Abstract
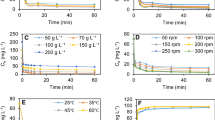
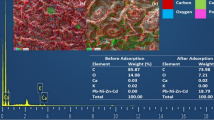
A basic investigation on the removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by using activated tea waste was conducted in batch conditions. An inexpensive and effective adsorbent was developed from waste tea leaves for the uptake of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. The influence of different experimental parameters—shaking time, particle size, adsorbent dose, initial pH, temperature, etc.—on lead uptake was evaluated. Lead is adsorbed by the developed adsorbent up to maximum of 99.7%. The initial Pb(II) concentrations were 5, 10, 15 and 20 mg/l in the experiment. The adsorption was found to be exothermic in nature. The Langmuir, Freundlich and Tempkin isotherm models were tried to represent the equilibrium data of Pb(II) adsorption. The adsorption data was fitted very well to the Langmuir isotherm model in the studied concentration range of Pb(II) adsorption. Isotherms have been used to determine thermodynamic parameters of the process: free energy change (ΔG°), enthalpy change (ΔH°) and entropy change (ΔS°). Column experiments were performed to study the practical applicability of the system. The kinetics and the factors controlling the adsorption process were also discussed. Activated tea waste is a better adsorbent compared to other adsorbents available in literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. J. P. Esteves, E. Valdman and S. G. F. Leite, Biotechnol. Lett., 22, 499 (2000).
V. K. Gupta and I. Ali, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 271, 321 (2004).
V. K. Gupta, M. Gupta and S. Sharma, Water Res., 35, 1125 (2001).
M. Sekar, V. Sakthi and S. Rengaraj, J. Colloid Interface. Sci., 279, 307 (2004).
M. Mouflih, A. Aklil and S. Sebti, J. Hazard. Mater., 119, 183 (2005).
D. Sabriye and C. Ali, J. Hazard. Mater., 138, 409 (2006).
R. Naseem and S. S. Tahir, Water Res., 35, 3982 (2001).
B. E. Reed, S. Arunachalam and B. Thomas, Environ. Progr., 13, 60 (1994).
C. Raji, K. P. Shubha and T. S. Anirudhan, Indian J. Environ. Health, 39, 230 (1997).
S.H. Abdel-Halim, A.M.A. Shehta and M. F. EI-Shahat, Water Res., 37, 1678 (2003).
R. Salim, M. Al-Subu and E. Dawod, J. Environ. Manage., 87, 521 (2008).
M. F. Sawalha, J. R. Peralta-Videa, B. Sanchez-Salcido and J. L. Gardea-Torresdey, J. Environ. Manage., 90, 1213 (2009).
B. Sen Gupta, M. Curran, S. Hasan and T. K. Ghosh, J. Environ. Manage., 90, 954 (2009).
X. S. Wang, Z. Z. Li and S.R. Tao, J. Environ. Manage., 90, 721 (2009).
S. S. Ahluwalia and D. Goyal, Eng. Life Sci., 5, 158 (2005).
B.M.W. P.K. Amarasinghe and R.A. Williams, Chem. Eng. J., 132, 299 (2007).
T.W. Tee and A.R.M. Khan, Environ. Technol. Lett., 9, 1223 (1988).
C.C.V. Cruz, A.C.A.D. Costa, C.A. Henriques and A. S. Luna, Bioresour. Technol., 91, 249 (2004).
G. Bitton, Waste water microbiology, Willey, Europe (1999).
B. Benguella and H. Benaissa, Water Res., 36, 2463 (2002).
D.O. Cooney, Adsorption design for wastewater treatment, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL (1999).
G. Mc Kay, Use of adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from wastewaters, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (1996).
M. J. Tempkin and V. Pyzhev, Acta Physiol. Chem. USSR, 12, 271 (1940).
C.H. Giles, T. H. Mc Ewan, S.W. Nakhwa and D. Smith, J. Chem. Soc., 4, 3973 (1960).
V.C. Taty-Costodes, H. Fauduet, C. Porte and A. Delacroixs, J. Hazard. Mater., 105, 121 (2003).
M. Dogan, M. Alkan, A. Turkyilmaz and Y. Ozdemir, J. Hazard. Mater., B109, 141 (2004).
H. Aydin, Y. Bulut and C. Yerlikaya, J. Environ. Manage., 87, 37 (2008).
M. K. Mondal, Int. J. Sus. Dev. Plann., 3, 377 (2008).
G. Z. Issabayeva, K.M. Aroua, N. Meriam and N. Sulaiman, Biores. Technol., 97, 2350 (2006).
J. Goel, K. Kadirvelu, C. Rajagopal and V. K. Garg, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 44, 1987 (2005).
S. Doyurum and C. Ali, J. Hazard. Mater., 138, 22 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, M.K. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption using activated tea waste. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 27, 144–151 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0304-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0304-6