Abstract
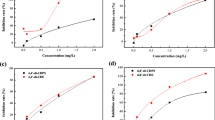
In this article, the toxic effects of Enrofloxacin (ENFX) on Scenedesmus obliquus were studied, through investigating the growth, photosynthetic pigments, and protein contents. The possible toxic mechanisms of ENFX were analyzed by determining the superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, malondialdehyde (MDA) content, proline content, and superoxide anion (O −2 ) generation rate. Results showed that the growth of algae was inhibited by ENFX and the 50% effective concentration (EC50) values for 24, 48, 72, and 96 h of ENFX were 88.39, 63.86, 45.10, and 59.16 mg·L−1, respectively. After treated with ENFX for 96 h, the contents of photosynthetic pigments decreased with the increase of ENFX concentration, the content of soluble protein and the activity of SOD increased and then decreased, and the generation rate of superoxide anion (O −2 ) increased continually. The contents of MDA and proline changed little in lower ENFX concentration groups, but increased rapidly when treated with higher concentration groups. These results suggested that ENFX affected the growth of S. obliquus, and the main toxicity mechanism was that algal cells generated the reactive oxygen species under ENFX stress, and then the reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced the oxidation damages of biologic macromolecules and changed the biomembrane permeability further.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daughton C G, Ternes T A. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environmental Health Perspectives, 1999, 107(Suppl 6): 907–938
Calamari D, Zuccato E, Castiglioni S, Bagnati R, Fanelli R. Strategic survey of therapeutic drugs in the rivers Po and Lambro in northern Italy. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(7): 1241–1248
Wiegel S, Aulinger A, Brockmeyer R, Harms H, Loffler J, Reincke H, Schmidt R, Stachel B, Von Tumpling W, Wanke A. Pharmaceuticals in the river Elbe and its tributaries. Chemosphere, 2004, 57(2): 107–126
Williams R T. Human Pharmaceuticals: Assessing the Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystems. Pensacola: Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) Press, 2005
Fent K, Weston A A, Caminada D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquatic Toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 2006, 76(2): 122–159
Daughton C G, Jones-Lepp T L. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in the Environment: Scientific and Regulatory Issues. American Chemical Society: Washington DC, 2001, 2–38
Halling-Sørensen B, Nors-Nielsen S, Lanzky P F, Ingerslev F, Holten-Lützhoft H C, Jørgensen S E. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment-a review. Chemosphere, 1998, 36(2): 357–393
Jones O A H, Voulvoulis N, Lester J N. Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment a review. Environmental Technology, 2001, 22(12): 1383–1394
Heberer T. Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: a review of recent research data. Toxicology Letters, 2002, 131(1–2): 5–17
Kolpin D K, Furlong E T, Meyer M T, Thurman M E, Zaugg S D, Barber L B, Buxton H T. Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(6): 1202–1211
Halling-Sørensen B. Inhibition of aerobic growth and nitrification of bacteria in sewage sludge by antibacterial agents. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2001, 40(4): 451–460
Kemper N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecological Indicators, 2008, 8(1): 1–13
Costanzo S D, Murby J, Bates J. Ecosystem response to antibiotics entering the aquatic environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2005, 51(1–4): 218–223
Xiong L, Xie P, Sheng X M, Wu Z B, Xie L Q. Toxicity of cypermethrin on growth, pigments, and superoxide dismutase of Scenedesmus obliquus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2005, 60(2): 188–192
Chen J M, Ma J Y, Cao W, Wang P W, Tong S M, Sun Y Z. Sensitivity of green and blue-green algae to methyl tert-butyl ether. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2009, 21(4): 514–519
US Environmental Protection Agency. Algae Assay Procedure Bottle Test, National Eutrophication Research Program. Corvallis, Oregon: US EPA. National Environmental Research Center, 1971, 1–82
Ministry of Agriculture of China. Determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin residues in animal food by high performance liquid chromatography. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug, 2003, 37(8): 11–13 (in Chinese)
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test. Paris: OECD, 2006, 7–9
Li H S. Principle and Technology of Plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2003, 134–137 (in Chinese)
Hao Z B, Cang J, Xu C. Experiment of Plant Physiology. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2004, 67–113 (in Chinese)
Zhang Z A, Chen Z Y. Experiment Technology of Plant Physiology. Changchun: Jilin University Press, 2008, 190–191 (in Chinese)
Wu Y B, Liao X D, Wang Z S, Chen Z L, Wang Y M. The growth inhibition toxicity of enrofloxacin to Haemafococcus pluvialis. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2005, 26(4): 99–101 (in Chinese)
Halling-Sørensen B. Algal toxicity of antibacterial agents used in intensive farming. Chemosphere, 2000, 40(7): 731–739
Wang X, Nie X P, Li K B. Acute toxicity of CPFX and TCCA to aquatic organisms. Ecologic Science, 2006, 25(2): 155–157 (in Chinese)
Nie X P, Lu J Y, Li X, Yang Y F. Toxic effects of norfloxacin on the growth and the activity of antioxidase of chlorella pyrenoidosa. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2007, 2(3): 327–332 (in Chinese)
Lu J Y, Li X, Yang Y T, Nie X P. Toxic effects of nutylated hydroxyanisole and norfloxacin on aquatic organisms. Ecologic Science, 2007, 26(1): 55–58 (in Chinese)
Wei C X, Zhang Y B, Guo J, Han B, Yang X, Yuan J L. Effects of silica nanoparticles on growth and photosynthetic pigment contents of Scenedesmus obliquus. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2010, 22(1): 155–160
Loggini B, Scartazza A, Brugnoli E, Navari-Izzo F. Antioxidant defense system, pigment composition and photosynthetic efficiency in two wheat cultivars subjected to drought. Plant Physiology, 1999, 119(3): 1091–1100
Gao J, Sun M Z, Wang Q Y. Effects of copper ion on the growth of Isochrysis zhanjiangensis. Marine Fisheries Research, 2007, 28(4): 54–58 (in Chinese)
Geoffroy L, Dewez D, Vernet G, Popovic R. Different physiological parameters used in evaluation of oxyfluorfen effect on S.obliquus: validity of parameters as biomarkers. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2003, 45(4): 439–454
Gurbuz F, Ciftci H, Akcil A. Biodegradation of cyanide containing effluents by Scenedesmus obliquus. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(1): 74–79
Alberte R S, Friedman A L, Gustafson D L, Rudnick MS, Lyman H. Light-harvesting systems of brown algae and diatoms. Isolation and characterization of chlorophyll a/c and chlorophyll a/fucoxanthin pigment-protein complexes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1981, 635(2): 304–316
Singh P K, Tewari R K. Cadmium toxicity induced changes in plant water relations and oxidative metabolism of Brassica juncea L. plants. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2003, 24(1): 107–112
Reinheckel T, Noack H, Lorenz S, Wiswedel I, Augustin W. Comparison of protein oxidation and aldehyde formation during oxidative stress in isolated mitochondria. Free Radical Research, 1998, 29(4): 297–305
Li N Y, Gao J F, Wang P H. The characteristics of induced protein in shoots of wheat seedlings under water stress. Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica, 1988, 24(1): 65–71 (in Chinese)
Ma J M, Li J, Zhang G N, Yang K J, Wang L, Wu Z B. Effects of POD and Hg2+ on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2004, 21(5): 531–538 (in Chinese)
Dixit V, Pandey V, Shyam R. Chromium ions inactivate electrontransport and enhance superoxide generation in vivo in pea (Pisum sativum L.cv. Azad) root mitochondria. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2002, 25(5): 687–693
Lurie S, Ronen R, Lipsker Z, Aloni B. Effects of paclobutrazol and chilling temperatures on lipids, antioxidants and ATPase activity of plasma membrane isolated from green bell pepper fruits. Physiologia Plantarum, 1994, 91(4): 593–598
Kishorekumar A, Jaleel C A, Manivannan P, Sankar B, Sridharan R, Murali P V, Panneerselvam R. Comparative effects of different triazole compounds on antioxidant metabolism of Solenostemon rotundifolius. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2008, 62(2): 307–311
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, van Breusegem F. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9 (10): 490–498
Aibibu N, Liu Y G, Zeng GM, Wang X, Chen B B, Song H X, Xu L. Cadmium accumulation in vetiveria zizanioides and its effects on growth, physiological and biochemical characters. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(16): 6297–6303
Sudhakar C, Lakshmi A, Giridarakumar S. Changes in the antioxidant enzymes efficacy in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl salinity. Plant Science, 2001, 161(3): 613–619
Khatun S, Ali M B, Hahn E J, Paek K Y. Copper toxicity in Withania somnifera: growth and antioxidant enzymes responses of in vitro grown plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2008, 64(3): 279–285
Halliwell B, Gutteridge J M C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. 3rd ed. New York: Oxford University Press Inc., 1999, 936
Esterbauer H, Schaur R J, Zollner H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malondaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 1991, 11(1): 81–128
Seljeskog E, Hervig T, Mansoor M A. A novel HPLC method for the measurement of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS). A comparison with a commercially available kit. Clinical Biochemistry, 2006, 39(9): 947–954
Altinordulu S, Eraslan G. Effects of some quinolone antibiotics on malondialdehyde levels and catalase activity in chicks. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2009, 47(11): 2821–2823
Wu Z T, Hou W R. Study on the relation between the influences of KT and ABA and MDA on SOD activity and SOD comformation and hydrophobicity changes. Chinese Biochemical Journal, 1997, 13(6): 716–718 (in Chinese)
Alia, Pardha Saradhi P. Proline accumulation under heavy metal stress. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1991, 138(5): 554–558
Alia, Pardha Saradhi P. Suppression in mitochondrial electron transport is the prime cause behind stress induced proline accumulation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1993, 193(1): 54–58
Alia, Pardha Saradhi P, Mohanty P. Proline in relation to free radical production in seedlings of Brassica juncea raised under sodium chloride stress. Plant and Soil, 1993, 155–156(1): 497–500
Dhir B, Sharmila P, Saradhi P P. Hydrophytes lack potential to exhibit cadmium stress induced enhancement in lipid peroxidation and accumulation of proline. Aquatic Toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 2004, 66(2): 141–147
Lin C C, Kao C H. Proline accumulation is associated with inhibition of rice seedling root growth caused by NaCl. Plant Science, 1996, 114(2): 121–128
Buetler T M, Cottet-Maire F, Krauskopf A, Ruegg U T. Does cyclosporin A generate free radicals? Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 2000, 21(8): 288–290
Hu Q Q, Xiong L, Tianpei X Z, Li W Y. Toxic effects of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) on Scenedesmus obliquus. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2008, 3(1): 87–92 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, H., Chen, L., Lu, N. et al. Toxic effects of enrofloxacin on Scenedesmus obliquus . Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 6, 107–116 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0327-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0327-1