Abstract
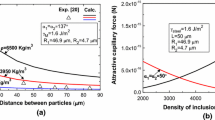
The quality of steel is limited, among others, by the contained non-metallic inclusions. A key factor in this context is the growth of micro-sized indigenous inclusions. Those are assumed to form larger inclusions or clusters by collision in the turbulent melt flow. In this study, a numerical model is established to investigate the collision probability of spherical and clustered non-metallic inclusions in steel by discrete particle simulations. A strong dependence of the agglomeration probability from the particle sizes, form and shear rate in the process is observed. Larger particles are hampered to coagulate because of the significant influence of the lubrication force. Thus, the maximum particle size of spherical particles is limited, while clustered agglomerates can still grow. From the simulation results, models for the determination of the collision coefficient are deduced for spherical particles and non-spherical particle clusters.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang, B.G. Thomas, in XXIV National Steelmaking Symposium, vol. 26 (Morelia, Mich, Mexico, 2003), p. 42.
H. Yu, C. Ji, B. Chen, C. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22, 17–23 (2015).
L. Zhang, JOM 65, 1138–1144 (2013).
Y. Miki, B.G. Thomas, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 30, 639–654 (1999).
H. Tozawa, Y. Kato, K. Sorimachi, T. Nakanishi, ISIJ Int. 39, 426–434 (1999).
H. Lei, D. Geng, J. He, ISIJ Int. 49, 1575–1582 (2009).
H. Lei, J. He, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28, 642–646 (2012).
H. Ling, L. Zhang, H. Li, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 2991–3012 (2016).
P.G. Saffman, J.S. Turner, J. Fluid Mech. 1, 16 (1956).
K. Higashitani, R. Ogawa, G. Hosokawa, Y. Matsuno, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 15, 299–304 (1982).
M. Cournil, F. Gruy, P. Gardin, H. Saint-Raymond, Chem. Eng. Process. 45, 586–597 (2006).
L. Zheng, A. Malfliet, P. Wollants, B. Blanpain, M. Guo, ISIJ Int. 56, 926–935 (2016).
H. Yin, H. Shibata, T. Emi, M. Suzuki, ISIJ Int. 37, 936–945 (1997).
R. Mittal, G. Iaccarino, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 37, 239–261 (2005).
H. Hu, N.A. Patankar, M.Y. Zhu, J. Comput. Phys. 169, 427–462 (2001).
K. Sasai, ISIJ Int. 56, 1013–1022 (2016).
C. Crowe, M. Sommerfeld, Y. Tsuji, Multiphase Flows with Droplets and Particles (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2012).
N. Martys, J. Rheol. 49, 401–424 (2005).
J. Israelachvili, Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 3rd edn. (Academic Press, Burlington, 2011), p. 256.
V. Smilauer, C. Emanuele, B. Chareyre, S. Dorofeenko, J. Duriez, N. Dyck, J. Elias, B. Er, A. Eulitz, A. Gladky, N. Guo, C. Jakob, F. Kneib, J. Kozicki, D. Marzougui, R. Maurin, C. Modenese, L. Scholtes, L. Sibille, J. Stransky, T. Sweijen, K. Thoeni, and C. Yuan, Yade Documentation, 2nd edn. The Yade Project (2015). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.34073
M v Smoluchowski, Z. Phys. Chem. 29U, 129–168 (1918)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for supporting the scientific work in terms of the Collaborative Research Centre “Multi-Functional Filters for Metal Melt Filtration—A Contribution towards Zero Defect Materials” (CRC 920, Subproject B06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haustein, M., Asad, A. & Schwarze, R. Collision of Micro-sized Non-metallic Inclusions in Liquid Steel Flows: A Computational Study. JOM 70, 2943–2949 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3113-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3113-8