Abstract
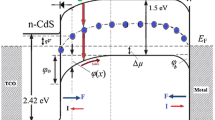
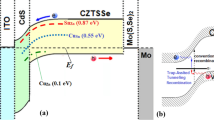
Ultrathin film solar cells based on CdS/CdTe (d CdTe ≤ 1 µm) suffer from two main issues: incomplete photo absorption and high degradation rate. The former is cured by light-trapping techniques, whereas the latter is a matter of fabrication details. Interdiffusion of the material components and formation of subsequent interlayers at the front/back region can change the optical/electrical properties and performance/stability of the device. We model the degradation of the ultrathin CdTe film devices considering the material interdiffusion and interlayers formation: CdTeS, CdZnTe, Cu x Te (i.e., Te/Cu bilayer), and oxide interlayers (i.e., CdTeO3). The diffusion rate of the materials is considered separately and the reactions that change the interlayer’s properties are studied. Additionally, a back contact of single-walled carbon nanotube showed a higher stability than the metallic contacts. A new time-dependent approach is applied to simulate the degradation rate due to formation of any interlayer. It is shown that the materials interdiffusion causes a defect increment under thermal stress and illumination. The metallic back contact accelerates the degradation, whereas single-walled carbon nanotubes show the highest stability. A SCAPS simulator was used because of its ability in defining the properties of the back contact and metastabilities at the interface layers. The properties of the layers were taken from the experimental data reported in the literature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Rowlands, S. Irvine, V. Barrioz, and D.A. Lamb, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 23, 015017 (2008).
A. Salavei, I. Rimmaudo, F. Piccinelli, and A. Romeo, Thin Solid Films 535, 257 (2013).
N. Paudel, K.A. Wieland, S. Asher, and A.D. Compaan, Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 22, 107 (2014).
Z. Bai, J. Yang, and D. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 143502 (2011).
W. Xia, H. Lin, H. Wu, C.W. Tang, and I. Irfan, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 128, 411 (2014).
N.E. Gorji, Appl. Phys. A 16, 1347 (2014).
H. Lin (Doctoral thesis, University of Rochester, 2012).
B.E. McCandlessa, S. Hegedus, R.W. Birkmire, and D. Cunningham, Thin Solid Films 431–432, 249 (2003).
K.D. Dobson, I. Visoly-Fisher, G. Hodes, and D. Cahen, Sol. Energy Mater. Solar Cells 62, 295 (2000).
I.V. Fisher, K.D. Dobson, G. Hodes, and D. Cahen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 13, 289 (2003).
V. Krishnakumar, A. Barati, H. Schimper, A. Klein, and W. Jaegermann, Thin Solid Films 535, 233 (2013).
A.J. Clayton, S.C. Irvine, E. Jones, and V. Barrioz, Sol. Energy Mater. Solar Cells 101, 68 (2012).
R. Dhere, Y. Zhang, M. Romero, R. Noufi, and T. Gassert, in Proceedings of the 33rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference—PVSC 2008 (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2008).
K.V. Krishna, V. Dutta, and K. Rao, Phys. Status Solidi A 198, 443 (2003).
E.W. Jones, V. Barrioz, S. Irvine, and D. Lamb, Thin Solid Films 517, 2226 (2009).
S. Irvine, V. Barrioz, A. Stafford, and K. Durose, Thin Solid Films 76, 480 (2005).
G. Kartopu, A.A. Taylor, A.J. Clayton, V. Barrioz, D.A. Lamb, and S. Irvine, J. Appl. Phys. 115, 104505 (2014).
G. Teeter, J. Appl. Phys. 102, 034504 (2007).
S. Hegedus, B. McCandless, R. Birkmire, in Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference—PVSC 2000 (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2000).
J. Zhou, X. Wu, A. Duda, G. Teeter, and S.H. Demtsu, Thin Solid Films 515, 7364 (2007).
V. Plotnikov (Doctoral thesis, University of Toledo, 2009).
A.B. Phillips, R. Zartman, P.V. Plotnikov, and A.D. Compaan, Nano Lett. 13, 5224 (2013).
M. Burgelman, K. Decock, S. Khelifi, and A. Abass, Thin Solid Films 535, 296 (2013).
M. Nardone, J. Appl. Phys. 115, 234502 (2014).
G. Xosrovashvili and N.E. Gorji, Int. J. Photoenerg. 784857 (2014).
T.D. Dzhafarov, S. Yesilkaya, and M. Caliskan, Sol. Energy Mater. Solar Cells 85, 371 (2005).
D. Krasikov, A. Knizhnik, B. Potapkin, and T. Sommerer, Thin Solid Films 535, 322 (2013).
N.E. Gorji, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 13, 743 (2014).
N.E. Gorji and M. Houshmand, Physica E 50, 122 (2013).
N.E. Gorji, IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 14, 983 (2014).
Acknowledgement
Prof. M. Burgelman and his colleagues are appreciated for providing us the SCAPS simulator. This work was funded by the Nano council of Iranian under National Elites Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Houshmand, M., Zandi, M.H. & Gorji, N.E. SCAPS Modeling for Degradation of Ultrathin CdTe Films: Materials Interdiffusion. JOM 67, 2062–2070 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1286-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1286-3