Abstract
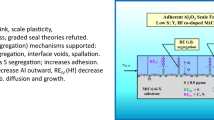
While interfacial sulfuris the primary chemical factor affecting Al2O3 scale adhesion, moisture-induced delayed spallation appears as a secondary, but impressive, mechanistic detail. Similarities with bulk metallic phenomena suggest that hydrogen embrittlement from ambient humidity, resulting from the reaction Alalloy+3(H2O)air=Al(OH)− 3+3H+ may be the operative mechanism. This proposal was tested on pre-oxidized René N5 by standard cathodic hydrogen charging in 1N H2SO4, as monitored by weight change, induced current, and microstructure. Cathodic polarization at −2.0 V abruptly stripped mature Al2O3 scales at the oxide-metal interface. Anodic polarization at +2.0V, however, produced alloy dissolution. Finally, with no applied voltage, the acid electrolyte produced neither scale spallation nor alloy dissolution. Thus, hydrogen charging was detrimental to alumina scale adhesion. Moisture-induced interfacial hydrogen embrittlement is concluded to be the cause of delayed scale spallation and desktop thermal barrier coating failures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Smialek, Moisture Induced Spallation and Interfacial Hydrogen Embrittlement of Al 2 O 3 Scales, NASA Technical Memorandum 214030 (Washington, D.C.: NASA, 2005).
J. L. Smialek, “Adherent Al2O3 Scales Formed on Undoped NiCrAl Alloys”, N.L. Peterson Mem. Symp. Proc. on Oxidation of Metals and Associated Mass Transport. ed. M.A. Dayananda, S.J. Rothman, and W.E. King (Warrendale, PA, TMS, 1987). pp. 297–313.
B.K. Tubbs and J.L. Smialek, “The Effect of Sulfur Removal on Scale Adhesion to PWA 1480”, Corrosion and Particle Erosion of Materials at High Temperature, ed. V. Srinivasan and K. Vedula, (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1989), pp. 459–487.
J.L. Smialek, “Adherent Scales Produced on Uncoated Superalloys: Desulfurized René 142 and René N5”. (Paper presented at the David L. Douglass Symposium on High Temperature Corrosion during the annual meeting of the Electrochemical Society, Miami Beach, FL, Oct 9–14, 1994), paper No. 535, 833–834.
J.L. Smialek et al, “Effects of Hydrogen Annealing, Sulfur Segregation and Diffusion on the Cyclic Oxidation Resistance of Superalloys: A Review”, Thin Solid Films, 253 (1994), p. 285–292.
J.L. Smialek, “Toward Optimum Scale and TBC Adhesion on Single Crystal Superalloys”, High Temperature Corrosion and Materials Chemistry, volume 98–9, ed. E.J. Opila et al. (Pennington, NJ: The Electrochemical Society, 1988), pp. 211–220.
J.L. Smialek and B.A. Pint, “Optimizing Scale Adhesion for Single Crystal Superalloys”, Mater. Sci. Forum, 369–372, (2001), pp. 459–646; also NASA TM 2000-210362.
J.L. Smialek and G.N. Morscher, “Delayed Alumina Scale Spallation on Rene N5+Y: Moisture Effects and Acoustic Emission”, Materials Science and Engineering: A 332 (1–2) (2002), pp. 11–24.
J.L. Smialek, “Scale Adhesion, Sulfur Content, and TBC Failure on Single Crystal Superalloys”, Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings 23, 4 (2002), pp. 485–495.
D.R. Sigler, “Adherence Behavior of Oxide Grown in Air and Synthetic Exhaust Gas on Fe−Cr−Al Alloys Containing Strong Sulfide-Forming Elements: Ca, Mg, Y, Ce, La, Ti, Zr”, Oxidation of Metals, 40 (1993), pp. 555–583.
M.A. Smith, W.E. Frazier, and B.A. Pregger, “Effect of Sulfur on the Cyclic Oxidation Behavior of a Single Crystalline, Nickel-Base Superalloy”, Materials Science and Engineering, A 203 (1995), pp. 388–398.
R. Janakiraman, G.H. Meier, and F.S. Pettit, “The Effect of Water Vapor on the Oxidation of Alloys that Develop Alumina Scales for Protection”, Metall, and Mat. Trans. 30A (1999), pp. 2905–2913; and in Cyclic Oxidation of High Temperature Materials, vol. 27, ed. M. Schütze and W.J. Quadakkers (London: European Federation of Corrosion, IOM, 1999), pp. 38–62.
M.C. Maris-Sida, G.H. Meier, and F.S. Pettit, “Some Water Vapor Effects during the Oxidation of Alloys that are α-Al2O3 Formers”, Metall. Trans. 34A (2003), pp. 2609–2619.
K. Onal Hance, “Effects of Water Vapor on the Oxidation Behavior of Alumina and Chromia Superalloys between 700°C and 1000°C” (Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pittsburgh, 2005).
C. Zhou, H. Xu, and S. Gong, “Influence of Water Vapor on the Cyclic-Oxidation Behavior of a Low-Pressure Plasma-Sprayed NiCrAlY Coating”, Oxid. Met., 62 (2004), pp. 195–206.
V. Sergo, and D.R. Clarke, “Observation of Subcritical Spall Propagation of a Thermal Barrier Coating”, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 81 (12) (1998), pp. 142–161.
V. Tolpygo and D.R. Clarke, “Spalling Failure of α-alumina Films Grown by Oxidation; Parts I and II”, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 278 (2000), pp. 142–161.
D. Renusch, H. Eschler, and M. Schutze, “Progress in Life Time Modelling of APS-TBC”, Mat. High Temp., 21 (2004), pp. 65–76.
H.E. Zschau et al., “Detection of Hydrogen in Hidden and Spalled Layers of Turbine Blade Coatings”, Nuclear Instruments and Methods B, in press (2005).
A.K. Kuruvilla and N.S. Stoloff, “Hydrogen Embrittlement of Ni3Al+B”, Scripta Metall., 19 (1985), pp. 83–88.
N.S. Stoloff and D.J. Duquette, “Moisture and Hydrogen-Induced Embrittlement of Iron Aluminides”, JOM, 45 (12) (1993), pp. 30–35.
C.T. Liu, E.H. Lee, and C.G. McKamey, “An Environmental Effect as the Major Cause for Room Temperature Embrittlement in FeAl”, Scripta Metall., 23 (1989), pp. 875–880.
C.T. Liu, “Ni3Al Aluminide Alloys”, Structural Intermetallics, ed. R. Darolia et al. (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1993), pp. 365–377.
N.S. Stoloff, “Hydrogen and Moisture-Induced Embrittlement of Nickel and Iron Aluminides, “Hydrogen Effects in Materials, ed. A.W. Thompson and N.R. Moody (Warrendale, FA: TMS, 1996), pp. 523–537.
C.T. Liu, et al, “Ordered Intermetallic Alloys: An Assessment”, Intermetallics, 5 (1997), pp. 579–596.
J. Gayda, R.L. Dreshfield, and T.P. Gabb, “The Effect of Porosity and γ/γ′ Eutectic Content on the Fatigue Bejavior of Hydrogen Charged PWA 1480”, Scripta Met. et Mat. 25 (1991), pp. 2589–2594.
J. Gayda, T.P. Gabb, and R.L. Dreshfield, “The Effect of Hydrogen on the Low Cycle Fatigue Behavior of a Single Crystal Superalloy,” Hydrogen Effects on Material Behavior ed. N.R. Moody and A.W. Thompson (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1990), pp. 591–601.
A.R. Troiano, “The Role of Hydrogen and Other Interstitials in the Mechanical Behavior of Metals”. 34th Edward De Mille Campbell Memorial Lecture”, ASM Transactions, 52 (1960), pp. 54–80.
R.P. Wei and M. Gao, “Hydrogen Embrittlement and Environmentally Assisted Crack Growth”, Hydrogen Effects on Material Behavior, ed. N.R. Moody and A.W. Thompson, (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1990), pp. 789–816.
R.H. Jones, “Hydrogen and Impurity-Induced Intergranular Crack Growth”, Hydrogen Effects on Material Behavior, ed. N.R. Moody and A.W. Thompson (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1990), pp. 817–843.
J.L. Smialek, “Effect of Moisture on Secondary Spallation of Alumina Scales on Y-doped René N5” (Paper presented at the 2002 TMS Annual Meeting, Water Vapor Effects on the Oxidation of High Temperature Materials Symposium, Seattle, WA, 18–22 February 2002).
J.L. Smialek, “Desk Top TBC Spallation and Interfacial Hydrogen Embrittlement of Alumina Scales” (Paper presented at the 2005 TMS Annual Meeting. Superalloys and Coatings for High Temperature Applications Symposium, San Francisco, CA, 13–17 February 2005).
J.L. Smialek, “Oxide Morphology and Spalling Model for NiAl”, Metall. Trans. 9A (1978), p. 308.
S.M. Weiderhorn, “Moisture Assisted Crack Growth in Ceramics”, Intl. J. Fract. Mech., 4 (1968), pp. 171–177.
D.M. Kotchick and R.E. Tressler, “Surface Damage and Environmental Effects on the Strain-Rate Sensitivity of the Strength of Sapphire and Silicon Carbide Filaments”, J. Mat. Sci. 10 (1975), pp. 608–612.
J.E. Ritter and J.N. Humenik, “Static and Dynamic Fatigue of Polycrystalline Alumina”, J. Mat. Sci., 14 (1979), pp. 626–632.
M. Reece and F. Gulu, “Indentation Fatigue of High Purity Alumina in Fluid Environments”, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 74 (1991), pp. 148–154.
M. Nagabhooshanam and V.R. Dunke, “Chemiomechanical Effects on Crack Propagation: Polycrystalline α-Al2O3”, J. Mat. Sci., 27 (1992), pp. 2377–2382.
S.M. Barinov et al., “Influence of Environment on Delayed Failure of Alumina Ceramics”, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 18 (1998), pp. 257–263.
M.E. Ebrahimi, J. Chevalier, and G. Fantozzi, “Slow Crack Growth Behavior in Alumina Ceramics”, J. Mater. Res., 15 (2000), pp. 142–147.
S.J. Cho et al: “Influence of Humidity on the Flexural Strength of Alumina”, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 20 (2000), pp. 761–764.
J.J. Kruzic, R.M. Cannon, and R.O. Ritchie, “Effects of Moisture on Grain-Boundary Strength, Fracture, and Fatigue Properties of Alumina”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 88 (2005), pp. 2236–2245.
Z.Y. Deng et al., “Modification of Al Particle Surfaces by γ-Al2O3 and its Effect on the Corrosion Behavior of Al”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88 (2005), pp. 977–979.
Z.Y. Deng et al. “Temperature Effect on Hydrogen Generation by the Reaction of γ-Al2O3-Modified Al Powder with Distilled Water”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 88 (2005), pp. 2975–2977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smialek, J.L. Moisture-induced delayed spallation and interfacial hydrogen embrittlement of alumina scales. JOM 58, 29–35 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-006-0064-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-006-0064-2