Abstract
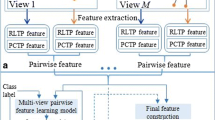
This paper proposed a novel multi-view interactive behavior recognition method based on local self-similarity descriptors and graph shared multi-task learning. First, we proposed the composite interactive feature representation which encodes both the spatial distribution of local motion of interest points and their contexts. Furthermore, local self-similarity descriptor represented by temporal-pyramid bag of words (BOW) was applied to decreasing the influence of observation angle change on recognition and retaining the temporal information. For the purpose of exploring latent correlation between different interactive behaviors from different views and retaining specific information of each behaviors, graph shared multi-task learning was used to learn the corresponding interactive behavior recognition model. Experiment results showed the effectiveness of the proposed method in comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on the public databases CASIA, i3Dpose dataset and self-built database for interactive behavior recognition.
摘要
本文提出了一种基于局部自相似描述符和图共享多任务学习的多视角交互行为识别方法. 首先, 提出了一种复合交互特征表示方法, 该方法对兴趣点局部运动的空间分布及其上下文进行编码. 其次, 为了减小观测角度变化对识别的影响并保留时序信息, 用时间金字塔词袋模型对局部自相似描述符进行表示. 为了从不同的视角探索不同交互行为之间的潜在关联, 并保留每种交互行为的特定信息, 采用图共享多任务学习学习相应的交互行为识别模型. 结果表明, 该方法在 CASIA、i3Dpose 公共数据集和自建交互行为识别数据库上相比其他方法识别率更高.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FERNANDO I, RICARDO P. Human actions recognition in video scenes from multiple camera viewpoints [J]. Cognitive Systems Research, 2019, 56: 223–232. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2019.03.010.
LIN Bo, FANG Bin, YANG Wei-bin. Human action recognition based on spatio-temporal three-dimensional scattering transform descriptor and an improved VLAD feature encoding algorithm [J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 348: 145–157. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.121.
HAN Fei, REILY B, HOFF W, ZHANG Hao. Space-time representation of people based on 3D skeletal data: A review [J]. Computer Vision & Image Understanding, 2017, 158(3): 85–105. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2017.01.011.
LIU J, WANG G. Skeleton based human action recognition with global context-aware attention LSTM networks [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(4): 1586–1599.
AMIRA B M, EZZEDDINE Z. Abnormal behavior recognition for intelligent video surveillance systems: A review [J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 91: 480–491. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.09.029.
LUVIZON D C, TABIA H, PICARD D. Learning features combination for human action recognition from skeleton sequences [J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2017, 99: 13–20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2017.02.001.
HUANG Z W, WAN C D. Deep learning on lie groups for skeleton-based action recognition [C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017: 1243–1252.
SHAHROUDY A, LIU J. NTU RGB+D: A large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis [C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA: IEEE, 2016: 1010–1019.
SHEN Y P, FOROOSH H. View-invariant action recognition from point triplets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(10): 1898–1905.
LI Jin-xing, ZHANG Bob, ZHANG David. Generative multi-view and multi-feature learning for classification [J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 45: 215–226. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2018.02.005.
LI R, TIAN T, SCLAROFF S. Simultaneous learning of nonlinear manifold and dynamical models for high-dimensional time series [C]// 11th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Rio de Janeiro, BRAZIL: IEEE, 2007:1687–1694.
ZHENG J J, JIANG Z L, PHILLIPS J. Cross-view action recognition via a transferable dictionary pair [C]// 23rd British Machine Vision Conference. Guildford, England: Springer-Verlag, 2012: 1–10.
LIU J G, SHAH M, KUIPERS B. Cross-view action recognition via view knowledge transfer [C]// 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. NJ, USA: IEEE, 2011: 3209–3216.
JUNEJO I N, DEXTER E, LAPTEV I. Cross-view action recognition from temporal self-similarities [C]// The European Conference on Computer Vision. Marseille, France: Springer, 2008: 293–306.
GAO Zan, ZHANG Hua, XU Guang-ping. Multi-view discriminative and structured dictionary learning with group sparsity for human action recognition [J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 112: 83–97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.08.034.
HSU Yen-pin, LIU Cheng-yin, CHEN Tzu-yang. Online view-invariant human action recognition using rgb-d spatio-temporal matrix [J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 60: 215–226. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.010.
HAO Tong, WU Dan, WANG Qian, SU Jin-sheng. Multi-view representation learning for multi-view action recognition [J]. J Vis Commun Image R, 2017, 48: 453–460. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2017.01.019.
YU T H, KIM T K, CIPOLLA R. Real-time action recognition by spatiotemporal semantic and structural forests [C]// Proceedings of the 21st British Mac hine Vision Conference. United Kingdom: Springer-Verlag, 2010: 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5244/C.24.52.
YUAN F, SAHBI H, PRINET V. Spatio-temporal context kernel for activity recognition [C]// Proceedings of the 1st Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2011: 436–440.
BURGHOUTS G J, SCHUTTE K. Spatio- temporal layout of human actions for improved bag-of-words action detection [J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2013, 34(15): 1861–1869. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2013.01.024.
LI N J, CHENG X, GUO H Y, WU Z Y. A hybrid method for human interaction recognition using spatio-temporal interest points [C]// The 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Stockholm, Sweden: IEEE, 2014: 2513–2518.
KONG Yu, JIA Yun-de, FU Yun. Interactive phrases: semantic descriptions for human interaction recognition [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(9): 1775–1788. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2303090.
SLIMANI K, BENEZETH Y, SOUAMI F. Human interaction recognition based on the co-occurrence of visual words [C]// Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Columbus, Ohio, USA: IEEE, 2014: 461–469. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2014.74.
CHO N G, PARK S H, PARK J S. Compositional interaction descriptor for human interaction recognition [J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 267: 169–181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.06.009.
HARRIS C, STEPHENS M J. A combined corner and edge detector [C]// Proceedings of Fourth Alvey Vision Conference. Manchester, England: IEEE, 1988: 147–151. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5244/C.2.23.
JUNEJO I, DEXTER E, LAPTEV I. Cross-view action recognition from temporal self-similarities [C]// European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2008: 293–306. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88688-4_22.
LAPTEV I, MARSZALEK M, SCHMID C. Learning realistic human actions from movies [C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, AK: 2008: 1–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587756.
HU YQ, AJMAL S, ROBYN O. Sparse approximated nearest points for image set classification [C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Colorado Springs, CO: IEEE, 2011: 121–128.
WRIGHT J, YANG A, GANESH A. Robust face recognition via sparse representation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(2): 210–227.
HUANG Zhi-wu, WANG Rui-ping, SHAN Shi-guang. Face recognition on large-scale video in the wild with hybrid Euclidean-and-Riemannian metric learning [J]. Mixture Research Article Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(10): 3113–3124. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2015.03.011.
ZHANG Z, HUANG K Q, TAN T N. Multi-thread parsing for recognizing complex events in videos [C]// European Conference on Computer Vision. Marseille, France: Springer, 2008: 738–751.
NIKOLAOS G, HANSUNG K, ADRIAN H. The i3DPost multi-view and 3D human action/interaction database [C]// 2009 Conference for Visual Media Production. London, England: IEEE, 2009:159–168.
SAEID M, FARZAD S, RANYA A. Online human interaction detection and recognition with multiple cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(3): 649–663.
CAVENT A, IKIZLER N. Histograms of sequences: A novel representation for human interaction recognition [J]. IET Computer Vision, 2018, 12(6): 844–854.
JI Yan-li, CHENG Hong, ZHENG Ya-li, LI Hao-xin. Learning contrastive feature distribution model for interaction recognition [J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 33: 340–349. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2015.10.001.
LIU B L, CAI H B, JI X F, LIU H H. Human-human interaction recognition based on spatial and motion trend feature [C]// IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2017: 4547–4551.
WU Fei, JING Xiao-yuan, YUE Dong. Multi-view discriminant dictionary learning via learning view-specific and shared structured dictionaries for image classification [J]. Neural Process Lett, 2017, 45(2): 649–666. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-016-9545-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(51678075) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017GK2271) supported by Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Lm., Guo, Wt. & Wang, H. Interaction behavior recognition from multiple views. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 101–113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4281-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4281-6
Key words
- local self-similarity descriptors
- graph shared multi-task learning
- composite interactive feature
- temporal-pyramid bag of words