Abstract
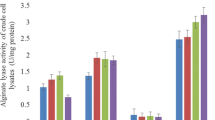
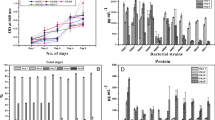
Carbohydrases secreted by marine Vibrio sp. YKW-34 with strong Laminaria cell wall degrading ability were screened, and among them alginate lyase was found to be dominant. The effects of medium composition and culturing condition on the production of alginate lyase by marine Vibrio sp. YKW-34 in flask were investigated in this study. In the culture medium of marine broth, no alginate lyase was produced. The activity of the alginate lyase, after being induced, reached 5 UmL−1. The best inoculum volume and inoculum age were 10% and 12 h, respectively. The optimal temperature for alginate lyase production was 25°C. The fermentation medium was composed of 0.5% of Laminaria powder and 0.2% of KNO3 with an initial acidity of pH 8.0. Alginate could induce alginate lyase production but not as efficiently as Laminaria powder did. The addition of fucoidan, cellulose and glucose had negative effect on the alginate lyase production. Other kinds of nitrogen sources, such as yeast extract, beef extract and peptone, had positive effect on the growth of the microorganism and negative effect on alginate lyase production. In addition, the time course of alginate lyase production under the optimized condition was described. The optimal harvest time was 48 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekseeva, S. A., I. Y. Bakunina, O. I. Nedashkovskaya, V. V. Isakov, V. V. Mikhailov, and T. N. Zvaygintseva, 2004. Intracellular alginolytic enzymes of the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas citrea KMM 3297. Biochemistry (Mosc), 69(3): 262–269.
Alexeeva, Y. V., E. P. Ivanova, I. Y. Bakunina, T. N. Zvaygintseva, and V. V. Mikhailov, 2002. Optimization of glycosidases production by Pseudoalteromonas issachenkonii KMM 3549T. Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 35: 343–346.
El-Katatny, M. H., A. M. Hetta, G. M. Shaban, and H. M. El-Komy, 2003. Improvement of cell wall degrading enzymes production by alginate encapsulated Trichoderma spp. Food Tech. Biotech., 41(3): 219–225.
Horn S. J., and K. Østgaard, 2001. Alginate lyase activity and acidogenesis during fermentation of Laminaria hyperborea. J. Appl. Phycol., 13: 143–152.
Hornbæk, T., A. K. Nielsen, J. Dynesen, and M. Jakobsen, 2004. The effect of inoculum age and solid versus liquid propagation on inoculum quality of an industrial Bacillus licheniformis strain. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 236: 145–151.
Hu, X. K., 2004. Industrialization for alginate lyase from Vibrio sp. 510-64 and their applizations. A Ph. D. dissertation. Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 37–59 (in Chinese).
Ian, W. S., 1995. Polysaccharide lyases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 16: 323–347.
Iwamoto, Y., R. Araki, K. Iriyama, T. Oda, H. Fukuda, S. Hayashida, et al., 2001. Purification and characterization of bifunctional alginate lyase from Alteromonas sp. strain No. 272. Biosci., Biotech., Biochem., 65: 133–142.
Iwamoto, Y., X. Xu, T. Tamura, T. Oda, and T. Muramatsu, 2003. Enzymatically depolymerized alginate oligomers that cause cytotoxic cytokine production in human mononuclear cells. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 67: 258–263.
Kennedy, L., K. McDowell, and I. W. Sutherland, 1992. Alginases from Azotobacter species. Journal of General Microbiology, 138: 2465–2471.
Kloareg, B., M. Demarty, and S. Mabeu, 1986. Polyanionic characteristics of purified sulfated homofucans from brown algae. Int. J. Biol. Macromole., 8: 380–386.
Liu, Y., X. L. Jiang, and H. S. Guan, 2001. Research advances on alginate lyases. J. Fish. Sci. Chin., 7(4): 99–103.
Momma K., M. Okamoto, Y. Mishima, S. Mori, W. Hashimoto, et al., 2000. A novel bacterial ATP-binding cassette transporter system that allows uptake of macromolecules. J. Bacteriol., 182: 3998–4004.
Nelson N., 1944. A photometric adaptation of the somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem., 153: 375–380.
Painter, T. J., 1983. Algal Polysaccharides. In: The Polysaccharides. Aspinall G. O., ed., Academic Press, New York, 196–285.
Schiller, N. L., S. R. Monday, C. Boyd, N. T. Keen, and D. E. Ohman, 1993. Characterization of the Pseudomonas alginate lyase gene (algL): Cloning, sequencing and expression in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol., 175: 780–789.
Scott, C. D., 1987. Immobilized cells: a review of recent literature. Enzyme Microb.Tech., 9: 66–73.
Sugano, Y., H. Nagae, K. Inagaki, T. Yamamoto, I. Terada, and Y. Yamazaki, 1995. Production and characteristics of some new β-agarases from a marine bacterium, Vibrio sp. strain JT0107. J. Ferment. Bioeng., 79(6): 549–554.
Uchida, M., 1995. Enzyme activities of marine bacteria involved in Laminaria-thallus decomposition and the resulting sugar release. Mar. Biol., 123(3): 639–644.
Wang, J. J., and J. C. H. Shih, 1999. Fermentation Production of Keratinase from Bacillus licheniformis PWD-1 and Recombinant B. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotech., 22: 608–616.
Yi, K. W., and I. S. Shin, 2006. Isolation of marine bacterium decomposing sea tangle (Laminaria japonica) to single cell detritus. Korean J. Food Sci. Tech., 38(2): 237–240.
Yonemoto, Y., H. Tanaka, T. Yamashita, N. Kitabatake, Y. Ishida, A. Kimura, et al., 1993. Promotion of germination and shoot elongation of some plants by alginate oligomers prepared with bacterial alginate lyase. J. Ferment. Bioeng., 75: 68–70.
Zhang, Z. Q., G. L. Yu, H. S. Guan, X. Zhao, Y. Q. Du, and X. L. Jiang, 2004. Preparation and structure elucidation of alginate oligosaccharides degraded by alginate lyase from Vibro sp. 510. Carbohyd. Res., 339: 1475–1481.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Lin, H. & Kim, S.M. Optimization of culturing condition and medium composition for the production of alginate lyase by a marine Vibrio sp. YKW-34. J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 97–102 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0097-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0097-y