Abstract
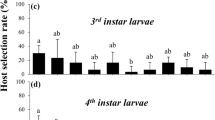
The influence of larval diet source in Sitophilus oryzae (L.), a primary grain feeder, on the choice of a new cereal host by young adult was investigated through a multiple choice comparative bioassay. For this purpose, virgin male and female adults, which had been reared as immatures in different grain commodities, were monitored according to their food preference in cylindrical arenas containing whole kernels of maize, rice, barley and wheat. The adults showed a clear individual preference for maize kernels, regardless of the previous food experience, sex and also the interval on which the adults are exposed to food. Males were much more mobile than females and visited more vigorously different commodities before the final choice. Female response was found to be related with male response to specific food sources. Hence, our results indicate that there was no natal habitat preference induction, since maize was, in most cases, the final commodity choice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agresti A (1992) A survey of exact inference for contingency tables. Stat Sci 7:131–153
Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG, Trematerra P (2006) Responses of Sitophilus oryzae (L.) and Tribolium confusum J. du Val to traps under pheromone and food volatiles. Eur J Entomol 103:371–378
Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG, Vayias BJ, Panoussakis EC (2008) Influence of grain type on the susceptibility of different Sitophilus oryzae (L.) populations, obtained from different rearing media, to three diatomaceous earth formulations. J Stored Prod Res 44:279–284
Baker JE (1988a) Development of four strains of Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) on barley, corn (maize), rice and wheat. J Stored Prod Res 24:193–198
Baker JE (1988b) Purification of an a-amylase inhibitor from wheat Triticum aestivum and its interaction with amylases from rice-weevil Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Insect Biochem 18:107–116
Barron AB (2001) The life and death of Hopkins’ host-selection principle. J Insect Behav 14:725–737
Blackiston DJ, Casey ES, Weiss MR (2008) Retention of memory through metamorphosis: Can a moth remember what it learned as a caterpillar? PLoS One 3:1–7
Campbell JF (2005) Fitness consequences of multiple mating on female Sitophilus oryzae L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ Entomol 34:833–843
Ceruti FC, Pinto Junior AR, de Carvalho RIN, Vianna E (2006) Response of Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) to different volatiles of wheat grains. In: Proceedings 9th international working conference on stored product protection. Campinas, Brazil, pp 701–705
Corbet SA (1985) Insect chemosensory responses: a chemical legaci hypothesis. Ecol Entomol 10:143–153
Cox PD, Collins LE (2002) Factors affecting the behavior of beetle pests in stored grain, with particular reference to the development of lures. J Stored Prod Res 38:95–115
Danho M and Haubruge E (2003) Optimal clutch size and oviposition strategy for the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais. In Proceedings of the 8th international working conference on stored product protection, 2002 July 22–26, York, UK. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 59–64
Danho M, Gaspar C, Haubruge E, Phillips JK, Faustini DL, Burkholder WE (2002) The impact of grain quantity on the biology of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): oviposition, distribution of eggs, adult emergence, body weight and sex ratio. J Stored Prod Res 38:259–266
Davis JM, Stamps JA (2004) The effect of natal experience on habitat preferences. Trends Ecol Evol 19:411–416
Dent KL, Earwaker PT, Holloway GJ (2003) Host selection behaviour by adults of legume and cereal breeding populations of Sitophilus oryzae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Bull Entomol Res 93:475–479
Dethier VG (1954) Evolution of feeding preferences in phytophagous insects. Evolution 8:33–54
Gelman A, Rubin DB (1992) Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat Sci 7:457–472
Gelman A, Carlin JB, Stern HS, Rubin DB (2004) Bayesian data analysis. Texts in statistical science, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, London, p 668
Giga DP, Smith RH (1985) Oviposition markers in Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) and C. rhodesianus (Pic.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae): asymmetry of interspecific responses. Agric Ecosyst Environ 12:229–233
Gill J (2002) Bayesian methods: a social and behavioral sciences approach. Chapman & Hall, London, p 459
Guedes NMP, Guedes RNC, Campbell JF, Throne JE (2010) Contest behaviour of maize weevil larvae when competing within seeds. Anim Behav 79:281–289
Halstead DGH (1963) External sex differences in stored-products Coleoptera. Bull Entomol Res 54:119–134
Jaenike J (1983) Induction of host preference in Drosophila melanogaster. Oecologia 58:320–325
Jaenike J (1988) Effects of early adult experience on host-selection in insects. Some experimental and theoretical results. J Insect Behav 1:3–15
Jermy T (1984) Evolution of insect/host relationships. Am Nat 124:609–630
Kiritani K (1965) Biological studies on the Sitophilus complex (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Japan. J Stored Prod Res 1:69–176
Levinson HZ, Kanaujia KR (1982) Feeding and oviposition behaviour of the granary weevil (Sitophilus granarius L.) induced by stored wheat, wheat extracts and dummies. Zeitschrift fur Angewandte Entomologie 93:292–305
Levinson HZ, Levinson A, Ren Z, Mori K (1990) Comparative olfactory perception of the aggregation pheromones of Sitophilus oryzae (L.), S. zeamais (Motsch.) and S. granarius (L.), as well as the stereoisomers of these pheromones. J Appl Entomol 110:203–213
Likhayo PW, Hodges RJ (2000) Field monitoring Sitophilus zeamais and Sitophilus oryzae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) using refuge and flight traps baited with synthetic pheromone and cracked wheat. J Stored Prod Res 36:341–353
Lunn DJ, Thomas A, Best N, Spiegelhalter D (2000) WinBUGS—a Bayesian modelling framework: concepts, structure, and extensibility. Stat Comput 10:325–337
Nardon Ch, Nardon P (2002) Nouveaux caractères distinctifs des larves et adultes des deux espèces jumelles Sitophilus oryzae (L.) et S. zeamais Mots. (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). Annales de la Société entomologique de France 38:239–246
Phillips TW, Jiang XL, Burkholder WE, Phillips JK, Tran HQ (1993) Behavioral responses to food volatiles by two species of stored-product Coleoptera, Sitophilus oryzae (Curculionidae) and Tribolium castaneum (Tenebrionidae). J Chem Ecol 19:723–734
Plarre R (1996) Three-dimensional distribution of Sitophilus granarius (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in wheat influenced by the synthetic aggregation pheromone. J Stored Prod Res 32:275–283
Plarre R (2010) An attempt to reconstruct the natural and cultural history of the granary weevil, Sitophilus granarius (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Eur J Entomol 107:1–11
R Development Core Team (2010) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Romero SA, Campbell JF, Nechols JR, With KA (2009) Movement behaviour in response to landscape structure: the role of functional grain. Landsc Ecol 24:39–51
Romero SA, Campbell JF, Nechols JR, With KA (2010) Movement behavior of red beetle: response to habitat cues and patch boundaries. Environ Entomol 39:919–929
Senthilkumar T, Javas DS, White NDG, Freud MS, Shafai C, Thomson DJ (2012) Characterization of volatile organic compounds released by granivorous insects in stored wheat. J Stored Prod Res 48:91–96
Singh K, Agrawal NS, Girish GK (1974) The oviposition and development of Sitophilus oryzae (L.) in different high-yielding varieties of wheat. J Stored Prod Res 10:105–111
Stamps JA, Davis JM (2006) Adaptive effects of natal experience on habitat selection by dispersers. Anim Behav 72:1279–1289
Trematerra P, Fontana F, Mancini M, Sciarretta A (1999) Influence of intact and damaged cereal kernels on the behaviour of rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleroptera: Curculionidae). J Stored Prod Res 35:265–276
Trematerra P, Sciarretta A, Tamasi E (2000) Behavioural responses to volatiles from durum wheat kernels and host selection in Oryzaephilus surinamensis (Linnaeus), Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) and Tribolium confusum J. du Val. Entomol Exp Appl 94:195–200
Trematerra P, Valente A, Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG (2007) Kernel-kernel interactions and behavioural responses of the adults maize weevil Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Appl Entomol Zool 42:129–135
Ukeh DA, Birkett MA, Bruce TJ, Allan EJ, Pickett JA, Luntz AJ (2010) Behavioral responses of the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais, to host (stored-grain) and non-host plant volatiles. Pest Manag Sci 66:44–50
Van Hemden HF, Sponagl B, Wagner E, Baker T, Ganguly S, Douloumpaka S (1996) Hopkins’ ‘host selection principle’, another nail in its coffin. Physiol Entomol 21:325–328
Van Hemden HF, Storek P, Douloumpaka S, Eleftherianos I, Poppy GM, Powell W (2008) Plant chemistry and aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae): imprinting and memory. Eur J Entomol 105:477–483
Walgenbach CA, Phillips JK, Faustini DL, Burkholder WE (1983) Male-produced aggregation pheromone of the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais, and interspecific attraction between three Sitophilus species. J Chem Ecol 9:831–841
Walling LL (2000) The Myriad plant responses to herbivores. J Plant Growth Regul 19:195–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editors: Yvan Rahbe and Heikki Hokkanen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trematerra, P., Lupi, C. & Athanassiou, C. Does natal habitat preference modulate cereal kernel preferences in the rice weevil?. Arthropod-Plant Interactions 7, 287–297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-012-9243-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-012-9243-y