Abstract
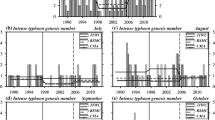
This paper analyzes the characteristics of super typhoons (STYs) over the western North Pacific (WNP) from 1965 to 2005 and describes the seasonal variability of STY activity. The relation between STY activity and the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) as well as the possible reason for the influence of the ENSO on STY activity are also investigated. The results showed that about one fifth of the tropical cyclones (TCs) over the WNP could reach the rank of STY. Most STYs appeared from July to November while there was a highest ratio between number of STYs and total number of TCs in November. Most STYs appeared east of the Philippine Sea. In El Niño years, affected by sea surface temperature (SST), monsoon trough and weak vertical wind shear, TC formation locations shifted eastward and there were more STYs than in La Niña years when the affecting factors changed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camargo, S. J., and Sobel, A. H., 2005. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone intensity and ENSO. J. Clim., 18: 2996–3006.
Chan, C. L., 2000. Tropical cyclone activity over the Western North Pacific associated with El Nino and La Nina events. J. Clim., 13: 2960–2972.
Chan, J. C. L., and Liu, K. S., 2004. Global warming and Western North Pacific typhoon activity from an observational perspective. J. Clim., 17: 4590–4602.
Chen, G. H., and Huang, R. H., 2006a. Research on climatological problems of tropical cyclone and typhoon activity in Western North Pacific. Adv. Earth Sci., 21(6): 610–616.
Chen, G. H., and Huang, R. H., 2006b. The effect of warm pool thermal states on tropical cyclone in West Northwest Pacific. J. Trop. Meteorol., 22(6): 527–532.
Chen, T.-C., and Wang, S.-Y., 2006. Interannual variation of the tropical cyclone activity over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim., 19: 5709–5720.
Chia, H. H., and Ropelewski, C. F., 2002. The interannual variability in the genesis location of tropical cyclones in the Northwest Pacific. J. Clim., 15: 2934–2944.
Frank, W. M., and Young, G. S., 2007. The interannual variability of tropical cyclones. Mon. Weather Rev., 135: 3587–3598.
Lei, X. T., and Chen, L. S., 2002. The latitudinal distribution of climatic characteristics on tropical cyclone activities in the WNP. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci., 13(2): 218–227.
Li, C. Y., 2000. Introduction of Climate Dynamics. 2nd edition. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 254–255.
Matsuura, T., Yumoto, M., and Iizuka, S., 2003. A mechanism of inter-decadal variability of tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn., 21: 105–117.
Paterson, L. A., Hanstrum, B. N., Davidson, N. E., and Weber, H. C., 2005. Influence of environmental vertical wind shear on the intensity of hurricane-strength tropical cyclones in the Australian region. Mon. Weather Rev., 133: 3644–3660.
Wang, B., and Chan, J. C. L., 2002. How strong ENSO events affect tropical storm activity over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim., 15(13): 1643–1658.
Wang, B., and Zhou, X., 2008. Climate variability and predictability of rapid intensification in tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys., 52: 1–16.
Wang, H., Ding, Y. H., and He, J. H., 2006. Influence of Western North Pacific summer monsoon changes on typhoon genesis. Acta Meteorol. Sin., 64(3): 345–356.
Webster, P. J., Holland, G. J., Curry, J. A., and Chang, H.-R., 2005. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science, 309: 1844–1846.
Yang, Y. X., 2005. Spatial-temporal variation feather of occurrence of tropical cyclone in Western North Pacific. Mar. Forecast., 22(1): 86–91.
Zhou, J. H., Shi, P. J., and Chen, X. W., 2002. Spatio-temporal variability of tropical cyclone activities in the Western North Pacific from 1949–1999. J. Nat. Disasters, 11(3): 44–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, F., Xu, S. Super typhoon activity over the western North Pacific and its relationship with ENSO. J. Ocean Univ. China 9, 123–128 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-010-0123-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-010-0123-8