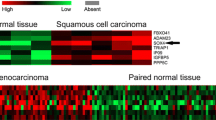
HMGB2 protein expression was higher in tumor tissue compared with adjacent tissue, and it could distinguish tumor tissue from adjacent tissue (area under the curve (AUC): 0.775, 95%confidence interval (95%CI): 0.720–0.830). Meanwhile, tumor HMGB2 protein high expression correlated with lymph node (LYN) metastasis and advanced TNM stage. Additionally, tumor HMGB2 protein high expression associated with worse disease-free survival (DFS), while HMGB2 protein expression did not correlate with overall survival (OS). Besides, HMGB2 mRNA expression was raised in tumor tissue compared with adjacent tissue, and it had a good value in differentiating tumor tissue from adjacent tissue (AUC: 0.875, 95% CI: 0.834–0.915). Furthermore, tumor HMGB2 mRNA high expression correlated with higher Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status score, LYN metastasis, and advanced TNM stage. Meanwhile, tumor HMGB2 mRNA high expression associated with shorter DFS and OS.
Conclusion
HMGB2 could be a biomarker that reflects disease features and prognosis of NSCLC, which is beneficial to improve clinical efficacy in NSCLC patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR (2019) Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc 94(8):1623–1640
Goldstraw P, Ball D, Jett JR et al (2011) Non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 378(9804):1727–1740
Reck M, Rabe KF (2017) Precision diagnosis and treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 377(9):849–861
Field JK, Oudkerk M, Pedersen JH, Duffy SW (2013) Prospects for population screening and diagnosis of lung cancer. Lancet 382(9893):732–741
Cheema PK, Rothenstein J, Melosky B et al (2019) Perspectives on treatment advances for stage III locally advanced unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol 26(1):37–42
Zappa C, Mousa SA (2016) Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5(3):288–300
Niu L, Yang W, Duan L et al (2020) Biological functions and theranostic potential of HMGB family members in human cancers. Ther Adv Med Oncol 12:1758835920970850
Grasser KD, Launholt D, Grasser M (2007) High mobility group proteins of the plant HMGB family: dynamic chromatin modulators. Biochim Biophys Acta 1769(5–6):346–357
Taniguchi N, Kawakami Y, Maruyama I, Lotz M (2018) HMGB proteins and arthritis. Hum Cell 31(1):1–9
Kucirek M, Bagherpoor AJ, Jaros J et al (2019) HMGB2 is a negative regulator of telomerase activity in human embryonic stem and progenitor cells. FASEB J 33(12):14307–14324
Kwon JH, Kim J, Park JY et al (2010) Overexpression of high-mobility group box 2 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 16(22):5511–5521
Fu D, Li J, Wei J et al (2018) HMGB2 is associated with malignancy and regulates Warburg effect by targeting LDHB and FBP1 in breast cancer. Cell Commun Signal 16(1):8
Zhang P, Lu Y, Gao S (2019) High-mobility group box 2 promoted proliferation of cervical cancer cells by activating AKT signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 120(10):17345–17353
Li S, Yang J, Xia Y et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes proliferation and Invasion via targeting miR-181a-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Res 26(2):289–296
Hu Z, Gu X, Zhong R, Zhong H (2018) Tumor-infiltrating CD45RO(+) memory cells correlate with favorable prognosis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Dis 10(4):2089–2099
Tian Y, Zhao K, Yuan L et al (2018) EIF3B correlates with advanced disease stages and poor prognosis, and it promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biomark 23(2):291–300
Pu J, Tan C, Shao Z et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA PART1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via targeting miR-590-3p/HMGB2 axis. Onco Targets Ther 13:9203–9211
Cai X, Ding H, Liu Y et al (2017) Expression of HMGB2 indicates worse survival of patients and is required for the maintenance of Warburg effect in pancreatic cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 49(2):119–127
Cui G, Cai F, Ding Z, Gao L (2019) HMGB2 promotes the malignancy of human gastric cancer and indicates poor survival outcome. Hum Pathol 84:133–141
Yang S, Ye Z, Wang Z, Wang L (2020) High mobility group box 2 modulates the progression of osteosarcoma and is related with poor prognosis. Ann Transl Med 8(17):1082
He ZH, Guo F, Hu XX et al (2020) Knockdown of HMGB2 inhibits proliferation and invasion of renal tumor cells via the p-38MAPK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(9):4729–4737
Tang C, Yang Z, Chen D et al (2017) Downregulation of miR-130a promotes cell growth and epithelial to mesenchymal transition by activating HMGB2 in glioma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 93:25–31
Wu ZB, Cai L, Lin SJ et al (2013) High-mobility group box 2 is associated with prognosis of glioblastoma by promoting cell viability, invasion, and chemotherapeutic resistance. Neuro Oncol 15(9):1264–1275
Syed N, Chavan S, Sahasrabuddhe NA et al (2015) Silencing of high-mobility group box 2 (HMGB2) modulates cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proteomics 15(2–3):383–393
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approved the current study.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, N., Zhu, T., Qin, D. et al. High-mobility group box 2 reflects exacerbated disease characteristics and poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Ir J Med Sci 191, 155–162 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02549-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02549-8