Abstract
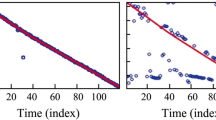
The problem of blind adaptive equalization of underwater single-input multiple-output (SIMO) acoustic channels was analyzed by using the linear prediction method. Minimum mean square error (MMSE) blind equalizers with arbitrary delay were described on a basis of channel identification. Two methods for calculating linear MMSE equalizers were proposed. One was based on full channel identification and realized using RLS adaptive algorithms, and the other was based on the zero-delay MMSE equalizer and realized using LMS and RLS adaptive algorithms, respectively. Performance of the three proposed algorithms and comparison with two existing zero-forcing (ZF) equalization algorithms were investigated by simulations utilizing two underwater acoustic channels. The results show that the proposed algorithms are robust enough to channel order mismatch. They have almost the same performance as the corresponding ZF algorithms under a high signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio and better performance under a low SNR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberge F, Duhamei P, Nikolava M (2002). Adaptive solution for blind identification/equalization using deterministic maximum likelihood. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 50(4), 923–936.
Chow TWS, Wang BY, NG KT (2002). Adaptive blind channel identification algorithm based on linear prediction for SIMO FIR systems. IEE Proceedings Vision, Image & Signal Processing, 149(4), 225–230.
Ding Z (1997). Matrix outer-product decomposition method for blind multiple channel identification. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 45(12), 3053–3061.
Gesbert D, Duhamei L (1997). Robust blind channel identification and equalization based on multistep predictors. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Munich, 3621–3624.
Giannakis GB, Halford SD (1997). Blind fractionally spaced equalization of noisy FIR channels: direct and adaptive solutions. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 45, 2277–2292.
Li XH, Fan H (2000). Linear prediction methods for blind fractionally spaced equalization. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 48(6), 1667–1675.
Liu H, Xu GH, Tong L (1994). A deterministic approach to blind identification of multi-channel FIR systems. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Adelaide, 581–584.
Meraim KA, Loubaton P, Moulines E (1997). A subspace algorithm for certain blind identification problems. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 43(2), 499–511.
Meraim KA, Moulines E, Loubaton P (1997). Prediction error method for second-order blind identification. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 45(3), 694–705.
Moulines E, Duhamei P, Cardoso J (1995). Subspace methods for the blind identification of multichannel FIR filters. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 43(2), 516–525.
Papadias CB, Slock DTM (1999). Fractionally spaced equalization of linear polyphase channels and related blind techniques based on multichannel linear prediction. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 47(3), 641–654.
Slock DTM (1994). Blind fractionally-spaced equalization, perfect-reconstruction filter banks and multichannel linear prediction. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Adelaide, 585–588.
Slock DTM, Papadias CB (1995). Further results on blind identification and equalization of multiple FIR channels. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Detroit, 1964–1967.
Stojanovic M (1996). Recent advances in high-speed underwater acoustic communications. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 21(2), 125–136.
Tong L, Xu G, Hassibi (1995). Blind channel identification based on second-order statistics: a frequency-domain approach. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 41(1), 329–334.
Tong L, Xu G, Kailath T (1994). Blind identification and equalization based on second-order statistics: a time domain approach. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 40(2), 340–349.
Tugnait JK (1999). Multistep linear predictors-based blind equalization of FIR/IIR single-input multiple-output channels with common zeros. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 47(6), 1689–1700.
Zhang YP (2005). Research on blind fractionally-spaced equalization algorithms for underwater acoustic communications. Ph.D thesis, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, 58–59 (in Chinese).
Zielinski A, Young H, Wu L (1995). Performance analysis of digital acoustic communication in a shallow water channel. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 20(4): 293–298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.60372086 and the Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of China under Grant No.200753.
Yinbing Zhang was born in 1983. He is a PhD candidate for underwater acoustic engineering. His research interests include underwater acoustic signal processing, communication signal processing and channel equalization.
Junwei Zhao was born in 1937. He is a professor of Northwestern Polytechnical University. His research interests include underwater acoustic signal processing, sonar technique, underwater acoustic communication, et al.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhao, J., Guo, Y. et al. Blind adaptive MMSE equalization of underwater acoustic channels based on the linear prediction method. J. Marine. Sci. Appl. 10, 113–120 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-011-1050-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-011-1050-9