Abstract
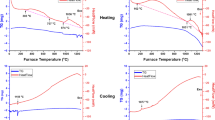
The present work represents a comparative study of impurity removal (sulfur, phosphorus, and carbon) from pig iron melt by the addition of lime powder and reduced fluxed iron ore pellets separately in a 5-kg-capacity induction melting furnace. Two types of reduced flux pellets (80% and 50%) of similar basicity (~3.06) were charged separately into the pool to obtain the different oxidizing atmospheres of the bath. Results showed that the rate of impurity removal increases up to 6 min of exposure time and decreases afterward. Only lime powder charging, sulfur (~77%), and a small fraction of carbon were removed from pig iron. Phosphorous (~41%), sulfur (~53%), and carbon (~96%) were removed simultaneously when 80% reduced fluxed pellets were used. The present study indicates that the optimum removal of impurities is possible by charging 80% reduced flux iron ore pellets from the pig iron melt.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.K. Dutta, A.B. Lele, and N.K. Pancholi, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 57, 467 (2004).
A.M. Chernyshev, Transl. Metall. 5, 11 (1967).
A. Rai, A.K. Mandal, K.K. Singh, and T.R. Mankhand, Int. J. Waste Resour. (IJWR) 3, 40 (2013).
A.K. Mandal, A. Sarkar, and O.P. Sinha, J. Inst. Eng. Ser. D 97, 69 (2016).
A.K. Mandal and O.P. Sinha, Miner. Process. Extr Metall. 126, 182 (2017).
R.C. Gupta, Theory and Experiments in Ferrous Metallurgy (New Delhi, India: PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., 2015).
A. Ghosh and A. Chatterjee, Iron Making and Steel Making: Theory and Practice (New Delhi: PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., 2012).
J. Pal, S. Ghorai, M.C. Goswami, D. Ghosh, D. Bandyopadhyay, and S. Ghosh, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 20, 329 (2013).
J.G. Harhai and D.A. Dukelow, JOM 18, 833 (1966).
A.K. Mandal, A. Sarkar, and O.P. Sinha, SGAT Bull. 13, 95 (2012).
R.H. Tupkary and V.R. Tupkary, An Introduction to Modern Steel Making (New Delhi, India: Khanna Publisher, 2012).
J. Kijac and M. Borgon, Metalurgija 47, 347 (2008).
K. Sadrnehaad, J. Eng. Islam. Repub. Iran 3, 37 (1990).
M. Motlagh, JOM 37, 59 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dishwar, R.K., Agrawal, S., Mandal, A.K. et al. Effect of Reduced Flux Iron Ore Pellets on Removal of Impurities from Pig Iron During Induction Melting: A New Phenomenon. JOM 70, 977–981 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2569-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2569-2