Abstract
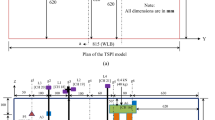
In order to investigate the seismic performance of geosynthetic reinforced and pile supported (GRPS) embankment under seismic loads, an input method for three-dimensional oblique incidence of P wave was proposed. This method is based on the explicit finite element method while considering the viscous-spring artificial boundary (VSAB) condition. Using the proposed method, a numerical study was conducted, and the influence of oblique incidence on the seismic response of GRPS embankment under the oblique incident P waves was analyzed. The results indicate that in comparison with vertical incidence, the oblique incidence can significantly increase the displacement, velocity and acceleration of key locations in the GRPS embankment. The existence of geosynthetics can alleviate the impact of seismic load on the response of the embankment to a certain degree. Moreover, the number of reinforcement layers and modulus of geogrid also greatly influence the seismic performance of GRPS embankment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RUSSELL D, PIERPOINT N. An assessment of design methods for piled embankments [J]. Ground Engineering, 1997, 24(2): 39–44.
ARIYARATHEN P, LIYANANPATHIRANA D S, LEO C. Comparison of different two dimensional idealizations for a geosynthetic-reinforced pile-supported embankment [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 13(6): 754–768.
LIU Hong-kai, XIA Tang-dai. Pile-soil stress analysis of geogridreinforced pile-supported embankment with piles arranged in triangle [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(11): 3957–3963. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Jun, ZHENG Jun-jie, MA Qiang. Performance of fixed geosynthetic technique of GRPS embankment [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(8): 2245–2254.
BRIANCON L, SIMON B. Performance of pile-supported embankment over soft soil: Full-scale experiment [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2012, 138(4): 551–561.
SHUKLA S K, KUMAR R. Overall slope stability of prestressed geosynthetic reinforced embankments on soft ground [J]. Geosynthetics International, 2008, 15(2): 165–171.
WACHMAN G S, BIOLZIL, LABUZ J F. Structural behavior of a pile-supported embankment [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2010, 136(1): 26–34.
EllS E A, ASLAM R. Arching in piled embankments: Comparison of centrifuge tests and predictive methods-Part 1 of 2 [J]. Ground Engineering, 2009, 42: 34–38.
LOW B K, TANG S K, CHOA V. Arching in piled embankments [J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1993, 120(11): 1917–1938.
KOSEKI, J. Use of geosynthetic to improve seismic performance of earth structures [J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2012, 34: 51–68.
TAHA A, HESHAM E, NAGGAR M, TURAN A. Experimental study on the seismic behaviour of geosynthetic-reinforced pilefoundation system [J]. Geosynthetics International, 2015, 22(2): 183–195.
QUANG T S, GHAZI H, PATRICK D B. Seismic stability analysis of piled embankments: A multiphase approach [J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2010, 34: 91–110.
WANG Jian, YAO Ling-kan, CHEN Qiang. Research on failure mode of road embankment Wenchuan great earthquake and deformation control of geogrid reinforcement [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(S1): 3387–3394. (in Chinese)
KUWANO J, MIYATA Y, KOSEKI J. Performance of reinforced soil walls during the 2011 Tohoku earthquake [J]. Geosynthetic International, 2014, 21(3): 1–18.
KOSEKI J, SHIBUYA S. Mitigation of disasters by earthquakes, tsunamis, and rains by means of geosynthetic-reinforced soil retaining walls and embankments [J]. Transportation Infrastructure Geotechnology, 2014, 1(3/4): 231–261.
LIU Jing-bo, LU Yan-dong. A direct method for analysis of dynamic soil-structure interaction [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1998, 31(3): 55–64. (in Chinese)
GAO Xin-jun. Seismic response analysis of longspan bridge considering earthquake and vertical trainloads [D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011. (in Chinese)
XU Qiang, CHEN Jian-yun, LI Jing. Influence of seismic input on response of Baihetan arch dam [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(6): 2437–2443.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(41202220, 41472278, 51478438) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects(20120022120003, 20134101120009) supported by the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China; Project(2652012065) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China; Project(14A560014) supported by the Key Project of Education Department in Henan Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Xj., Qian, H., Guo, Yc. et al. Seismic response analysis of GRPS embankment under oblique incident P wave. J. Cent. South Univ. 23, 721–728 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3117-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3117-x