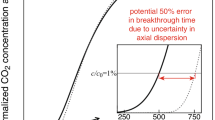
Abstract
A multi-cell model was developed to analyze the behavior of a simulated moving bed process for adsorptive para-xylene separation from other xylene isomers. A novel technology for a semi-batch mode adsorption experiment was developed and used for fast and accurate data collection. Interaction parameters between different species for a multi-component extended Langmuir isotherm were estimated from single and multi-component adsorption experiments and implemented into the model. The parameters such as porosities, particle density and mass transfer coefficients were obtained from adsorbent analysis and commercial plant operation. To resolve the problem of high dimensionality, a cell-by-cell approach was proposed to solve the model. The recovery and purity of para-xylene as well as the concentration profile calculated from the model were in good agreement with the actual data. The effects of channeling and feed composition change were simulated, and they turned out to be physically meaningful. The simulation model will be used for operation condition optimization, trouble shooting, and productivity enhancement including a configuration change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Pang, Global petrochemical review, UOP’s Korea Technology Seminar, Jejudo (2004).
G. Ash, K. Barth, G. Hotier, L. Mank and P. Renard, Revue De L Institut Francais Du Petrole, 49, 541 (1994).
D. B. Broughton and C. G. Gerhold, US Patent 2,985,589 (1961).
D. B. Broughton, R. W. Neuzil, J. M. Pharis and C. S. Brearley, Chem. Eng. Prog., 66, 70 (1970).
M. M. Kearney and K. L. Hieb, US Patent 5,102,553 (1992).
J. Kim, N. Abunasser and P. Wankat, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22, 619 (2005).
O. Ludemann-Hombourger, M. Bailly and R. M. Nicoud, Sep. Sci. Technol., 35, 1285 (2000).
O. Ludemann-Hombourger, R. M. Nicoud and M. Bailly, Sep. Sci. Technol., 35, 1829 (2000).
H. Schramm, M. Kaspereit, A. Kienle and A. Seidel-Morgenstern, Chem. Eng. Technol., 25, 1151 (2002).
UOP, Parex process, www.uop.com (accessed).
D. C. S. Azevedo, S. B. Neves, A. E. Rodrigues, C. L. Cavalcante Jr. and S. P. Ravagnani, Anais do I Encontro Brasileiro sobre Adsorção, Fortaleza, 93 (1997).
J. Gu, W. Jiang and X. Gu, J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol., 23, 725 (1997).
K. Lee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26, 468 (2009).
Y. Lim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 21, 836 (2004).
C. Migliorini, M. Mazzotti and M. Morbidelli, AIChE J., 45, 1411 (1999).
M. Minceva and A. E. Rodrigues, Sep. Sci. Technol., 38, 1463 (2003).
M. Minceva and A. E. Rodrigues, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 41, 3454 (2002).
Z. Tong, Z. Ge and C. Yang, ACTA PETROLEI SINICA PETROLEUM PROCESSING SECTION, 11, 36 (1995).
C.-N. Wei, Diagnosis of manufacturing plant problems through process model parameter update, International Federation of Automation Control Conference, Maastricht (1989).
R. H. Fowler and E. A. Guggenheim, Statistical thermodynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1939).
E. Glueckauf, Trans. Faraday Soc., 51, 1540 (1955).
G. Guiochon, S. Golshan-Shirazi and A. M. Katti, Fundamentals of nonlinear and preparative chromatography, Academic Press, Boston (1994).
D. M. Ruthven, Principles of adsorption and adsorption processes, Wiley-Interscience (1984).
F. Charton and R. M. Nicoud, J. Chromatography A, 702, 97 (1995).
U. P. Ernst and J. T. Hsu, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 28, 1211 (1989).
J. J. Van Deemter, F. J. Zuiderweg and A. Klinkenberg, Chem. Eng. Sci., 5, 1 (1956).
Grace Davison, Adsorbents for process application, www.gracedavison.com (accessed).
D. W. Breck, Zeolite molecular sieves: Structure, chemistry and use, John Wiley & Sons, New York (USA) (1974).
C. W. Gear, Numerical initial value problems in ordinary differential equations, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1971).
A. L. Myers and W. D. Seider, Introduction to chemical engineering and computer calculations, Prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1976).
C. Beauvais, A. Boutin and A. H. Fuchs, Adsorption-Journal of the International Adsorption Society, 11, 279 (2005).
I. Langmuir, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 40, 1361 (1918).
R. M. Nicoud, G. Fuchs, P. Adam, M. Bailly, E. Küsters, F. D. Antia, R. Reuille and E. Schmid, Chirality NY, 5, 267 (1993).
H. Freundlich, Colloid and capillary chemistry, 3rd German Edn. Methuen, London (1926).
S. Sips, J. Chem. Phys., 16, 490 (1948).
J. K. Moon, D. K. Keum and W. K. Lee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 6, 172 (1989).
A. L. Myers and J. M. Prausnitz, AIChE J., 11, 121 (1965).
T. H. Chilton and A. P. Colburn, Trans. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng., 26, 178 (1931).
S. Ergun, Chem. Eng. Prog., 48, 89 (1952).
J. Kozeny, Sitzungsberichte der Akademie der Wissenschaften in Wien, MATHEMATISCH-naturwissenschaftliche Klasse, Abteilung IIa, 136, 271 (1927).
J. Lee and N. C. Shin, Korea Patent Korean Patent issued, 0589122 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Shin, N.C., Lim, Y. et al. Modeling and simulation of a simulated moving bed for adsorptive para-xylene separation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 27, 609–618 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0078-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0078-x