Abstract
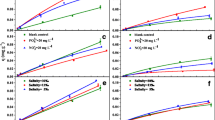
Sulfonamides (SAs) are one class of the most widely used antibiotics around the world. Their fate and transport in the aquatic environment is of great concern. In this study, adsorption of four SAs—sulfadiazine (SD), sulfamethoxazole (SMZ), sulfadimethoxine (SDM) and sulfamethazine (SM2)—in single-solute and multi-solute systems on sediments of Dianchi (DC) Lake and Taihu (TH) Lake, China was investigated with batch experiments. In the single-solute adsorption system, the Langmuir model and the dual-mode model described the adsorption process better than the Freundlich model. Model fitness was better on DC sediment than on TH sediment. The order of adsorption capacity approximately followed a decreasing order of SDM>SD>SM2>SMZ on both sediments, which was likely attributed to the distinctly different water solubility of the four SAs. In the multi-solute system, the order of adsorption capacity was SM2>SDM>SD>SMZ, which was probably related to the compound speciation caused by the pH values of the experimental solution. In the multi-solute system, both competitive and cooperative adsorption played important roles in the adsorption of sulfonamides on sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurwadkar S T, Adams C D, Meyer M T, Kolpin D W. Effects of sorbate speciation on sorption of selected sulfonamides in three loamy soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2007, 55(4): 1370–1376
Zhang L. The current situation in production, marketing and tendency of sulfonamides. China Pharmacy, 2005, 16(8): 571–573 (in Chinese)
McEvoy G K. AHFS Drug Information. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, 2004
Ingerslev F, Halling-Sørensen B. Biodegradability properties of sulfonamides in activated sludge. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2000, 19(10): 2467–2473
Miao X S, Bishay F, Chen M, Metcalfe C D. Occurrence of antimicrobials in the final effluents of wastewater treatment plants in Canada. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(13): 3533–3541
Chang H, Hu J Y, Wang L Z, Shao B. Occurrence of sulfonamide antibiotics in sewage treatment plants. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(4): 514–520
Kolpin D W, Furlong E T, Meyer M T, Thurman E M, Zaugg S D, Barber L B, Buxton H T. Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(6): 1202–1211
Managaki S, Murata A, Takada H, Tuyen B C, Chiem N H. Distribution of macrolides, sulfonamides, and trimethoprim in tropical waters: ubiquitous occurrence of veterinary antibiotics in the Mekong Delta. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(23): 8004–8010
Holm J V, Ruegge K, Bjerg P L, Christensen T H. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical organic compounds in the groundwater downgradient of a landfill (grindsted, denmark). Environmental Science & Technology, 1995, 29(5): 1415–1420
Hirsch R, Ternes T, Haberer K, Kratz K L. Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. The Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 225(1–2): 109–118
Sacher F, Gabriel S, Metzinger M, Stretz A, Wenz M, Lange F T, Brauch H J, Blankenhorn I. Arzneimittelwirkstoffe im grundwasser—ergebnisseines monitoring-programms in Baden-Württemberg (Active pharmaceutical ingredients in groundwater—the results of a monitoring program in Baden-Württemberg [Germany]). Vom Wasser, 2002, 99: 183–196 (in German)
Kim S C, Carlson K. Temporal and spatial trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in aqueous and river sediment matrices. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(1): 50–57
Uno K, Aoki T, Kleechaya W, Ruangpan L, Tanasomwang V. Pharmacokinetics of oxolinic acid in black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon Fabricius, and the effect of cooking on residues. Aquaculture and Research, 2006, 37(8): 826–833
Xu J, Wu L S, Chang A C. Degradation and adsorption of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in agricultural soils. Chemosphere, 2009, 77(10): 1299–1305
Xu J, Chen W P, Wu L S, Green R, Chang A C. Leachability of some emerging contaminants in reclaimed municipal wastewater-irrigated turf grass fields. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2009, 28(9): 1842–1850
Xu J, Chen W, Wu L, Chang A C. Adsorption and degradation of ketoprofen in soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2009, 38(3): 1177–1182
Zhang G, Liu X, Sun K, Zhao Y, Lin C. Sorption of tetracycline to sediments and soils: assessing the roles of pH, the presence of cadmium and properties of sediments and soils. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China, 2010, 4(4): 421–429
Wang B, Huang J, Deng S, Yang X, Yu G. Addressing the environmental risk of persistent organic pollutants in China. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2012, 6(1): 2–16
Wang Z H, Ding S Y, Zhang S X, Shen J Z. Structure-activity relationship of 17 sulfonamides binding to antibody by molecular modeling technique. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(23): 2613–2619 (in Chinese)
Thiele-Bruhn S, Seibicke T, Schulten H R, Leinweber P. Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particlesize fractions. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2004, 33(4): 1331–1342
Gao J, Pedersen J A. Adsorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to clay minerals. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(24): 9509–9516
Lin C E, Chang C C, Lin W C. Migration behavior and separation of sulfonamides in capillary zone electrophoresis III Citrate buffer as a background electrolyte. Journal of Chromatography A, 1997, 768(1): 105–112
Xu X R, Li X Y. Sorption and desorption of antibiotic tetracycline on marine sediments. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(4): 430–436
Jin C X, Chen Q Y, Liu J J, Zhou Q X. Research on the adsorption/desorption characteristics of sulfamonomethoxine on the soil. Environmental Pollution and Control, 2010, 32(5): 47–51 (in Chinese)
Chen H, Zhang J Q, Zhong M, Li S S, Dong Y H. Adsorption of sulfonamides on paddy soil of Taihu Lake region. China Environmental Science, 2008, 28(4): 309–312 (in Chinese)
Kong J J, Pei Z G, Wen B, Shan X Q, Chen Z L. Adsorption of sulfadiazine and sulfathiazole by soils. Environmental Chemistry, 2008, 27(6): 736–741 (in Chinese)
Pignatello J J, Xing B. Mechanisms of slow sorption of organic chemicals to natural particles. Environmental Science & Technology, 1995, 30(1): 1–11
Xing B, Pignatello J J. Time-dependent isotherm shape of organic compounds in soil organic matter: Implications for sorption mechanism. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1996, 15(8): 1282–1288
Gu B, Mehlhorn T L, Liang L, McCarthy J F. Competitive adsorption, displacement, and transport of organic matter on iron oxide: I. Competitive adsorption. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(11): 1943–1950
Xin M H, Li M C, Lan X R, Xie Y, Zhang X S. Competitive absorption of modified chitosan to phenolic pollutants. Environmental Science and Technology, 2007, 30(7): 71–74 (in Chinese)
Zhang W M, Xu Z W, Pan B C, Zhang Q J, Du W, Zhang Q R, Zheng K, Zhang Q X, Chen J L. Adsorption enhancement of laterally interacting phenol/aniline mixtures onto nonpolar adsorbents. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(11): 2044–2049
Zhang W M, Xu Z W, Pan B C, Zhang Q J, Zhang Q R, Du W, Pan B J, Zhang Q X. Cooperative effect of lateral acid-base interaction on 1-naphthol/1-naphthylamine binary adsorption onto nonpolar polymer adsorbents. Separation and Purification Technology, 2007, 55(2): 141–146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Z., Xu, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Adsorption of sulfonamides on lake sediments. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 7, 518–525 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-013-0500-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-013-0500-9