Abstract
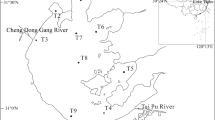
In this paper, we assessed the ecological and biodiversity status in the Bohai Sea through a quantitative survey on macrofaunal community at 25 stations in Laizhou Bay and adjacent waters in the autumn of 2006. We tested the robustness and effectiveness of taxonomic distinctness as an ecological indictor by analyzing its correlation with species richness and natural environmental variables and by analyzing other ecological indicators (Shannon-Wiener H′ and W statistics from Abundance Biomass Comparison curve). Results so obtained indicated that the benthic environment of the study waters in general is not under major impact of anthropogenic disturbance, but some stations in Laizhou Bay and along the coast of the Shandong Peninsula and even in the central Bohai Sea might be moderately disturbed and showed signs of ecological degradation. The taxonomic distinctness measures Δ+ and Λ+ were independent of sampling effort and natural environment factors and were compliant to other ecological indicators. Further application of the taxonomic distinctness indicator to assess marine biodiversity and ecosystem health on a larger regional scale with historical data seems promising.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, L. Q., 2004. Environment assessment and study on the total quantity control of pollution in the Laizhou Bay. Master Thesis. Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
Clarke, K. R. and Warwick, R. M., 1998. A taxonomic distinctness index and its statistical properties. J. Appl. Ecol., 35: 523–531.
Clarke, K. R. and Warwick, R. M., 2001a. A further biodiversity index applicable to species list: variation in taxonomic distinctness. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 216: 265–278.
Clarke, K. R. and Warwick, R. M., 2001b. Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation. 2nd edn. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth, 172pp.
Deng, J. Y. and Jin, X. S., 2000. Study on fishery biodiversity and its conservation in Laizhou Bay and Yellow River Estuary. Zool. Res., 21(1): 76–82 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo, Y. Q., Somerfield, P. J., Warwick, R. M., and Zhang, Z. N., 2001. Large-scale patterns in the community structure and biodiversity of free-living nematodes in the Bohai Sea, China. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U. K., 81: 755–763.
Guo, Y. Q., Warwick, R. M., Zhang, Z. N., and Mu, F. H., 2002. Free-living marine nematodes as a pollution indicator of the Bohai Sea. J. Environ. Sci., 14(4): 558–562.
Guo, Y. Q., Zhang, Z. N., and Mu, F. H., 2003. Study on biodiversity of nematode in the Bohai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 25(2): 106–113 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hall, S. J. and Greenstreet, S. P. R., 1998. Taxonomic distinctness and diversity measures: responses in marine fish communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 166: 227–229.
Han, J., Zhang, Z. N., and Yu, Z. S., 2003. Macrobenthic species diversity in southern and central Bohai Sea, China. Biodivers. Sci., 11(1): 20–27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Heino, J., Soininen, J., Lappalainen, J., and Virtanen, R., 2005. The relationship between species richness and taxonomic distinctness in freshwater organisms. Limnol. Oceanogr., 50: 978–986.
Huang, Z. G., 2008. Marine Species and Their Distributions in China’s Seas. 2nd edn. China Ocean Press, Beijing, 1191pp (in Chinese).
Jin, X. S., 2004. Long-term changes in fish community structure in the Bohai Sea, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 59: 163–171.
Leonard, D. R. P., Clarke, K. R., Somerfield P. J., and Warwick, R. M., 2006. The application of an indicator based on taxonomic distinctness for UK marine biodiversity assessments. J. Environ. Manag., 78: 52–62.
Li, R. G., 2003. Macrobenthos on the Continental Shelves and Adjacent Waters, China Sea. China Ocean Press, Beijing, 245pp (in Chinese).
Ma, S. S., Zhao, J., and Chen, B. J., 2006. Analyses and synthetic evaluation on environmental quality of Laizhou Bay. Mar. Fish. Res., 27(5): 13–16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mouillot, D., Gaillard, S., Aliaume, C., Verlaque, M., Belsher, T., and Troussellier, M., 2005. Ability of taxonomic diversity indices to discriminate coastal lagoon environments based on macrophyte communities. Ecolog. Indic., 5: 1–17.
Price, A. R. G., Keeling, M. J., and O’Callaghan, C. J., 1999. Ocean-scale patterns of ‘biodiversity’ of Atlantic asteroids determined from taxonomic distinctness and other measures. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. Lond., 66: 187–203.
Rogers, S. I., Clarke, K. R., and Reynolds, J. D., 1999. The taxonomic distinctness of coastal bottom-dwelling fish communities of the North-east Atlantic. J. Anim. Ecol., 68: 769–782.
Salas, F., Patrício, J., Marcos, C., Pardal, M. A., Pérez-Ruzafa, A., and Marques, J. C., 2006. Are taxonomic distinctness measures compliant to other ecological indicators in assessing ecological status? Mar. Pollut. Bull., 52: 162–174.
Somerfield, P. J., Olsgard, F., and Carr, M. R., 1997. A further examination of two new taxonomic distinctness measures. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 154: 303–306.
Ward, A. R., 1975. Studies on the free-living marine nematodes of Liverpool Bay. II. Influence of sediment composition on the distribution of marine nematodes. Mar. Biol., 30: 217–225.
Warwick, R. M., and Clarke, K. R., 1995. New ‘biodiversity’ measures reveal a decrease in taxonomic distinctness with increasing stress. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 129: 301–305.
Warwick, R. M., and Clarke, K. R., 1998. Taxonomic distinctness and environmental assessment. J. Appl. Ecol., 35: 532–543.
Warwick, R. M., 1986. A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities. Mar. Biol., 92: 557–562.
Warwick, R. M., and Clarke, K. R., 2001. Practical measures of marine biodiversity based on relatedness of species. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol.: An Annu. Rev., 39: 207–231.
Xu, B. D., Jin, X. S., and Liang, Z. L., 2005a. The taxonomic diversity of fish communities in the Yellow Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China, 35(4): 629–634 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu, B. D., Jin, X. S., and Liang, Z. L., 2005b. Calculation of hierarchical diversity of fish in the Huanghai and Bohai Seas. J. Ocean Univ. China, 35(1): 25–28 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, J. Q., Cui, W. L., Zhang, H. L., and Xu, Z. J., 2003. Marine ecosystem health structure and function index assessment in the west of Laizhou Bay. Mar. Sci. Bull., 22(5): 58–63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu, L. S., 2006. The Huanghe (Yellow) River: Recent changes and its countermeasures. Contin. Shelf Res., 26: 2281–2298.
Zhang, H. and Lu, J. J., 2007. Calculation of the taxonomic diversity of fish communities in the Yangtze River Estuary. J. East China Norm. Univ., 2007(2): 11–22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Z. H., Zhu, M. Y., Wang, Z. L., and Wang, J., 2006. Monitoring and managing pollution load in Bohai Sea, P. R. China. Ocean Coast. Manag., 49: 706–716.
Zhang, Z. N., Tu, L. H., and Yu, Z. S., 1990a. Preliminary study on the macrofauna in the Huanghe River estuary and its adjacent waters. (1) The biomass. J. Ocean Univ. Qingdao, 20(1): 31–45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Z. N., Tu, L. H., and Yu, Z. S., 1990b. Preliminary study on the macrofauna in the Huanghe River estuary and its adjacent waters. (2) In relation to the sedimentary environment. J. Ocean Univ. Qingdao, 20(2): 45–52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Z. N., Zhou, H., and Mu, F. H., 2001a. Biodiversity and neutral model analyses on nematode community in Bohai Sea, China. Acta Ecol. Sin., 21(11): 1808–1814 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Z. N., Zhou, H., Guo, Y. Q., and Mu, F. H., 2001b. Comparative study of the nematode community structure in the submarine delta of Huanghe River estuary and its adjacent waters. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin., 32(4): 436–444 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou, H., Hua, E., and Zhang, Z. N., 2010. Community structure of macrobenthos in Laizhou Bay and adjacent waters. J. Ocean Univ. China, 40(8): 80–87 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou, H., Zhang, Z. N., Liu, X. S., Tu, L. H., and Yu, Z. S., 2007. Changes in the shelf macrobenthic community over large temporal and spatial scales in the Bohai Sea, China. J. Mar. Syst., 67: 312–321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Hua, E. & Zhang, Z. Taxonomic distinctness of macrofauna as an ecological indicator in Laizhou Bay and adjacent waters. J. Ocean Univ. China 9, 350–358 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-010-1717-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-010-1717-x