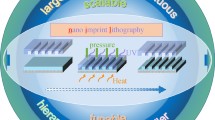
Abstract
Photonic nanojets (PNJs) have a wide range of applications in laser processing, nanolithography, optical high-density storage, super-resolution microscopy, and other fields due to their processing capacity to overcome the diffraction limit. Herein, we control static microsphere be developed into the motion state to fabricate vector graphics nano-grooves. The microspheres roll on the substrate while the laser is kept synchronously irradiated, and the overlapping PNJ ablated craters form patterned grooves on the indium-tin oxide (ITO) substrate. Thus, PNJ has been expanded from “point” processing to “line” processing. The fabricated nano grooves have high continuity and consistency. Whereas, the precise customization of critical groove dimension can be achieved via modulation in diameter and kinetics of dielectric microshperes. Furthermore, by etching vectographs on an ITO conductive glass substrate, we demonstrated the advantages and potential of the proposed method in nanopatterning. The proposed method effectively reduces the cost and complexity of photonic nanojets applied in nanopatterning. The proposed nanopatterning methodology will play a vital role in the fabrication of semiconductor materials, sensors, microfluidic devices, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), biomedicine, nanoscience and nanoengineering.
摘要
光子纳米射流由于其具有克服衍射极限的处理能力,在激光加工、纳米光刻、光学高密度存 储、超分辨率显微等领域有着广泛的应用。本文通过将静态微球转变为运动状态,在激光同步辐照 下,重叠烧蚀的坑在ITO基板上形成图形化的纳米凹槽。由此,光子纳米射流从“点”加工扩展到 “线”加工。所制备的纳米沟槽具有良好的连续性和一致性。此外,沟槽的尺寸形貌可以通过调控微 球直径和刻蚀速度来实现。最后,通过在ITO玻璃衬底上刻蚀矢量图,证明了该方法在微纳制造方面 的优势和潜力。此方法将在半导体材料、传感器、微流控器件、表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)、生物医 学、纳米科学和纳米工程等领域发挥重要作用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
XU Hai-yuan, ZHONG Si-hua, ZHUANG Yu-feng, et al. Controllable nanoscale inverted Pyramids for highly efficient quasi-omnidirectional crystalline silicon solar cells [J]. Nanotechnology, 2018, 29: 015403. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa9a96.
KUANG Ping, EYDERMAN S, HSIEH M L, et al. Achieving an accurate surface profile of a photonic crystal for near-unity solar absorption in a super thin-film architecture [J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(6): 6116–6124. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b01875.
WANG Yan, LIU Yao-ping, YANG Li-xia, et al. Micro-structured inverted pyramid texturization of Si inspired by self-assembled Cu nanoparticles [J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(2): 907–914. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr08126f.
WILBERS J G E, BERENSCHOT J W, TIGGELAAR R M, et al. 3D-fabrication of tunable and high-density arrays of crystalline silicon nanostructures [J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2018, 28: 044003.
YANG Jing, LI Jia-bao, DU Zhe-ren, et al. Laser hybrid micro/nano-structuring of Si surfaces in air and its applications for SERS detection [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6657. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06657.
NEUBRECH F, HUCK C, WEBER K, et al. Surface-enhanced infrared spectroscopy using resonant nanoantennas [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(7): 5110–5145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00743.
YOKOGAWA S, BURGOS S P, ATWATER H A. Plasmonic color filters for CMOS image sensor applications [J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(8): 4349–4354. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/nl302110z.
PENG Kui-qing, WANG Xin, LI Li, et al. High-performance silicon nanohole solar cells [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(20): 6872–6873. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja910082y.
NAM S, CHOI I, FU Chi-cheng, et al. Graphene nanopore with a self-integrated optical antenna [J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(10): 5584–5589. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/nl503159d.
KIM C S, AHN S H, JANG D Y. Review: Developments in micro/nanoscale fabrication by focused ion beams [J]. Vacuum, 2012, 86(8): 1014–1035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2011.11.004.
KUSSEROW T, WULF M, ZAMORA R, et al. Processing of photonic crystals in InP membranes by focused ion beam milling and plasma etching [J]. Microelectronic Engineering, 2013, 102: 25–28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2012.02.019.
STANFORD M G, LEWIS B B, IBERI V, et al. In situ mitigation of subsurface and peripheral focused ion beam damage via simultaneous pulsed laser heating [J]. Small, 2016, 12(13): 1779–1787. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201503680.
KRÁTKÝ S, URBÁNEK M, KOLAŘÍK V. PEC reliability in 3D E-beam DOE nanopatterning [J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2015, 21(S4): 230–235. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/s1431927615013422.
PEREZ-ROLDAN M J, MULDERS J L, TROMPENAARS P F. Oxygen-assisted purification of platinum structures deposited by ion and electron beam induced processes [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2017, 50(20): 205307. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa69e2.
WINKLER R, SCHMIDT F P, HASELMANN U, et al. Direct-write 3D nanoprinting of plasmonic structures [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(9): 8233–8240. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b13062.
MAKOTO O. Nanoimprint Graphoepitaxy for molecularly oriented nanofabrication [J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science & Technology, 2017, 30: 519–525.
TAKEI S, HANABATA M. Sub-70 nm resolution patterning of high etch-resistant epoxy novolac resins using gas permeable templates in ultraviolet nanoimprint lithography [J]. Applied Physics Express, 2016, 9: 056501.
PAUN I A, POPESCU R C, MUSTACIOSU C C, et al. Laser-direct writing by two-photon polymerization of 3D honeycomb-like structures for bone regeneration [J]. Biofabrication, 2018, 10(2): 025009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/aaa718.
HIGGINS D A, EVERETT T A, XIE Ai-fang, et al. Highresolution direct-write multiphoton photolithography in poly (methylmethacrylate) films [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(18): 184101. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2200476.
KHAN A, WANG Zeng-bo, SHEIKH M A, et al. Laser micro/nano patterning of hydrophobic surface by contact particle lens array [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 258(2): 774–779. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.08.089.
PAN Heng, HWANG D J, KO S H, et al. High-throughput near-field optical nanoprocessing of solution-deposited nanoparticles [J]. Small, 2010, 6(16): 1812–1821. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201000345.
KHAN A, WANG Zeng-bo, SHEIKH M A, et al. Parallel near-field optical micro/nanopatterning on curved surfaces by transported micro-particle lens arrays [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, 43(30): 305302. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/43/30/305302.
BRODOCEANU D, ALHMOUD H Z, ELNATHAN R, et al. Fabrication of silicon nanowire arrays by near-field laser ablation and metal-assisted chemical etching [J]. Nanotechnology, 2016, 27(7): 075301. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/7/075301.
WALLER E H, KARST J, von FREYMANN G. Photosensitive material enabling direct fabrication of filigree 3D silver microstructures via laser-induced photoreduction [J]. Light: Advanced Manufacturing, 2021, 2(2): 228–233.
SERRA P, PIQUÉ A. Laser-induced forward transfer: Fundamentals and applications [J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(1): 1800099.
GUO W, WANG Z B, LI L, et al. Near-field laser parallel nanofabrication of arbitrary-shaped patterns [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(24): 243101. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2748035.
MICHELETTO R, FUKUDA H, OHTSU M. A simple method for the production of a two-dimensional, ordered array of small latex particles [J]. Langmuir, 1995, 11: 3333–3336. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/LA00009A012.
WU Yan, JI Ling-fei, LIN Zhen-yuan, et al. Substrate effect of laser surface sub-micro patterning by means of self-assembly SiO2 microsphere array [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 357: 832–837. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.066.
PENA A, WANG Zeng-bo, WHITEHEAD D, et al. Direct writing of micro/nano-scale patterns by means of particle lens arrays scanned by a focused diode pumped Nd: YVO4 laser [J]. Applied Physics A, 2010, 101(2): 287–295. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-5819-5.
SEDAO X, DERRIEN J Y, ROMER G, et al. Laser surface micro-/nano-structuring by a simple transportable micro-sphere lens array [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 112: 103111.
DEEPAK KALLEPALLI L N, GROJO D, CHARMASSON L, et al. Long range nanostructuring of silicon surfaces by photonic nanojets from microsphere Langmuir films [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2013, 46(14): 145102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/46/14/145102.
KO Y H, MAGNUSSON R. Wideband dielectric metamaterial reflectors: Mie scattering or leaky Bloch mode resonance? [J]. Optica, 2018, 5(3): 289. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/optica.5.000289.
Funding
Projects(LZ20E050003, LD22E050001) supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Contributors
CAO Yu and HOU Zhi-shan provided the concept. ZHOU Zhuang-zhuang carried out the experiment and wrote the draft of the manuscript. XUE Wei and ALI Hassan analyzed the experimental data. CAO Yu reviewed the manuscript. ZHOU Zhuang-zhuang and CAO Yu replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
ZHOU Zhuang-zhuang, ALI Hassan, HOU Zhi-shan, XUE Wei, and CAO Yu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Zz., Ali, H., Hou, Zs. et al. Enhanced photonic nanojets for submicron patterning. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 3323–3334 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5116-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5116-4