Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this report is to review our experience with talonavicular joint arthrodesis for the treatment of severe valgus foot deformities in older children and adolescents with cerebral palsy (CP).
Methods
The clinical, radiographic, and gait parameters results after talonavicular joint arthrodesis were retrospectively reviewed in 32 patients (59 feet) with valgus deformities of the foot. The surgery was performed as part of multiple simultaneous surgeries for the treatment of gait disorders. The mean age of the patients was 13.9 years (range 9–20 years) and the mean follow-up was 40 months (range 18.3–66.7 months).
Results
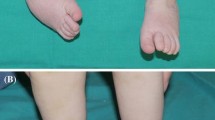
The clinical and radiographic measurements improved significantly (P = 0.000). There were no significant changes in gait parameters. Symptoms were relieved in most patients with symptomatic preoperative feet. The most frequent complication was pseudoarthrosis, which occurred in seven feet. We found a high rate of satisfaction of patients (or parents) and most of them recommended the procedure to other patients with the same condition.
Conclusion
Talonavicular joint arthrodesis is a reliable technique that provides both functionally and cosmetically good results with a low rate of complications in the treatment of severe pes planus valgus in older children and adolescents with CP. Careful examination should rule out concomitant ankle valgus deformities. A stable fixation of the arthrodesis is recommended.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennet GC, Rang M, Jones D (1982) Varus and valgus deformities of the foot in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 24:499–503
Gage JR (1991) Gait analysis in cerebral palsy. Mac Keith Press, London, p 157
Gage JR, Schwartz ML (2004) Pathological gait and lever-arm dysfunction. In: Gage JR (ed) The treatment of gait problems in cerebral palsy. Mac Keith Press, London, p 197
Herring JA (2002) Disorders of the brain—cerebral palsy. In: Herring JA (ed) Tachdjian’s pediatric orthopaedics, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 1150
Dennyson WG, Fulford GE (1976) Subtalar arthrodesis by cancellous grafts and metallic internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 58:507–510
Mosca VS (1995) Calcaneal lengthening for valgus deformity of the hindfoot. Results in children who had severe, symptomatic flatfoot and skewfoot. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77(4):500–512
Novacheck TM (2004) Diplegia and quadriplegia: pathology and treatment. In: Gage JR (ed) The treatment of gait problems in cerebral palsy. Mac Keith Press, London, pp 360–362
Bleck EE (1997) Cerebral palsy. In: Staheli LT (ed) Pediatric orthopaedic secrets. Hanley and Belfus, Philadelphia, p 355
Williams PF, Menelaus MB (1977) Triple arthrodesis by inlay grafting—a method suitable for the undeformed or valgus foot. J Bone Joint Surg Br 59(3):333–336
Monson R, Gibson DA (1978) Long-term follow-up of triple arthrodesis. Can J Surg 21(3):249–251
Tenuta J, Shelton YA, Miller F (1993) Long-term follow-up of triple arthrodesis in patients with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 13(6):713–716
Andreacchio A, Orellana CA, Miller F, Bowen TR (2000) Lateral column lengthening as treatment for planovalgus foot deformity in ambulatory children with spastic cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 20(4):501–505. doi: 10.1097/00004694-200007000-00015
Turriago CA, Duplat JL, Larrota CO, Mieth KW (2001) Tratamiento del pie plano valgo espástico mediante triple artrodesis por doble abordaje: presentación de una técnica modificada. Rev Colomb Ortop Traumatol 15(1):52–56
Harper MC (1999) Talonavicular arthrodesis for the acquired flatfoot in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res 365:65–68. doi:10.1097/00003086-199908000-00008
Fortin PT (2001) Posterior tibial tendon insufficiency. Isolated fusion of the talonavicular joint. Foot Ankle Clin 6(1):137–151. doi:10.1016/S1083-7515(03)00087-1
Weinraub GM, Heilala MA (2007) Isolated talonavicular arthrodesis for adult onset flatfoot deformity/posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 24(4):745–752. doi:10.1016/j.cpm.2007.06.004
Chen CH, Huang PJ, Chen TB, Cheng YM, Lin SY, Chiang HC, Chen LC (2001) Isolated talonavicular arthrodesis for talonavicular arthritis. Foot Ankle Int 22(8):633–636
Ljung P, Kaij J, Knutson K, Pettersson H, Rydholm U (1992) Talonavicular arthrodesis in the rheumatoid foot. Foot Ankle 13(6):313–316
Fogel GR, Katoh Y, Rand JA, Chao EY (1982) Talonavicular arthrodesis for isolated arthrosis: 9.5-year results and gait analysis. Foot Ankle 3(2):105–113
Wei SY, Sullivan RJ, Davidson RS (2000) Talo-navicular arthrodesis for residual midfoot deformities of a previously corrected clubfoot. Foot Ankle Int 21(6):482–485
Schulze W, Richter J, Russe O, Ingelfinger P, Muhr G (2002) Surgical treatment of talus fractures: a retrospective study of 80 cases followed for 1–15 years. Acta Orthop Scand 73(3):344–351. doi:10.1080/000164702320155374
Evans D (1975) Calcaneo-valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Br 57:270–278
Gallien R, Morin F, Marquis F (1989) Subtalar arthrodesis in children. J Pediatr Orthop 9(1):59–63
Stein H, Simkin A, Joseph K (1981) The foot–ground pressure distribution following triple arthrodesis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 98(4):263–269. doi:10.1007/BF00378879
Saltzman CL, Fehrle MJ, Cooper RR, Spencer EC, Ponseti IV (1999) Triple arthrodesis: twenty-five and forty-four-year average follow-up of the same patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81(10):1391–1402
Mosca VS (1998) The child’s foot: principles of management. J Pediatr Orthop 18:281–282. doi:10.1097/00004694-199805000-00001
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Fernando Ortiz MD for his help in the statistical analysis of this report and Dr James Gage MD and Dr. Pablo Rosselli MD for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Turriago, C.A., Arbeláez, M.F. & Becerra, L.C. Talonavicular joint arthrodesis for the treatment of pes planus valgus in older children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. J Child Orthop 3, 179–183 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-009-0168-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-009-0168-7