Abstract
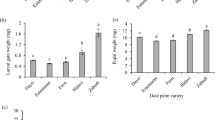
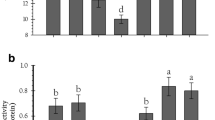
The pink stem stalk borer, Sesamia cretica Lederer, is the main insect pest of sugarcane, Saccharum officinarum L., in Iran and worldwide. This paper assesses the effects of six sugarcane cultivars on the feeding performance and enzymatic activity of S. cretica under controlled conditions. It also investigates the biochemical traits of sugarcane cultivars (total phenolic, flavonoids, and anthocyanins contents) and explores their relationship with the nutritional physiology of S. cretica. The study findings indicated remarkable differences in the nutritional properties and digestive function of S. cretica on various sugarcane cultivars. The S. cretica larvae reared on cultivar CP48-103 were indicated to have the highest ECI, RGR, and ECD values. In addition, the larvae fed on cultivar CP73-21 showed the lowest values of RCR and RGR. The S. cretica larvae induced the highest proteolytic activity during feeding with CP48-103, CP57-614, and CP73-21 cultivars. The fifth instar larvae demonstrated the highest and lowest amylolytic activity when fed with cultivars IRC99-01 and CP57-614, respectively. Moreover, significant variations in the phytochemical metabolites were detected among the sugarcane cultivars. Significant negative or positive correlations were found between the tested parameters of S. cretica and the biochemical characteristics of sugarcane cultivars. The cluster analysis results showed that cultivar CP73-21 was relatively unsuitable for S. cretica feeding: it was a suggested candidate to grow in regions with typically high pest infestation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi Z, Golizadeh A, Soufbaf M, Hassanpour M, Jafari-Nodoushan A, Akhavan HR (2019) Relationship between performance of carob moth, Ectomyelois ceratoniae Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and phytochemical metabolites in various pomegranate cultivars. Front Physiol 10:1425
Arbabtafti R, Fathipour Y, Ranjbar Aghdam H (2021) Temperature-dependent demography of two geographically isolated populations of Sesamia cretica (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ Entomol 50(4):909–918
Arcenaux G (1965) Cultivated sugarcane of the world and their botanical derivation. Proc Int Soc Sugar Cane Technol 12:844–854
Bernfeld P (1955) Amylases, a and b. Meth Enzymol 1:149–158
Elpidina EN, Vinokurov KS, Gromenko VA, Rudenshaya YA, Dunaevsky YE, Zhuzhikov DP (2001) Compartmentalization of proteinases and amylases in Nauphoeta cinerea midgut. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 48:206–216
Ezzeldin HA, Sallam AAA, Helal TY, Fouad HA (2009) Effect of some materials on Sesamia cretica infesting some maize and sorghum varieties. Arch Phytopath Plant Protec 42(3):277–290
Gvozdenac SM, Prvulovi DM, Radovanovi MN, Ovuka S, Mikli VJ, Canski JMA et al (2018) Life history of Plodia interpunctella Hübner on sunflower seeds: effects of seed qualitative traits and the initial seed damage. J Stored Prod Res 79:89–97
Haukioja E, Ossipov V, Lempa K (2002) The interactive effects of leaf maturation and phenolics on consumption and growth of a geometrid moth. Entomol Exp Appl 104:125–136
Hemati SA, Naseri B, Ganbalani GN, Dastjerdi HR, Golizadeh A (2012a) Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities and feeding responses of Helicoverpa armigera (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) on different host plants. J Econ Entomol 105(4):14391446
Hemati SA, Naseri B, Ganbalan GN, Dastjerdi HR, Golizadeh A (2012b) Effect of different host plants on nutritional indices of the pod borer helicoverpa armigera. J Insect Sci 12(55):1–15
Hemmati SA, Takalloo Z, Taghdir M, Mehrabadi M, Balalaei S, Moharramipour S, Sajedi RH (2021) The trypsin inhibitor pro-peptide induces toxic effects in Indianmeal moth Plodia Interpunctella. Pest Biochem Physiol 171:104730
Hosseininaveh V, Bandani AR, Azmayeshfard P, Hosseinkhani S, Kazzazi M (2007) Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities in Trogoderma granarium Everts (Dermestidae: Coleoptera). J Stored Prod Res 43:515–522
Inc SPSS (2007) SPSS base 16.0 user’s guide. SPSS Incorporation Chicago, IL
Jalaeian M, Mohammadzadeh M, Mohammadzadeh M, Borzoui E (2021) Rice cultivars affect fitness-related characteristics and digestive physiology of the rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Stored Prod Res 93:101821
Karasov WH, Martinez del Rio C, Caviedes-Vidal E (2011) Ecological physiology of diet and digestive systems. Annu Rev Physiol 73:69–93
Kim DO, Chun OK, Kim KJ, Moon HY, Lee CY (2003) Quantification of polyphenolics and their antioxidant capacity in fresh plums. J Agric Food Chem 51:6509–6515
Lee KP (2007) The interactive effects of protein quality and macronutrient imbalance on nutrient balancing in an insect herbivore. J Exp Biol 210:3236–3244
Liu ZD, Li DM, Gong PY, Wu KJ (2004) Life table studies of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on different host plants. Environ Entomol 33:1570–1576
Mardani-Talaee M, Nouri-Ganblani G, Razmjou J, Hassanpour M, Naseri B, Asgharzadeh A (2016) Effects of chemical, organic and bio-fertilizers on some secondary metabolites in the leaves of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum) and their impact on life table parameters of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 109:1231–1240
Naseri B, Majd-Marani Sh (2020) Assessment of eight rice cultivars flour for feeding resistance to Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J Stored Prod Res 88:101650
Nathan SS, Chung PG, Murugan K (2005) Effect of biopesticides applied separately or together on nutritional indices of the rice leaf folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Phytoparasitica 33:187–195
Price PW, Bouton CE, Gross P, Mcpheron BA, Thompson JN, Weise AE (1980) Interaction among three trophic levels: influence of plants on interactions between insect herbivores and natural enemies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:41–65
Ranjbar Aghdam H, Kamali K (2002) In vivo rearing of Sesamia cretica and Sesamia nonagrioides botanephaga. J Entomol Soc Iran 22:63–78
Sadeghi R, Eshrati MR, Mortazavian SMM, Jamshidnia A (2019) The effects of the essential oils isolated from four ecotypes of cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) on the blood cells of the pink stem borer, Sesamia cretica Ledere (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Kansas Entomol Soc 92(1):390–399
Scriber JM, Slansky F (1981) The nutritional ecology of immature insects. Ann Rev Entomol 26:183–211
Sedighi L, Ranjbar Aghdam H, Imani S, Shojai M (2016) Comparative demography of Sesamia cretica Lederer (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on its two the most important natural hosts, maize and sugarcane. J Agr Sci Tech 18:1807–1818
Sharma HC, Sujana G, Rao DM (2009) Morphological and chemical components of resistance to pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera in wild relatives of pigeonpea. Arthropod Plant Interact 3:151–161
Shishehbor P, Hemmati SA (2021) Investigating of secondary metabolites in bean cultivars and their impact on nutritional performance of Spodoptera littoralis (Lep.: Noctuidae). Bull Entomol Res 112:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485321000948
Slinkard K, Singleton VL (1977) Total phenol analysis: automation and comparison with manual methods. Am J Enol Vitic 28:49–55
Soltani Orang F, Ranjbar Aghdam H, Abbasipour H, Askarianzadeh A (2014) Effect of temperature on developmental rate of Sesamia cretica (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) immature stages. Insect Sci 14:197
Temerak SA, Negm AA (1979) Impact and differential effect of certain biomortality factors on the eggs and newly-hatched larvae of the pink borer, Sesamia cretica Lederer on two sugarcane varieties. Z Angew Entomol 88:313–318
Tomberlin JK, Sheppard DC, Joyace JA (2002) Susceptibility of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae and adults to four insecticides. J Econ Entomol 95:598–602
Tsai JH, Wang JJ (2001) Effects of host plant on biology and life table parameters of Aphis spiraecola (Hom: Aphididae). Environ Entomol 30:44–50
Turfan O, Turkyılmaz M, Yemis O, Ozkan M (2011) Anthocyanin and colour changes during processing of pomegranate (Punica granatum L., cv. Hicaznar) juice from sacs and whole fruit. Food Chem 129:1644–1651
Waldbauer GP (1968) The consumption and utilization of food by insects. Adv Insect Physiol 5:229–288
War AR, Paulraj MG, War MY, Ignacimuthu S (2011) Differential defensive response of groundnut to Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Plant Interact 6:1–11
War AR, Paulraj MG, Ahmad T, Buhroo AA, Hussain B, Ignacimuthu S, Sharma HC (2012) Mechanisms of plant defense against insect herbivores. Plant Signal Behav 7:1306–1320
Wright DJ, Verkert RHJ (1995) Integration of chemical and biological control systems for arthropods; evaluation in a multitrophic context. Pestic Sci 44:207–218
Zahedi A, Razmjou J, Rafiee-Dastjerdi H, Leppla NC, Golizadeh A, Hassanpour M, Ebadollahi A (2019) Tritrophic interactions of cucumber cultivar, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae), and its predator Hippodamia variegata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Econ Entomol 112:1774–1779
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, which is greatly appreciated.
Funding
This research was funded by Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, (Grant No. SCU.AP99.323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, AB, BH, and SAH; methodology, BH and SAH; software, AB and SAH; validation, AB, BH, and SAH; formal analysis, AB and SAH; investigation, AB, BH, HRA, and SAH; resources, AB, BH, HRA, and SAH; data curation, AB, BH, and SAH; writing—original draft preparation, AB; writing—review and editing, BH and SAH; visualization, BH and SAH; supervision, BH, HRA, and SAH; project administration, BH; and funding acquisition, BH. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any experiment on human or animal performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Vartika Mathur.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babamir-Satehi, A., Habibpour, B., Aghdam, H.R. et al. Interaction between feeding efficiency and digestive physiology of the pink stem borer, Sesamia cretica Lederer (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), and biochemical compounds of different sugarcane cultivars. Arthropod-Plant Interactions 16, 309–316 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-022-09898-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-022-09898-w