Abstract
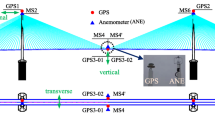
Structure damage identification and alarming of long-span bridge were conducted with three-dimensional dynamic displacement data collected by GPS subsystem of health monitoring system on Runyang Suspension Bridge. First, the effects of temperature on the main girder spatial position coordinates were analyzed from the transverse, longitudinal and vertical directions of bridge, and the correlation regression models were built between temperature and the position coordinates of main girder in the longitudinal and vertical directions; then the alarming indices of coordinate residuals were conducted, and the mean-value control chart was applied to making statistical pattern identification for abnormal changes of girder dynamic coordinates; and finally, the structural damage alarming method of main girder was established. Analysis results show that temperature has remarkable correlation with position coordinates in the longitudinal and vertical directions of bridge, and has weak correlation with the transverse coordinates. The 3% abnormal change of the longitudinal coordinates and 5% abnormal change of the vertical ones caused by structural damage are respectively identified by the mean-value control chart method based on GPS dynamic monitoring data and hence the structural abnormalities state identification and damage alarming for main girder of long-span suspension bridge can be realized in multiple directions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KO J M, NI Y Q. Technology developments in structural health monitoring of large-scale bridges [J]. Engineering Structures, 2005, 27(12): 1715–1725.
LI Ai-qun, DING You-liang, WANG Hao, GUO Tong. Analysis and assessment of bridge health monitoring mass data-Progress in research/development of “Structural Health Monitoring” [J]. Technological Sciences, 2012, 55(8): 2212–2224.
SONG Zi-shou, LI Hu-sheng. Research on wavelet de-noising for bridge alarming [C]// 2010 International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation. Changsha, 2010: 235–239.
NI Y Q, HUA X G, FAN K Q, KO J M. Correlating modal properties with temperature using long-term monitoring data and support vector machine technique [J]. Engineering Structures, 2005, 27(12): 1762–1773.
DING You-liang, LI Ai-qun, LIU Tao. Environmental variability study on the measured responses of Runyang Cable-stayed Bridge using wavelet packet analysis [J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2008, 51(5): 517–528.
PATJAWIT W. KANOK-NUKULCHAI W. Health monitoring of highway bridges based on a global flexibility index [J]. Engineering Structures, 2005, 27(9): 1385–1391.
CHEN Zhi-wei, CAI Qin-lin, LEI Ying, ZHU Song-ye. Damage detection of long-span bridges using stress influence lines incorporated control charts [J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2014, 57(9): 1689–1697.
NI Y Q, HUA X G, WONG K Y, KO J M. Assessment of bridge expansion joints using long-term displacement and temperature measurement [J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2007, 21(2): 143–151.
MIAO Chang-qing, DENG Yang, DING You-liang, LI Ai-qun. Damage alarming for bridge expansion joints using novelty detection technique based on long-term monitoring data [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(1): 226–235.
DENG Yang, LI Ai-qun, DING You-liang, SUN Peng. Damage identification of expansion joints in long span bridge using long-term monitoring data [J]. Journal of Southeast University: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 41(2): 336–341. (in Chinese)
MIAO Chang-qing, LI Ai-qun, HAN Xiao-lin, LI Zhao-xia, JI Lin, YANG Yu-dong. Monitor strategy for the structural health monitoring system of Runyang bridge [J]. Journal of Southeast University: Natural Science Edition, 2005, 35(5): 780–785. (in Chinese).
SOHN S, CZARNECKI J A, FARRAR C R. Structural health monitoring using statistical process control [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2000, 126(11): 1356–1363.
FUGATE M L, SOHN H, FARRAR C R. Vibration-based damage detection using statistical process control [J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2001, 15(4): 707–721.
YI Ting-hua, GUO Qing, LI Hong-nan. The research on detection methods of GPS abnormal monitoring data based on control chart [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(8): 133–141. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Q W, FAN L C, YUAN W C. Traffic-induced variability in dynamic properties of cable-stayed bridge [J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 2002, 31(11): 2015–2021.
DENG Yang, DING You-liang, LI Ai-qun. Structural condition assessment of long-span suspension bridges using long-term monitoring data [J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2010, 9(1): 123–131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(51078080) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(20130969010 ) supported by Aeronautical Science Foundation of China; Project(2011Y03-6) supported by Traffic Transportation Technology Project of Jiangsu Province, China; Project(BK2012562) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Cq., Wang, M., Tian, Hj. et al. Damage alarming of long-span suspension bridge based on GPS-RTK monitoring. J. Cent. South Univ. 22, 2800–2808 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2811-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2811-4