Abstract
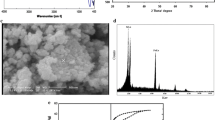
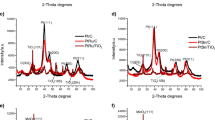
A novel Ultrasonic Assisted Membrane Reduction (UAMR)-hydrothermal method was used to prepare flower-like Pt/CeO2 catalysts. The texture, physical/chemical properties, and reducibility of the flower-like Pt/CeO2 catalysts were characterized by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM), N2 adsorption, and hydrogen temperature programmed reduction (H2-TPR) techniques. The catalytic performance of the catalysts for treating automobile emission was studied relative to samples prepared by the conventional wetness impregnation method. The Pt/CeO2 catalysts fabricated by this novel method showed high specific surface area and metal dispersion, excellent three-way catalytic activity, and good thermal stability. The strong interaction between the Pt nanoparticles and CeO2 improved the thermal stability. The Ce4+ ions were incorporated into the surfactant chains and the Pt nanoparticles were stabilized through an exchange reaction of the surface hydroxyl groups. The SEM results demonstrated that the Pt/CeO2 catalysts had a typical three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical porous structure, which was favorable for surface reaction and enhanced the exposure degree of the Pt nanoparticles. In brief, the flower-like Pt/CeO2 catalysts prepared by UAMR-hydrothermal method exhibited a higher Pt metal dispersion, smaller particle size, better three-way catalytic activity, and improved thermal stability versus conventional materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He H, Dai H X, Ng L H, Wong K W, Au C T. Pd-, Pt-, and Rh-Loaded Ce0.6Zr0.35Y0.05O2 three-way catalysts: an investigate on performance and redox properties. Journal of Catalysis, 2002, 206(1): 1–13
Ikryannikova L N, Aksenov A A, Markaryan G L, Muravéva G P, Kostyuk B G, Kharlanov A N, Lunina E V. The redox treatments influence on the structure and properties of M2O3-CeO2-ZrO2 (M = Y, La) solid solutions. Applied Catalysis A, General, 2001, 210(1–2): 225–235
Heo I, Choung J W, Kim P S, Nam I S, Song Y I, In C B, Yeo G K. The alteration of the performance of field-aged Pd-based TWCs towards CO and C3H6 oxidation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 92(1–2): 114–125
Papavasiliou A, Tsetsekou A, Matsouka V, Konsolakis M, Yentekakis I V. An investigation of the role of Zr and La dopants into Ce1 − x − yZrxLayOδ enriched γ-Al2O3 TWC washcoats. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2010, 382(1, 30): 73–84
Papavasiliou A, Tsetsekou A, Matsouka V, Konsolakis M, Yentekakis I V, Boukos N. Development of a Ce-Zr-La modified Pt/γ-Al2O3 TWCs washcoat: effect of synthesis procedure on catalytic behavior and thermal durability. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 90(1–2): 162–174
Papavasiliou A, Tsetsekou A, Matsouka V, Konsolakis M, Yentekakisb I V, Boukos N. Synergistic structural and surface promotion of monometallic (Pt) TWCs: effectiveness and thermal aging tolerance. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2011, 106(1–2): 228–241
Courtois X, Perrichon V. Distinct roles of copper in bimetallic copper-rhodium three-way catalysts deposited on redox supports. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2005, 57(1–15): 63–72
Joo S H, Park J Y, Tsung C K, Yamada Y, Yang P D, Somorjai G A. Thermally stable Pt/mesoporous silica core-shell nanocatalysts for high-temperature reactions. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(2): 126–131
Lim B, Jiang M J, Camargo P H C, Cho E C, Tao J, Lu X M, Zhu Y M, Xia Y N. Pd-Pt bimetallic nanodendrites with high activity for oxygen reduction. Science, 2009, 324(5932): 1302–1305
Qiao B T, Wang A Q, Yang X F, Allard L F, Jiang Z, Cui Y T, Liu J Y, Li J, Zhang T. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx. Nature Chemistry, 2011, 3(8): 634–641
Liu L C, Guan X, Li Z M, Zi X H, Dai H X, He H. Supported bimetallic AuRh/γ-Al2O3 nanocatalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by propylene. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 90(1–2): 1–9
Liu L C, Wei T, Zi X H, He H, Dai H X. Research on assembly of nano-Pd colloid and fabrication of supported Pd catalysts from the metal colloid. Catalysis Today, 2010, 153(3–4): 162–169
Chen G Z, Xu C X, Song X Y, Xu S L, Ding Y, Sun S X. Template-free synthesis of single crystalline like CeO2 hollow nanocubes. Crystal Growth & Design, 2008, 8(12): 4449–4453
Pan C S, Zhang D S, Shi L Y, Fang J H. Template-free synthesis, controlled conversion, and CO oxidation properties of CeO2 nanorods, nanotubes, nanowires, and nanocubes. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2008, 2008(15): 2429–2436
Yu R B, Yan L, Zheng P, Chen J, Xing X R. Controlled synthesis of CeO2 flower-like and well-aligned nanorod hierarchical architectures by a phosphate-assisted hydrothermal route. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(50): 19896–19900
Han W Q, Wu L J, Zhu Y M. Formation and oxidation state of CeO2 − x nanotubes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(37): 12814–12815
Wang S R, Zhang J, Jiang J Q, Liu R, Zhu B L, Xu M, Wang Y, Cao J, Li M, Yuan Z, Zhang S, Huang W, Wu S. Porous ceria hollow microspheres: synthesis and characterization. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2009, 123(1–3): 349–353
Zhong L S, Hu J S, Cao A M, Song W G, Wan L J. 3D flower like ceria micro/nanocomposite structure and its application for water treatment and CO removal. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(7): 1648–1655
Sun C W, Sun J, Xiao G L, Zhang H R, Qiu X P, Li H, Chen L Q. Mesoscale organization of nearly monodisperse flower like ceria microspheres. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(27): 13445–13452
Li H F, Lu G Z, Dai Q G, Wang Y Q, Guo Y, Guo Y L. Hierarchical organization and catalytic activity of high-surface-area mesoporous ceria microspheres prepared via hydrothermal routes. Appied Materials and Interfaces, 2010, 2(3): 838–846
Zhou H P, Wu H S, Shen J, Yin A X, Sun L D, Yan C H. Thermally stable Pt/CeO2 hetero-nanocomposites with high catalytic activity. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(14): 4998–4999
Rioux R M, Hsu B B, Grass M E, Song H, Somorjai G A. Influence of particle size on reaction selectivity in cyclohexene hydrogenation and dehydrogenation over silica-supported mono-disperse Pt particles. Catalysis Letters, 2008, 126(1–2): 10–19
Wei Y C, Liu J, Zhao Z, Chen Y S, Xu C M, Duan A J, Jiang G Y, He H. Highly active catalysts of gold nanoparticles supported on three-dimensionally ordered macroporous LaFeO3 for soot oxidation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(10): 2326–2329
Wei Y C, Liu J, Zhao Z, Duan A J, Jiang G Y, Xu C M, Gao J S, He H, Wang X P. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Ce0.8Zr0.2O2-supported gold nanoparticles: synthesis with controllable size and super-catalytic performance for soot oxidation. Energy and Environmental Science, 2011, 4(8): 2959–2970
Kang S B, Kwon H J, Nam I S, Song Y I, Oh S H. Activity function for describing alteration of three way catalyst performance over palladium only three way catalysts by catalyst mileage. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(9): 5499–5509
Concepcion P, Corma A, Silvestre A. Chemoselective hydrogenation catalysts: Pt on meso-structured CeO2 nanoparticles embedded within ultrathin layers of SiO2 binder. Journal of American ChemistrySociety, 2004, 126(17): 5523–5532
Ellis A V, Wilson M A. Carbon exchange in hot alkaline degradation of glucose. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2002, 67(24): 8469–8474
Sun C W, Li H, Zhang H R, Wang Z X, Chen L Q. Controlled synthesis of CeO2 nanorods by a solvothermal method. Nanotechnology, 2005, 16(9): 1454–1463
Terribile D, Trovarelli A, Llorca J, Leitenburg C D, Dolcetti G. The synthesis and characterization of mesoporous high-surface area ceria prepared using a hybrid organic/inorganic route. Journal of Catalysis, 1998, 178(1): 299–308
Yang B Y, Montgomery R. Alkaline degradation of glucose: effect of initial concentration of reactants. Carbohydrate Research, 1996, 280(1): 27–45
Hinokuma S, Fujii H, Okamoto M, Ikeue K, Machida M. Metallic Pd nanoparticles formed by Pd-O-Ce interaction: a reason for sintering induced activation for CO oxidation. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(22): 6183–6190
Shinjoh H, Hatanaka M, Nagai Y, Tanabe T, Takahashi N, Yoshida T, Miyake Y. Suppression of noble metal sintering based on the support anchoring effect and its application in automotive three way catalysis. Topics in Catalysis, 2009, 52(13–20): 1967–1971
Nagai Y, Hirabayashi T, Dohmae K, Takagi N, Minami T, Shinjoh H, Matsumoto S. Sintering inhibition mechanism of platinum supported on ceria-based oxideand Pt-oxide-support interaction. Journal of Catalysis, 2006, 242(1): 103–109
Zimmer P, Tschöpe A, Birringer R. Temperature programmed reaction spectroscopy of ceria and Cu/Ceria supported oxide catalyst. Journal of Catalysis, 2002, 205(2): 339–345
Silvestre-Albero J, Rodríguez-Reinoso F, Sepúlveda-Escribano A. Improved metal-support interaction in Pt/CeO2-SiO2 catalysts after zinc addition. Journal of Catalysis, 2002, 210(1): 127–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, Z., Liu, X., Ma, D. et al. Novel synthetic approaches and TWC catalytic performance of flower-like Pt/CeO2 . Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 8, 483–495 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-013-0595-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-013-0595-z