Abstract
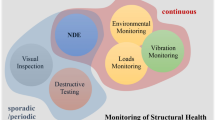
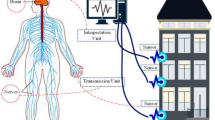
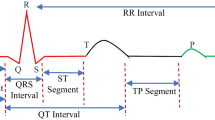
In the last years, the occurrence of natural hazards around the world has evinced the necessity of having structural health monitoring schemes that can allow the continuous assessment of the structural integrity of the civil structures or infrastructures, in order to avoid potential economic or human loses; further, it also allows the application of new sensing technologies and signal processing algorithms. An important step in a structural health monitoring strategy is the appropriate selection of the sensor used to measure the required physical variable. Although several reviews have been published, they focus on presenting and/or explaining the methodologies and signal processing techniques used in structural health monitoring. This article presents a state-of-the-art review of the sensing technologies used in structural health monitoring. Further, some candidate sensor technologies with potential of use in this area are also reviewed, where the main issues that affect their implementation in real-life schemes are also discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amezquita-Sanchez JP, Hojjat A (2016) Signal processing techniques for vibration-based health monitoring of smart structures. Arch Comput Methods Eng 23:1–15. doi:10.1007/s11831-014-9135-7
Gattulli V, Lepidi M, Potenza F (2016) Dynamic testing and health monitoring of historic and modern civil structures in Italy. Struct Monit Maint 3:71–90. doi:10.12989/smm201631071
Perez-Ramirez CA, Amezquita-Sanchez JP, Hojjat A, Valtierra-Rodriguez M, Romero-Troncoso RJ, Dominguez-Gonzalez A, Osornio-Rios RA (2016) Time-frequency techniques for modal parameters identification of civil structures from acquired dynamic signals. J Vibroeng 18:3164–3185. doi:10.21595/jve201617220
Amezquita-Sanchez, JP, Hojjat, A (2015) Feature extraction and classification techniques for health monitoring of structures Sci Iran Trans A Civ Eng 6:1931–1940. Available at http://www.scientiairanica.com/en/ManuscriptDetail?mid=3227. Accessed 25 Sep 2016
Webb GT, Vardanega PJ, Middleton, CR (2015) Categories of SHM deployments: technologies and capabilities. J Bridge Eng 20:04014118. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)BE1943-55920000735
Wijesinghe B, Zacharie S, Mish K, Baldwin J (2013) Design and development of in situ fatigue sensors for structural health monitoring of highway bridges. J Bridge Eng 18:297–307. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)BE1943-55920000361
Sun H, Mordret A, Prieto GA, Toksöz MT, Büyüköztürk O (2017) Bayesian characterization of buildings using seismic interferometry on ambient vibrations. Mech Syst Signal Process 85:468–486. doi:10.1016/jymssp201608038
Karapetrou S, Manakou M, Bindi D, Petrovic B, Pitilakis K (2016) “Time-building specific” seismic vulnerability assessment of a hospital RC building using field monitoring data. Eng Struct 112:114–132. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201601009
Santos A, Silva M, Santos R, Figueiredo E, Sales C, Costa JC (2016) A global expectation-maximization based on memetic swarm optimization for structural damage detection. Struct Health Monit 15:610–625. doi:10.1177/1475921716654433
Dilena M, Morassi A (2011) Dynamic testing of a damaged bridge. Mech Syst Signal Process 25:1485–1507. doi:10.1016/jymssp201012017
Gomez HC, Ulusoy HS, Feng QM (2013) Variation of modal parameters of a highway bridge extracted from six earthquake records. Earthquake Eng Struct Dyn 42:565–579. doi:10.1002/eqe2227
Franco JM, Marulanda J, Caicedo JM (2015) Modal identification of a full-scale building under seismic excitation using the fast mode identification technique. Exp Tech. doi:10.1111/ext12164
Foti D, Gattulli V, Potenza F (2014) Output-only identification and model updating by dynamic testing in unfavorable conditions of a seismically damaged building. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 29:659–675. doi:10.1111/mice12071
Chang K-C, Kim C-W (2016) Modal-parameter identification and vibration-based damage detection of a damaged steel truss bridge. Eng Struct 122:156–173. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201604057
Bursi OS, Kumar A, Abbiati G, Ceravolo R (2014) Identification, model updating, and validation of a steel twin deck curved cable-stayed footbridge. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 29:703–722. doi:10.1111/mice12076
Zhou HF, Ni YQ, Ko JM (2011) Structural damage alarming using auto-associative neural network technique: exploration of environment-tolerant capacity and setup of alarming threshold. Mech Syst Signal Process 25:1508–1526. doi:10.1016/jymssp201101005
Moser P, Moaveni B (2013) Design and deployment of a continuous monitoring system for the dowling hall footbridge. Exp Tech 37:15–26. doi:10.1111/j1747-1567201100751x
Morovati V, Kazemi MT (2016) Detection of sudden structural damage using blind source separation and time–frequency approaches. Smart Mater Struct 25:055008. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/25/5/055008
Dragos K, Smarsly K (2016) Distributed adaptive diagnosis of sensor faults using structural response data. Smart Mater Struct 25:105019. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/25/10/105019
Jang S, Spencer Jr BF, Sim S-H (2012) A decentralized receptance-based damage detection strategy for wireless smart sensors. Smart Mater Struct 21:055017. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/21/5/055017
Osornio-Rios RA, Amezquita-Sanchez JP, Romero-Troncoso RJ, Garcia-Perez A (2012) MUSIC-ANN analysis for locating structural damages in a truss-type structure by means of vibrations. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 27:687–698. doi:10.1111/j1467-8667201200777x
Ubertini F, Comanducci G, Cavalagli N, Pisello AL, Materazzi AL, Cotana F (2017) Environmental effects on natural frequencies of the San Pietro bell tower in Perugia, Italy, and their removal for structural performance assessment. Mech Syst Signal Process 82:307–322. doi:10.1016/jymssp201605025
Saisi A, Gentile C, Guidobaldi M (2015) Post-earthquake continuous dynamic monitoring of the Gabbia Tower in Mantua, Italy. Constr Build Mater 81:101–112. doi:10.1016/jconbuildmat201502010
Lorenzoni F, Casarin F, Modena C, Caldon M, Islami K, da Porto F (2013) Structural health monitoring of the Roman Arena of Verona, Italy. J Civil Struct Health Monit 3:227–246. doi:10.1007/s13349-013-0065-0
Elyamani A, Caselles O, Roca P, Clapes J (2016) Dynamic investigation of a large historical cathedral. J Civil Struct Health Monit. doi:10.1002/stc1885
Li QS, Zhi L-H, Tuan AY, Kao C-S, Su S-C, Wu C-F (2011) Dynamic behavior of Taipei 101 tower: field measurement and numerical analysis. J Struct Eng 137:143–155. doi:10.1061/ASCEST1943-541X0000264
Li Z, Park HS, Adeli H (2016) New method for modal identification of super high-rise building structures using discretized synchrosqueezed wavelet and Hilbert transforms. Struct Des Tall Spec Build. doi:10.1002/tal1312
Ni YQ, Xia Y, Lin W, Chen WH, Ko JM (2012) SHM benchmark for high-rise structures: a reduced-order finite element model and field measurement data. Smart Struct Syst 4–5:411–426. doi:10.12989/sss2012104_5411
Gueguen P, JolivetV, Michel C, Schveitzer A-N (2010) Comparison of velocimeter and coherent lidar measurements for building frequency assessment. Bull Earthquake Eng 8:327–338. doi:10.1007/s10518-009-9137-2
Farahani RV, Penumadu D (2016) Damage identification of a full-scale five-girder bridge using time-series analysis of vibration data. Eng Struct 115:129–139. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201602008
Su WC, Huang CS, Chen CH, Liu CY, Huang HC, Le QT (2014) Identifying the modal parameters of a structure from ambient vibration data via the stationary wavelet packet. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 29:738–757. doi:10.1111/mice12115
Dai K, Boyajian D, Liu W, Chen S-E, Scott J, Schmieder M (2014) Laser-Based Field Measurement for a Bridge Finite-Element Model Validation. J Perform Constr Facil 28:04014024. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CF1943-55090000484
Sung Y-C, Lin T-K, Chiu Y-T, Chang K-C, Chen K-L, Chang C-C (2016) A bridge safety monitoring system for prestressed composite box-girder bridges with corrugated steel webs based on in-situ loading experiments and a long-term monitoring database. Eng Struct 126:571–585. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201608006
Benedettini F, Dilena M, Morassi A (2015) Vibration analysis and structural identification of a curved multi-span viaduct. Mech Syst Signal Process 54–55:84–107. doi:10.1016/jymssp201408008
Lin T-K, Chang Y-S (2017) Development of a real-time scour monitoring system for bridge safety evaluation. Mech Syst Signal Process 82:503–518. doi:10.1016/jymssp201605040
Farahani RV, Penumadu D (2016) Full-scale bridge damage identification using time series analysis of a dense array of geophones excited by drop weight. Struct Control Health Monit 23:982–997. doi:10.1002/stc1820
Valla M, Gueguen P, Augère B, Goular D, Perrault, M (2015) Remote modal study of reinforced concrete buildings using a multipath lidar vibrometer. J Struct Eng 141:D4014005. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001087
Bergamo O, Campione G, Donadello S, Russo G (2015) In-situ NDT testing procedure as an integral part of failure analysis of historical masonry arch bridges. Eng Fail Anal 57:31–55. doi:10.1016/jengfailanal201507019
Liao Y, Kiremidjian AS, Rajagopal R, Loh, C-H (2016) Angular velocity-based structural damage detection. In: Proceedings of the sensors and smart structures technologies for civil, mechanical, and aerospace systems conference, Las Vegas, Nevada, United States, March 20, 2016, Jerome P Lynch, SPIE. doi:10.1117/122219398
Sung SH, Lee JH, Park JW, Koo KY, Jung HJ (2014) Feasibility study on an angular velocity-based damage detection method using gyroscopes. Meas Sci Technol 25:075009. doi:10.1088/0957-0233/25/7/075009
Sung SH, Park JW, Nagayama T, Jung HJ (2014) A multiscale sensing and diagnosis system combining accelerometers and gyroscopes for bridge health monitoring. Smart Mater Struct 23:015005. doi:10.1088/09641726/23/1/015005
Li H, Dong S, El-Tawil S, Kamat VR (2013) Relative displacement sensing techniques for postevent structural damage assessment: review. J Struct Eng 139:1421–1434, doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000729
Antonelli K, Astakhov VP, Bandyopadhyay A et al (1999) Displacement measurement, linear and angular. In: Webster JG, Eren H (eds) The measurement, instrumentation and sensors handbook on CD-ROM. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Im SB, Hurlebaus S, Kang YJ (2013) Summary review of GPS technology for structural health monitoring. J Struct Eng 139:1653–1664. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000475
Su WC, Liu CY, Huang CS (2014) Identification of instantaneous modal parameter of time-varying systems via a wavelet-based approach and its application. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 29:279–298. doi:10.1111/mice12037
Saisi A, Gentile C, Ruccolo A (2016) Pre-diagnostic prompt investigation and static monitoring of a historic bell-tower. Constr Build Mater 122:833–844. doi:10.1016/jconbuildmat201604016
McGetrick PJ, Kim C-W, González A, O Brien EJ (2015) Experimental validation of a drive-by stiffness identification method for bridge monitoring. Struct Health Monit 14:317–331. doi:10.1177/1475921715578314
He L, Lian J, Ma B (2014) Intelligent damage identification method for large structures based on strain modal parameters. J Vib Control 20:1783–1795. doi:10.1177/1077546312475150
Loh C-H, Chan C-K, Chen SF, Huang S-K (2016) Vibration-based damage assessment of steel structure using global and local response measurements. Earthquake Eng Struct Dyn 45:699–718. doi:10.1002/eqe2680
Murià-Vila D, Sánchez-Ramírez AR, Huerta-Carpizo CH, Aguilar G, Camargo Pérez J, Carrillo Cruz RE (2014) Field tests of elevated viaducts in Mexico City. J Struct Eng 141:04016074. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001527
Li S, Zuo Z, Zhai C, Xu S, Xie L (2016) Shaking table test on the collapse process of a three-story reinforced concrete frame structure. Eng Struct 118:156–166. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201603032
Stavridis A, Ahmadi F, Mavros M, Shing PB, Klingner RE, McLean D (2016) Shake-table tests of a full-scale three-story reinforced masonry shear wall structure. J Struct Eng 142:D4014001. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001086
Le HX, Hwang E-S (2016) Investigation of deflection and vibration criteria for road bridges KSCE. J Civ Eng. doi:10.1007/s12205-016-0532-3
Han H, Wang J, Meng X, Liu (2016) Analysis of the dynamic response of a long span bridge using GPS/accelerometer/anemometer under typhoon loading. Eng Struct 122:238–250. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201604041
Erdogan H, Gülal E (2013) Ambient vibration measurements of the Bosphorus suspension bridge by total station and GPS. Exp Tech 37:16–23. doi:10.1111/j1747-1567201100723x
Chatzis MN, Chatzi EN, Smyth AW (2015) An experimental validation of time domain system identification methods with fusion of heterogeneous data. Earthquake Eng Struct Dyn 44:523–547. doi:10.1002/eqe2528
Islam MN, Zareie S, Alam MS, Seethaler RJ (2016) Novel method for interstory drift measurement of building frames using laser-displacement sensors. J Struct Eng 142:06016001. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001471
Park J-W, Lee K-C, Sim S-H, Jung H-J, Spencer BF Jr (2016) Traffic safety evaluation for railway bridges using expanded multisensor data fusion. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 31:749–760. doi:10.1111/mice12210
Gokanakonda S, Ghantasala MK, Kujawski D (2016) Fatigue sensor for structural health monitoring: design, fabrication and experimental testing of a prototype sensor. Struct Control Health Monit 23:237–251. doi:10.1002/stc1765
Priyantha Wijesinghe BHM, Zacharie SA, Mish KD, Baldwin JD (2013) Design and development of in situ fatigue sensors for structural health monitoring of highway bridges. J Bridge Eng 18:297–307. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)BE1943-55920000361
Papazian JM, Nardiello J, Silberstein RP, Welsh G, Grundy D, Craven C, Evans L, Goldfine N, Michaels JE, Michaels TE, Li Y, Laird C (2007) Sensors for monitoring early stage fatigue cracking. Int J Fatigue 29:1668–1680. doi:10.1016/jijfatigue200701023
Nor NM, Ibrahim A, Bunnori NM, Saman HM, Saliah SNMS, Shahidan S (2014) Diagnostic of fatigue damage severity on reinforced concrete beam using acoustic emission technique. Eng Fail Anal 41:1–9. doi:10.1016/jengfailanal201307015
Li H, Huang Y, Chen WL, Ma ML, Tao DW (2011) Estimation and warning of fatigue damage of FRP stay cables based on acoustic emission techniques and fractal theory. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 26:500–512. doi:10.1111/j1467-8667201000713x
Mutlib NK, Baharom SB, El-Shafie A, Nuawi MZ (2016) Ultrasonic health monitoring in structural engineering: buildings and bridges. Struct Control Health Monit 23:409–422. doi:10.1002/stc1800
Deng Y, Liu Y, Feng D-M, Li A-Q (2015) Investigation of fatigue performance of welded details in long-span steel bridges using long-term monitoring strain data. Struct Control Health Monit 22:1343–1358. doi:10.1002/stc1747
Rajan SS, Jaya KP, Lakshmanan N (2009) Development of load cells for simultaneous measurement of drag, lift, and moment for section models of bridge decks under wind load. Exp Tech 33:38–45. doi:10.1111/j1747-1567200900532x
Ferreira JG, Branco F (2015) Measurement of vertical deformations in bridges using an innovative elastic cell system. Exp Tech 39:13–20. doi:10.1111/j1747-1567201200852x
Sideris P, Aref AJ, Filiatrault A (2014) Large-scale seismic testing of a hybrid sliding-rocking posttensioned segmental bridge system. J Struct Eng 140:04014025. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000961
Okazaki T, Lignos DG, Hikino T, Kajiwara K (2013) Dynamic response of a chevron concentrically braced frame. J Struct Eng 139:515–525. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000679
Lin Y-C, Sause R, Ricles J (2013) Seismic performance of a large-scale steel self-centering moment-resisting frame: MCE hybrid simulations and quasi-static pushover tests. J Struct Eng 139:1227–1236. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000661
Abdullah ABM, Rice JA, Hamilton HR, Consolazio, GR (2016) Experimental and numerical evaluation of unbonded posttensioning tendons subjected to wire breaks. J Bridge Eng 21:04016066. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)BE1943-55920000940
Astroza R, Ebrahimian H, Contel JP, Restrepo JI, Hutchinson TC (2016) System identification of a full-scale five-story reinforced concrete building tested on the NEES-UCSD shake table. Struct Control Health Monit 23:535–559. doi:10.1002/stc1778
Modares M, Waksmanski N (2013) Overview of structural health monitoring for steel bridges. Pract Period Struct Des Constr 18:187–191. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)SC1943-55760000154
Moreu F, Kim RE, Spencer Jr BF (2016) Railroad bridge monitoring using wireless smart sensors. Struct Control Health Monit. doi:10.1002/stc1863
Santini Bell E, Lefebvre PJ, Sanayei M, Brenner B, Sipple JD, Peddle J (2013) Objective load rating of a steel-girder bridge using structural modeling and health monitoring. J Struct Eng 139:1771–1779. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000599
Fu CC, Zhang N (2011) Investigation of bridge expansion joint failure using field strain measurement. J Perform Constr Facil 25:309–316. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CF1943-55090000171
Liu R, Ji B, Wang M, Chen C, Maeno H (2015) Numerical evaluation of toe-deck fatigue in orthotropic steel bridge deck. J Perform Constr Facil 29:04014180. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CF1943-55090000677
Chen Z, Xu Y, Wang X (2012) SHMS-based fatigue reliability analysis of multiloading suspension bridges. J Struct Eng 138:299–307. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000460
Siriwardane SASC, Ohga M, Dissanayake PBR, Kaita T (2010) Structural appraisal-based different approach to estimate the remaining fatigue life of railway bridges. Struct Health Monit 9:323–339. doi:10.1177/1475921710361320
Seo J, Hosteng T, Phares B, Wacker J (2016) Live-load performance evaluation of historic covered timber bridges in the United States. J Perform Constr Facil 30:04015094. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CF1943-55090000852
Gokce H, Catbas F, Gul M, Frangopol D (2013) Structural identification for performance prediction considering uncertainties: case study of a movable bridge. J Struct Eng 139:1703–1715. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000601
Saiidi M, Vosooghi A, Nelson R (2013) Shake-table studies of a four-span reinforced concrete bridge. J Struct Eng 139:1352–1361. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000790
Srinivas V, Sasmal S, Ramanjaneyulu K, Ravisankar K (2014) Performance evaluation of a stone masonry–arch railway bridge under increased axle loads. J Perform Constr Facil 28:363–375. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CF1943-55090000407
Nishikata A, Zhu Q, Tada E (2014) Long-term monitoring of atmospheric corrosion at weathering steel bridges by an electrochemical impedance method. Corros Sci 87:80–88. doi:10.1016/jcorsci201406007
Zhang H, Yang R, He Y, Tian GY, Xu L, Wu R (2016) Identification and characterisation of steel corrosion using passive high frequency RFID sensors. Measurement 92:421–427. doi:10.1016/jmeasurement201606041
Perveen K, Bridges GE, Bhadra S, Thomson DJ (2014) Corrosion potential sensor for remote monitoring of civil structure based on printed circuit board sensor. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 63:2422–2431. doi:10.1109/TIM20142310092
Shaikh H, Sivaibharasi N, Sasi B, Anita T, Amirthalingam R, Rao BPC, Jayakumar T, Khatak HS, Raj B (2005) Use of eddy current testing method in detection and evaluation of sensitisation and intergranular corrosion in austenitic stainless steels. Corros Sci 48:1462–1482. doi:10.1016/jcorsci200505017
Jirarungsatian C, Prateepasen A (2010) Pitting and uniform corrosion source recognition using acoustic emission parameters. Corros Sci 52:187–197. doi:10.1016/jcorsci200909001
Carkhuff B, Cain R (2003) Corrosion sensors for concrete bridges. IEEE Instrum Meas Mag 6:19–24. doi:10.1109/MIM20031200279
Zárate B, Caicedo J, Yu J, Ziehl P (2012) Probabilistic prognosis of fatigue crack growth using acoustic emission data. J Eng Mech 138:1101–1111. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)EM1943-78890000414
Yao Y, Tung S-TE, Glisic B (2014) Crack detection and characterization techniques—an overview. Struct Control Health Monit 21:1387–1413. doi:10.1002/stc1655
Yapar O, Basu PK, Volgyesi P, Ledeczi A (2015) Structural health monitoring of bridges with piezoelectric AE sensors. Eng Fail Anal 56:150–169. doi:10.1016/jengfailanal201503009
Wolf J, Pirskawetz S, Zang A (2015) Detection of crack propagation in concrete with embedded ultrasonic sensors. Eng Fract Mech 146:161–171. doi:10.1016/jengfracmech201507058
Benedetto A (2013) A three dimensional approach for tracking cracks in bridges using GPR. J Appl Geophys 97:37–44. doi:10.1016/jjappgeo201212010
Alavi AH, Hasni H, Jiao P, Borchani W, Lajnef N (2017) Fatigue cracking detection in steel bridge girders through a self-powered sensing concept. J Constr Steel Res 128:19–38. doi:10.1016/jjcsr201608002
Xiang J, Liang M (2012) Wavelet-Based Detection of beam cracks using modal shape and frequency measurements. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 27:439–454. doi:10.1111/j1467-8667201200760x
Krakhmal’ny TA, Evtushenko SI, Krakhmal’naya MP (2016) New system of monitoring of a condition of cracks of small reinforced concrete bridge constructions In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering (ICIE), Chelyabinsk, Russian Federation, May 19–20, 2016, Andrey A. Radionov. Procedia Eng. doi:10.1016/jproeng201607322
Hong A, Ubertini F, Betti R (2011) Wind analysis of a suspension bridge: identification and finite-element model simulation. J Struct Eng 137:133–142. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0000279
Kim S, Park J, Kim H (2016) Damping identification and serviceability assessment of a cable-stayed bridge based on operational monitoring data. J Bridge Eng. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)BE1943-55920001004
Chen X (2014) Analysis of multimode coupled buffeting response of long-span bridges to nonstationary winds with force parameters from stationary wind. J Struct Eng 141:04014131. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001078
Kwon D, Spence S, Kareem A (2014) Performance evaluation of database-enabled design frameworks for the preliminary design of tall buildings. J Struct Eng 141:04014242. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001229
Huang M, Lou W, Chan C, Lin N, Pan X (2013) Peak distributions and peak factors of wind-induced pressure processes on tall buildings. J Eng Mech 139:1744–1756. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)EM1943-78890000616
Diana G, Rocchi D, Belloli M (2015) Wind tunnel: a fundamental tool for long-span bridge design. Struct Infrastruct Eng 11:533–555. doi:10.1080/157324792014951860
Wang J, Xu Z, Fan X, Lin J (2016) Thermal effects on curved steel box girder bridges and their countermeasures. J Perform Constr Facil. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CF1943-55090000952
Farreras-Alcover I, Chryssanthopoulos MK, Andersen JE (2015) Regression models for structural health monitoring of welded bridge joints based on temperature, traffic and strain measurements. Struct Health Monit 14:648–662. doi:10.1177/1475921715609801
Yarnold M, Moon F, Aktan AE (2015) Temperature-based structural identification of long-span bridges. J Struct Eng 141:04015027. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001270
Zhang Y, O’Connor S, van der Linden G, Prakash A, Lynch J (2016) SenStore: a scalable cyberinfrastructure platform for implementation of data-to-decision frameworks for infrastructure health management. J Comput Civ Eng 30:04016012. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CP1943-54870000560
Torres-Arredondo M-A, Sierra-Pérez J, Tibaduiza D-A, McGugan M, Rodellar J, Fritzen C-P (2015) Signal-based nonlinear modelling for damage assessment under variable temperature conditions by means of acousto-ultrasonics. Struct Control Health Monit 22:1103–1118. doi:10.1002/stc1735
Santos J, Cremona C, Orcesi A, Silveira P (2016) Early damage detection based on pattern recognition and data fusion. J Struct Eng. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001643
Hedegaard B, French C, Shield C (2016) Effects of cyclic temperature on the time-dependent behavior of posttensioned concrete bridges. J Struct Eng 142:04016062. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST1943-541X0001538
Kromanis R, Kripakaran P, Harvey B (2016) Long-term structural health monitoring of the Cleddau bridge: evaluation of quasi-static temperature effects on bearing movements. Struct Infras Eng 12:1342–1355. doi:10.1080/1573247920151117113
Yang Y, Dorn C, Mancini T, Talken Z, Kenyon G, Farrar C, Mascareñas D (2017) Blind identification of full-field vibration modes from video measurements with phase-based video motion magnification. Mech Syst Signal Process 85:567–590. doi:10.1016/jymssp201608041
Oh BK, Hwang JW, Kim Y, Cho T, Park HS (2015) Vision-based system identification technique for building structures using a motion capture system. J Sound Control 356:72–85. doi:10.1016/jjsv201507011
Chen C-C, Wu W-H, Tseng H-Z, Chen C-H, Lai G (2015) Application of digital photogrammetry techniques in identifying the mode shape ratios of stay cables with multiple camcorders. Measurement 75:134–146. doi:10.1016/jmeasurement201507037
Yeum CM, Dyke SJ (2015) Vision-based automated crack detection for bridge inspection. Comput Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 30:759–770. doi:10.1111/mice12141
Andreaus U, Baragatti P, Casini P, Iacoviello D (2016) Experimental damage evaluation of open and fatigue cracks of multi-cracked beams by using wavelet transform of static response via image analysis. Struct Control Health Monit. doi:10.1002/stc1902
Enckell M, Andersen JE, Glisic B, Silfwerbrand J (2013) New and emerging technologies in structural health monitoring: part I civil and environmental engineering. In: Kutz M (ed) Handbook of measurement in science and engineering. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 1–78. doi:10.1002/9781118436707hmse001
Mukhopadhyay SC, Ihara I (2011) Sensors and technologies for structural health monitoring: a review. In: Mukhopadhyay SC (ed) New developments in sensing technology for structural health monitoring. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–14, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-21099-0_1
Helmi K, Taylor T, Zarafshan A, Ansari F (2015) Reference free method for real time monitoring of bridge deflections. Eng Struct 103:116–124. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201509002
Rodrigues C, Félix C, Lage A, Figueiras J (2010) A development of a long-term monitoring system based on FBG sensors applied to concrete bridges. Eng Struct 32:1993–2002. doi:10.1016/jengstruct201002033
Antunes P, Lima H, Varum H, André P (2012) Optical fiber sensors for static and dynamic health monitoring of civil engineering infrastructures: abode wall case study. Measurement 45:1695–1705. doi:10.1016/jmeasurement201204018
Tan CH, Shee YG, Yap BK, Mahamd Adikan FR (2016) Fiber Bragg grating based sensing system: early corrosion detection for structural health monitoring. Sens Actuators A 246:123–128. doi:10.1016/jsna201604028
Sahay P, Kaya M, Wang C (2013) Fiber loop ringdown sensor for potential real-time monitoring of cracks in concrete structures: an exploratory study. Sensors 13:39–57. doi:10.3390/s130100039
Perez-Ramirez CA, Almanza-Ojeda DL, Guerrero-Tavares JN, Mendoza-Galindo FJ, Estudillo-Ayala JM, Ibarra-Manzano MA (2014) An architecture for measuring joint angles using a long period fiber grating-based sensor. Sensors 14:24483–24501. doi:10.3390/s141224483
Sirohi J, Chopra I (2010) Piezoceramic actuators and sensors. In: Blockley R, Shyy W (eds) Encyclopedia of aerospace engineering, vol 6. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 1–14. doi:10.1002/9780470686652eae231
Ruiz D, Bellido JC, Donoso A (2016) Optimal design of piezoelectric modal transducers. Arch Comput Methods Eng. doi:10.1007/s11831-016-9200-5
Kong Q, Robert RH, Silva P, Mo YL (2016) Cyclic crack monitoring of a reinforced concrete column under simulated pseudo-dynamic loading using piezoceramic-based smart aggregates. Appl Sci 6:341. doi:10.3390/app6110341
Guofeng D, Linsheng H, Qingzhao K, Gangbing S (2016) Damage detection of pipeline multiple cracks using piezoceramic transducers. J Vibroeng 18:2828–2838. doi:10.21595/jve201617040
Wang RL, Gu H, Song G (2013) Active sensing based bolted structure health monitoring using piezoceramic transducers. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 9:583205. doi:10.1155/2013/583205
Yan S, Wu J, Sun W, Ma H, Yan H (2013) Development and application of structural health monitoring system based on piezoelectric sensors. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 9:270927. doi:10.1155/2013/270927
Funding
This work was funded in part by the Mexican Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT) by the scholarships: 304844 and 289377, and by the project SEP-CONACyT CB-2015/254697.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno-Gomez, A., Perez-Ramirez, C.A., Dominguez-Gonzalez, A. et al. Sensors Used in Structural Health Monitoring. Arch Computat Methods Eng 25, 901–918 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-017-9217-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-017-9217-4