Abstract
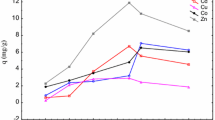
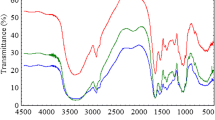
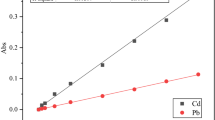
The biosorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+ onto the immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) was investigated in this study. Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and the effect of pH were studied. The results indicated that the biosorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+ on the immobilized S. cerevisiae was fast at initial stage and then became slow. The maximum biosorption of heavy metal ions on immobilized S. cerevisiae were observed at pH 4 for Cd2+ and Cu2+. by the pseudo-second-order model described the sorption kinetic data well according to the high correlation coefficient (R 2) obtained. The biosorption isotherm was fitted well by the Langmuir model, indicating possible mono-layer biosorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+ on the immobilized S. cerevisiae. Moreover, the immobilized S. cerevisiae after the sorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+ could be regenerated and reused.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saygideger S, Gulnaz O, Istifli E S, Yucel N. Adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions by Lemna minor L.: effect of physicochemical environment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2005, 126(1–3): 96–104
Malkoc E, Nuhoglu Y. Investigations of nickel (II) removal from aqueous solutions using tea factory waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2005, 127(1–3): 120–128
Mashitah M D, Azila Y, Bhatia S. Biosorption of cadmium (II) ions by immobilized cells of Pycnoporus sanguineus from aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(11): 4742–4748
Vasudevan P, Padmavathy V, Dhingra S C. Kinetics of biosorption of cadmium on Baker’s yeast. Bioresource Technology, 2003, 89(3): 281–287
Aksu Z, Egretli G, Kutsal T. A comparative study for the biosorption characteristics of chromium(VI) on ca-alginate, agarose and immobilized C. vulgaris in a continous packed bed column. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 1999, A32(2): 295–316
Say R, Denizli A, Arica M Y. Biosorption of cadmium(II), lead (II) and copper(II) with the filamentous fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Bioresource Technology, 2001, 76(1): 67–70
Ghorbani., Younesi H, Ghasempouri S M, Zinatizadeh A A, Amini M, Daneshi A. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of cadmium biosorption in an aqueous solution by S. cerevisiae. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 145: 267–275
Dang V B H, Doan H D, Dang-Vu T, Lohi A. Equilibrium and kinetics of biosorption of cadmium(II) and copper(II) ions by wheat straw. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(1): 211–219
Veglio F, Beolchini F. Removal of metals by biosorption: a review. Hydrometallurgy, 1997, 44(3): 301–316
Volesky B. Biosorption and me. Water Research, 2007, 41(18): 4017–4029
Tunali S, Akar T, Ozcan A S, Kiran I, Ozcan A. Equilibrium and kinetics of biosorption of lead(II) from aqueous solutions by Cephalosporium aphidicola. Separation and Purification Technology, 2006, 47(3): 105–112
Vilar V J P, Botelho C M S, Loureiro J M, Boaventura R A R. Biosorption of copper by marine algae Gelidium and algal composite material in a packed bed column. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(13): 5830–5838
Cochrane E L, Lu S, Gibb SW, Villaescusa I. A comparison of lowcost biosorbents and commercial sorbents for the removal of copper from aqueous media. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 137(1): 198–206
Wang J L, Chen C. Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a review. Biotechnology Advances, 2006, 24(5): 427–451
Göksungur Y, Üren S, Güvenç U. Biosorption of cadmium and lead ions by ethanol treated waste baker’s yeast biomass. Bioresource Technology, 2005, 96(1): 103–109
Wang J L. Biosorption of copper (II) by chemically modified biomass of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Process Biochemistry, 2002, 37(8): 847–850
Vianna L L N, Andrade M C, Jacques R N. Screening ofwaste biomass from saccharomayces cerevisiae, Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus lentus fermentation for removal of Cu, Zn and Cd by biosorption, World Journal of Microbiology Biotechnology. 2000, 16: 437–4
Özer A, Özer D, Ekiz H I. The equilibrium and kinetic modelling of the biosorption of copper(II) ions on Cladophora crispata. Adsorpt-J Int Adsorpt Soc, 2004, 10: 317–326
Bakkaloglu I, Butter T J, Evison L M, Holland F S, Hancock I C. Screening of various types biomass for removal and recovery of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Ni) by biosorption, sedimentation and desorption. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 38(6): 269–277
Matheickal J T, Yu Q. Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by marine algae Ecklonia radiata. Water Science and Technology, 1996, 34(9): 1–7
Chang J S, Huang J C, Chang C C, Tarn T J. Removal and recovery of lead fixed-bed biosorption with immobilized bacterial biomass. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 38(4–5): 171–178
Kratochvil D, Volesky B, Demopoulos G. Optimizing Cu removal/ recovery in a biosorption column. Water Research, 1997, 31(9): 2327–2339
Arica M Y, Kaçar Y, Genç O. Entrapment of white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor in Ca-alginate beads: preparation and biosorption kinetic analysis for cadmium removal from an aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 2001, 80(2): 121–129
Bayramoglu G, Bektas S, Arica M Y. Biosorption of heavy metals on immobilized white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Journal of Hazardous Matererals. 2003, 101: 285–300.
Volesky B, Weber J, Park JM. Continuous-flow metal biosorption in a regenerable Sargassum column. Water Resarch, 2003, 37: 297–306
Cussler E L. Diffusion-Mass Transfer in Fluid Systems (trans.Wang X Y, Jiang Z Y). 2th ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002, 199 (in Chinese)
Ho Y S, McKay G. The sorption of lead(II) ions on peat response to comment. Water Resarch, 1999, 33: 578–584
McKay G, Ho Y S. Pseudo-second-order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemstry, 1999, 34: 451–465
Aksu Z. Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of nickel (II) ions onto Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochemistry, 2002, 38(1): 89–99
Cruz C, Costa A, Henriques C, Luna A. Kinetic modeling and equilibrium studies during cadmium biosorption by dead Sargassum sp. Biomass. Bioresource Technology, 2004, 91: 249–257
Sag Y, Kutsal T. The selective biosorption of chromium(VI) and copper(II) ions from binary metal mixtures by R. arrhizus. Process Biochemstry, 1996, 31: 561–572
Módenes A N, de Abreu Pietrobelli J M T, Espinoza-Quiñones F R. Cadmium biosorption by non-living aquatic macrophytes Egeria densa. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 60(2): 293–300
de Abreu Pietrobelli J M T, Módenes A N, Espinoza-Quiñones F R, Fagundes-Klen M R, Kroumov A. Removal of copper ions by nonliving aquatic macrophytes egeria densa. International Journal Bioautomation, 2009, 12(1): 21–32
Saeed A, Iqbal M. Bioremoval of cadmium from aqueous solution by black gram husk (Cicer arientinum). Water Research, 2003, 37(14): 3472–3480
Kratochvil D, Volesky B. Biosorption of Cu from ferruginous wastewater by algal biomass. Water Resarch, 1998, 32(9): 2760–2768
Chu K H, Hashim M A, Phang S M, Samuel V B. Biosorption of cadmium by algal biomass: adsorption and desorption characteristics. Water Science and Technology, 1997, 35(7): 115–122
Pradhan S, Rai L C. Copper removal by immobilized M. aeruginosa in continuous flow columns at different bed heights: study of the adsorption/desorption cycle. World Journal of Microbiology Biotechnology, 2001, 17: 829–832
Lázaro N, Sevilla A L, Morales S, Marqúes A M. Heavy metal biosorption by gellan gum gel beads. Water Resarch, 2003, 37: 2118–2126
Davis T A, Volesky B, Mucci A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Resarch, 2003, 37: 4311–4330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zan, F., Huo, S., Xi, B. et al. Biosorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+ on immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 6, 51–58 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0206-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0206-9