Abstract
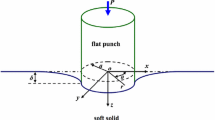
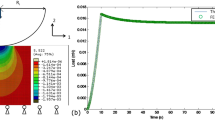
Although both spherical and flat tips have been used in nanoindentation studies of soft biomaterials, care must be taken in selecting and validating a tip for a specific application. This article compares the moduli measured using spherical nanoindentation, flat tip (specifically, a flattened cone) nanoindentation, and unconfined compression testing of three polyacrylamide gels with nominal moduli between 10 kPa and 50 kPa. Although spherical indentation moduli were consistent with compression testing moduli and were independent of indentation depth, the flat tip results showed a significant increase in modulus with depth when analyzed using a flat punch model. Alternative methods are proposed to analyze the flat tip data to bring the flat tip results into alignment with the moduli measured using the other mechanical testing techniques.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M Ebenstein, Handbook of Nanoindentation with Biological Applications, ed. M.L. Oyen (Singapore: Pan Stanford Publishing, 2010), pp. 279–324.
D.M. Ebenstein and L.A. Pruitt, Nano Today 1, 26 (2006).
O. Franke, M. Goken, and A.M. Hodge, J. Met. 60, 49 (2008).
J.D. Kaufman, G.J. Miller, E.F. Morgan, and C.M. Klapperich, J. Mater. Res. 23, 1472 (2008).
M.L. Oyen, Exp. Tech. 37, 73 (2013).
J. Deuschle, S. Enders, and E. Arzt, J. Mater. Res. 22, 3107 (2007).
D.M. Ebenstein, J. Mater. Res. 26, 1026 (2011).
J.D. Kaufman and C.M. Klapperich, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2, 312 (2009).
S. Piccarolo, A. Falsone, and A.M. Poulose, Meas. Sci. Technol. 21, 065701–065708 (2010).
D.M. Ebenstein and K.J. Wahl, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298, 652 (2006).
S. Gupta, F. Carrillo, C. Li, L. Pruitt, and C. Puttlitz, Mater. Lett. 61, 448 (2007).
J.C. Kohn and D.M. Ebenstein, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 20, 316 (2013).
C.L. Slaboch, M.S. Alber, E.D. Rosen, and T.C. Ovaert, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 10, 75 (2012).
M. Galli, K.S.C. Comley, T.A.V. Shean, and M.L. Oyen, J. Mater. Res. 24, 973 (2009).
N.K. Simha, H. Jin, M.L. Hall, S. Chiravarambath, and J.L. Lewis, J. Biomech. Eng. 129, 767 (2007).
D.M. Ebenstein, and L.A. Pruitt, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 69A, 222 (2004).
K. Liu, M.R. VanLandingham, and T. Ovaert, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2, 355 (2009).
T. Niu and G. Cao, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 47, 385303 (2014).
P.L. Leong and E.F. Morgan, Acta Biomater. 4, 1569 (2008).
A.B. Mann and J.B. Pethica, Langmuir 12, 4583 (1996).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
M. Zhang, Y.P. Zheng, and F.T. Mak, Med. Eng. Phys. 19, 512 (1997).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Matthew Heintzelman for preparation of the polyacrylamide gels and Professor Wendelin Wright and Dr. Jove Graham for valuable feedback during preparation of the manuscript. K.J.T. was funded through the Program for Undergraduate Research at Bucknell University. The nanoindenter used in this study was obtained through the support of the National Science Foundation (MRI-1040319). Conclusions and recommendations expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, K.J., Ebenstein, D.M. Comparison of Spherical and Flat Tips for Indentation of Hydrogels. JOM 67, 713–719 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1332-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1332-9