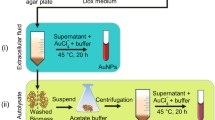
Abstract
In this study, the fungus Hormoconis resinae was screened from soil near a refinery and was found to produce stable gold nanoparticles extracellularly. The kinetics of the reaction was studied using UV-Vis spectroscopy and was further characterized by x-ray diffraction, energy dispersive x-ray (EDX) analysis, and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. These analyses revealed that the gold nanoparticles are spherical and in nano-regime. The most important feature of Hormoconis resinae fungi is the following fact: they have a widespread presence in soil and can produce huge biomass. Such a cheap source of material gives the opportunity for cost-effective preparation of various gold-based nanostructures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Stephen and S.J. Maenaughton, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 10 (1999), pp. 230–233.
R.K. Mehra and D.R. Winge, J. Cell. Biochem., 45 (1991), pp. 30–40.
G. Southam and T.J. Beveridge, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 58 (1994), pp. 4527–4530.
D. Fortin and T.J. Beveridge, in Biomineralisation, ed. E. Baeuerlein (Verlag, Germany: Wiley-VCH, 2000), p. 294.
M. Sastry, A. Ahmad, M.I. Khan, and R. Kumar, in Nanobiotechnology, ed. C.M. Niemeyer and C.A. Mirkin (Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH, 2004), pp. 126–135.
S. Mann, Biomimetic Materials Chemistry (New York: VCH, 1996).
T.J. Beveridge and R.G.E. Murray, J. Bacteriol., 141 (1980), pp. 876–877.
P. Mukherjee et al., Angew. Chem., 40 (2001), pp. 3585–3588.
M. Sastry, A. Ahmad, N.I. Islam, and R. Kumar, Current Sci., 85 (2003), pp. 162–170.
P. Mukherjee et al., ChemBioChem., 5 (2002), pp. 461–463.
A. Ahmad et al., Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 28 (2003), pp. 313–318.
N. Duran et al., J. Nanobiotechnol., 3 (2005), pp. 8–15.
D. Mandal et al., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 69 (2006), pp. 485–492.
J. L. Gardea-Torresdey et al., Nano Lett., 2 (2002), pp. 397–401.
A. Ahmad et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 124 (2002), pp. 12108–12109.
A. Ahmad et al., Langmuir, 19 (2003), pp. 3550–3553.
A.N. Mishra et al., NATCHEE 2010, Proceedings of International Conference, ed. L.D. Khemani and S. Dass (India: Tata McGraw-Hill, 2010), pp. 205–210.
R. Varshney et al., Digest J. Nanomat. and Biostruct., 4 (2009), pp. 349–355.
S.S. Nigam, in Laboratory Test Methods in Microbiology (Issued by Defence Research Laboratory (Materials), Ministry of Defence, Kanpur, 1965).
Anonymous, HERB, IMI, Handbook (Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Ferry Lane, Kew, Surrey, England, 1960).
V. Armendariz et al., J. Nanoparticle Res., 6 (2004), pp. 377–382.
S. Senapati et al., Small, 1 (2005), pp. 517–520.
He Shiying et al., Materials Letters, 61 (2007), pp. 3984–3987.
P. Mulvaney, Langmuir, 12 (1996), pp. 788–800.
K.L. Kelly et al., J. Phys. Chem. B, 107 (2003), pp. 668–677.
M.A. EL-Sayed, Acc. Chem. Res., 34 (2001), pp. 257–264.
M. Maye et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 124 (2002), pp. 4958–4959.
T.J. Norman et al., J. Phys. Chem. B, 106 (2002), pp. 7005–7012.
S. Shiv Shankar et al., J. Mater. Chem., 13 (2003), pp. 1822–1826.
J.W. Jeffrey, Methods in Crystallography (New York: Academic Press, 1971).
S. Shiv Shankar et al., Nat. Mater., 3 (2004), pp. 482–488.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, A.N., Bhadauria, S., Gaur, M.S. et al. Extracellular microbial synthesis of gold nanoparticles using fungus Hormoconis resinae . JOM 62, 45–48 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-010-0168-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-010-0168-6