Abstract
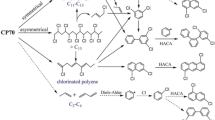
The recalcitrant nature of pyrene and other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) lies in part in their low solubility in water, rendering them less susceptible to chemical and biological degradation. To overcome this remediation obstacle, this work investigates the use of a 2-stage ozonation process, first in nonpolar hexane phase then in polar aqueous phase, for the treatment of hydrophobic contaminants using pyrene as a model compound. The objectives of this research are to break down pyrene by using ozonation, identify the intermediates of pyrene, show a general degradation pathway of pyrene subject to ozonation and test the biodegradability of intermediates and byproducts of pyrene in the aqueous phase. The first stage briefly ozonates the contaminant at high concentration in organic solvent hexane, which facilitates very efficient conversion of the hydrophobic compounds into ring-opened polar intermediates containing alcohol, aldehyde, and acid functional groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zeng, P. K. A. Hong and D. A. Wavrek, Wat. Res., 34, 1157 (2000).
Y. Zeng, P. K. A. Hong and D. A. Wavrek, Environ. Sci. Tech., 34, 854 (2000).
E. S. Hong, H. S. Kim, S. L. Lee, J. S. Chung, E. W. Shin, K. Ryu and I. K. Yoo, J. Korean Society of Environmental Engineers, 28(5), 573 (2006).
C. Danheux, L. Hanoteau, R. H. Martin and G. Van Binst, Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg., 72, 289 (1963).
M. G. Sturrock and R. A. Duncan, J. Org. Chem., 33, 2149 (1968).
A. A. Kefely, S. K. Rakovski, D. M. Shopov, S. D. Razumovskii, R. S. Rakovski and G. E. Zaikov, J. Poly. Sci., 19, 2175 (1981).
B. Legube, S. Guyon, H. Sugimitsu and M. Dore, Wat. Res., 20, 197 (1986).
A. Kommuller, M. Cuno and U. Wiesmann, Wat. Sci. Tech., 35, 57 (1997).
F. A. Stich and D. Bhattacharyya, Environ. Prog., 6(4), 224 (1987).
C. Y. Chang and J. N. Chen, Haz. Ind. Wastes, 25th Mid-Atlantic Industrial Waste Conference, 491 (1993).
J. N. Chen and C. Y. Chang, Tox. Environ. Chem., 59, 7 (1997).
A. R. Freshour, S. Mawhinney and D. Bhattacharyya, Wat. Res., 30, 1949 (1996).
J. J. Yao, Z. H. Huang and S. J. Masten, Wat. Res., 32, 3001 (1998).
J. J. Yao, Z. H. Huang and S. J. Masten, Wat. Res., 32, 3235 (1998).
P. K. A. Hong and J. C. Chao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 43, 7710 (2004).
F. J. Beltran, G. Ovejero, J. M. Encinar and J. Rivas, Ozonation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 34, 1595 (1995).
APHA, AWWA, WPCF (WEF), Part 4500, Ozone (residual), proposed, Indigo Colorimetric Method, 18th ed., American Public Health Association: Washington, (1992).
P. Bailey, Ozonation in organic chemistry, Academic Press, New York Vll Chapters III–V (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, YI., Hong, A. Ozonation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in hexane and water: Identification of intermediates and pathway. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 24, 1003–1008 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0111-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0111-x