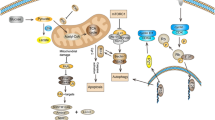
Abstract
The market for protein-drugs has steadily increased due their increased use as alternatives to traditional small molecule drugs. While some therapeutic proteins have been produced in microbial systems, mammalian cell systems such as Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are widely used as the host cell system. To increase the efficiency of producing therapeutic proteins, many researchers have attempted to solve the critical problems that occur in mammalian cell systems. As a result, several serum-free media and advanced culture methods have been developed, and protein productivity has increased considerably through the development of efficient selection methods. However, the prevalence of apoptosis during mammalian cell culture still remains a significant problem. Based on the understanding of apoptotic mechanisms and related proteins, anti-apoptotic engineering has steadily progressed. In this study, we review the strategies that have been developed for high-level production of recombinant proteins in the CHO cell system via a selection of clones, target-gene amplification, optimization of culture systems and an inhibition of apoptosis through genetic modification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Walsh, Nat. Biotechnol., 21, 865 (2003).
F.M. Wurm, Nat. Biotechnol., 22, 1393 (2004).
D. K. Robinson and K.W. Memmert, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 38, 972 (1991).
T.H.J. Kwaks and A. P. Otte, Trends Biotechnol., 24, 137 (2006).
T. J. Wilson and I. Kola, Methods Mol. Biol., 158, 83 (2001).
G. Urlaub and L. A. Chasin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 77, 4216 (1980).
G. Urlaub, E. Kas, A. M. Carothers and L. A. Chasin, Cell, 33, 405 (1983).
M.G. Pallavicini, P. S. DeTeresa, C. Rosette, J.W. Gray and F.M. Wurm, Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 401 (1990).
C. Gandor, C. Leist, A. Fiechter and F.A.M. Asselbergs, FEBS Lett., 377, 290 (1995).
M. Wirth, J. Bode, G. Zettlmeissl and H. Hauser, Gene, 73, 419 (1988).
S.M. Browne and M. Al-Rubeai, Trends Biotechnol., 25, 425 (2007).
M. S. Sinacore, D. Drapeau and S. R. Adamson, Mol. Biotechnol., 15, 249 (2000).
M. J. De Jesus, P. Girard, M. Bourgeois, G. Baumgartner, B. Jacko, H. Amstutz and F.M. Wurm, Biochem. Eng. J., 17, 217 (2004).
N. I. Walker, B. V. Harmon, G. C. Gobe and J. F. Kerr, Methods Achiev. Exp. Pathol., 13, 18 (1988).
A.H. Wyllie, R.G. Morris, A. L. Smith and D. Dunlop, J. Pathol., 142, 66 (1984).
S.A. Susin, N. Zamzami and G. Kroemer, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1366, 151 (1998).
X. Liu, C.N. Kim, J. Yang, R. Jemmerson and X. Wang, Cell, 86, 147 (1996).
A. Ashkenazi, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 420 (2002).
S. Oyadomari, E. Araki and M. Mori, Apoptosis, 7, 335 (2002).
J.M. Adam and S. Cory, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 14, 715 (2002).
T. Subramanian and G. Chinnadurai, J. Cell. Biochem., 89, 1102 (2003).
E.H.Y. Cheng, B. Levine, L.H. Boise, C.B. Thomson and J.M. Hardwick, Nature, 379, 554 (1996).
A. J. Mastrangelo and M. J. Betenbaugh, Trends Biotechnol., 16, 88 (1998).
N. Arden and M. J. Betenbaugh, Trends Biotechnol., 22, 174 (2004).
A. Sanfeliu and G. Stephanopoulos, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 64, 46 (1999).
J.A. Zanghi, W.A. Renner, J. E. Bailey and M. Fussenegger, Biotechnol. Prog., 16, 319 (2000).
R.R. Balcarcel and G. Stephanopoulos, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 76, 1 (2001).
A. Tinto, C. Gabernet, J. Vives, E. Prats, J. J. Cairo, L. Cornudella and F. Godia, J. Biotechnol., 95, 205 (2002).
T.M. Sauerwald, G.A. Oyler and M. J. Betenbaugh, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 81, 329 (2003).
S. L. McKenna and T.G. Cotter, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 67, 165 (2000).
J. Vives, S. Juanola, J. J. Cairo and F. Godia, Metab. Eng., 5, 124 (2003).
J. Vives, S. Juanola, J. J. Cairo, E. Prats, L. Cornudella and F. Godia, Biotechnol. Prog., 19, 84 (2003).
A. J. Mastrangelo, J. M. Hardwick, F. Bex and M. J. Betenbaugh, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 67, 544 (2000).
Y. H. Sung and G.M. Lee, Biotechnol. Prog., 21, 50 (2005).
B. Figueroa, T.M. Sauerwald, G.A. Oyler, J.M. Hardwick and M. J. Betenbaugh, Metab. Eng., 5, 230 (2003).
E.B. Lasunskaia, I. I. Fridlianskaia, Z. A. Darieva, M. S.R. da Silva, M. M. Kanashiro and B.A. Margulis, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 81, 496 (2003).
S. O. Hwang and G.M. Lee, J. Biotechnol., 139, 89 (2009).
N. S. Kim and G.M. Lee, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 78, 217 (2002).
Y.H. Sung, J. S. Lee, S. H. Park, J. Koo and G. M. Lee, Metab. Eng., 9, 452 (2007).
W. J. Rhee, E. J. Kim and T.H. Park, Biotechnol. Prog., 15, 1028 (1999).
W. J. Rhee and T. H. Park, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 271, 186 (2000).
W. J. Rhee, E. J. Kim and T. H. Park, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 295, 779 (2002).
S. S. Choi, W. J. Rhee and T.H. Park, Biotechnol. Prog., 18, 874 (2002).
E. J. Kim, W. J. Rhee and T. H. Park, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 285, 224 (2001).
E. J. Kim, H. J. Park and T. H. Park, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 308, 523 (2003).
H. J. Park, E. J. Kim, T. Y. Koo and T. H. Park, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 33, 466 (2003).
E. J. Kim, W. J. Rhee and T. H. Park, Biotechnol. Prog., 20, 324 (2004).
W. J. Rhee, E.H. Lee and T.H. Park, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 14, 645 (2009).
E. J. Kim and T. H. Park, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 8, 76 (2003).
W. J. Rhee, E.H. Lee, J. H. Park, J. E. Lee and T.H. Park, Biotechnol. Prog., 23, 1441 (2007).
S. S. Choi, W. J. Rhee and T.H. Park, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 91, 793 (2005).
S. S. Choi, W. J. Rhee, E. J. Kim and T. H. Park, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 95, 459 (2006).
J.G. Park, S. S. Choi and T. H. Park, Process Biochem., 42, 8 (2007).
T.Y. Koo, J.H. Park, H. H. Park and T.H. Park, Process Biochem., 44, 146 (2009).
Z. Wang, J. H. Park, H. H. Park, W. Tan and T. H. Park, Process Biochem., in press, doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2010.03.029 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tai Hyun Park is a Professor in the School of Chemical and Biological Engineering at Seoul National University in Korea. He received his B.S. degree (Seoul National University, Korea), M.S. degree (KAIST, Korea), and Ph.D. degree (Purdue University) all in Chemical Engineering and was a postdoctoral fellow at the University of California at Irvine. He worked for several years at the LG Biotech Research Institute and taught at Sung Kyun Kwan University before joining Seoul National University in 1997. He was a visiting professor at the University of California at Irvine and Cornell University. His research interests include cellular engineering, olfactory and taste biosensor, nanobiotechnology, biohydrogen, and biorefinery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Park, H.H. & Park, T.H. Cellular engineering for the high-level production of recombinant proteins in mammalian cell systems. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 27, 1042–1048 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0278-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0278-4