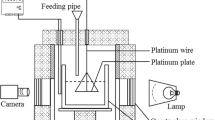
Abstract
Modern smelter potlines often undergo process excursions, which are attributed to “solubility problems” of the alumina used. Assigning the problem to a specific property is, however, a challenge, compounded by the fact that the alumina has usually undergone secondary treatments through a dry scrubbing system prior to arrival at the cell. With a better understanding there is the potential for avoiding some of the troubles experienced in these “alumina solubility” problems but there is a need to clarify what are the relevant chemical and physical properties of the alumina that are having the impact. Published and unpublished data are drawn together here to provide further insight into the alumina solubility issues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Homsi, “Alumina Requirements for Smelting,” Proc. 7th Australasian Aluminium Smelting Technology Workshop” (2001), pp. 426–455.
K. Grjotheim and B.J. Welch, Aluminium Smelter Technology—A Pure and Applied Approach (Dusseldorf: Al Verlag, 1988), pp. 46–48.
J. Thonstad, P. Johansen, and E.W. Kristensen, “Some Properties of Alumina Sludge” Light Metals 1980, ed. C.J. McMinn (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1980), pp. 227–239.
G.I. Kuschel, “The Effect of Alumina Properties and Smelter Operating Conditions on the Dissolution Behaviour of Alumina” (Ph.D. thesis, University of Auckland, 1989).
G.I. Kuschel and B.J. Welch, “The Effect of Alumina Properties and Smelter Operating Conditions on the Dissolution Behaviour of Alumina,” Proc. 2nd Int. Alumina Quality Workshop (Perth, Australia, AQW Committee, 1990), pp. 58–70.
R.G. Haverkamp, “Surface and Dissolution Studies of Fluorinated Aluminas” (Ph.D. thesis, University of Auckland, 1992).
N. Wai-poi, “Continuous Feeding of Alumina for Complete Dissolution in Cryolite-Based Melts” (Ph.D. thesis, University of Auckland, 1994).
R.G. Haverkamp, B.J. Welch, and J.B. Metson, “The Influence of Fluorination on the Dissolution Rate of Alumina in Smelter Electrolyte,” Light Metals 1994, ed. Ulrich Mannweiler (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1994), pp. 365–370.
X. Liu, S.F. George, and V.A. Wills, “Visualization of Alumina Dissolution in Cryolitic Melts,” Light Metals 1994, ed. Ulrich Mannweiler (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1994), pp. 259–364.
P. Navarro, “Optimizing Alumina Feeding Strategy for Different Pot Technologies, Work Practices, and Process Parameters” (Presentation at TMS Annual Meeting 2006—Special Session on Alumina Quality, San Antonio, Texas, March 12–16, 2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welch, B.J., Kuschel, G.I. Crust and alumina powder dissolution in aluminum smelting electrolytes. JOM 59, 50–54 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-007-0065-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-007-0065-9