Abstract
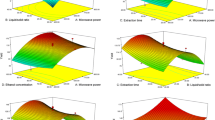
To study the stereostructure by X-ray and the technology of extracting acankoreanogenin from the leaves of Acanthopanax gracilistylus W. W. Smith (AGS), the crystal structure was measured with a Bruker APEX-II area-detector diffractometer instrument and the technology of extracting in combination hydrolysis in situ (ECHS) was compared with these of traditional methods. The crystal belongs to the monoclinic system, space group P21, with unit cell parameters: a=(8.3652±0.0006) nm, b=(24.721±0.002) nm, and c=(14.5587±0.0011) nm, α=90 °, β=97.850 (4) °, γ=90 °, V=2982.51 nm3, D c = 1.179 mg/m3, and the molecular number (Z) of elementary structures was 2. The comparisons show that the extraction rate of acankoreanogenin with ECHS methods is much higher than that of traditional methods. Then, central composite design-response surface methodology (CCD-RSM) was adopted for optimizing the extraction rate of ECHS methods. The optimized values of extraction parameters are as follows: for the for extraction process of acid hydrolysis are that extraction time 110.8 min, solvent-herb ratio 11.5 and acid content 5.25%; the best extraction process of basic hydrolysis are that extract time 120 min, solvent-herb ratio 8.7 and the alkali content 8.79%. Finally, the extracts were purified with decolorizing carbon after alkali solution and acid-isolation and purity of acankoreanogenin was 98.7%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chinese Pharmacopoeia committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China [M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2010: 61. (in Chinese)
LIU Xiang-qian. Studies on the active constituents of Acanthopanax gracilistylus W.W. Smith [D]. Korea: Kyung Hee University, 2003: 9–11.
FAN Xue-gong, LIU Hong-bo, LIU Xiang-qian. The use of acankoreoside A and acankoreanogenin with anti-inflammation activity: China, ZL200710198460.x [P]. 2010, 02. (in Chinese)
ZOU Qin-peng. Studies on anti-HMGB1 activities of triterpenoids from leaves of two Acanthopanax Miq. Plants [D]. Changsha: Central South University College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering. 2012: 34–38. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Bao-xin, LI Ning, ZHANG Zu-ping, LIU Hong-bo, ZHOU Rong-rong, ZHONG Bai-yun, ZOU Ming-xiang, DAI Xia-hong, XIAO Mei-fang, LIU Xiang-qian, FAN Xue-gong. Protective effect of Acanthopanax gracilistylus-extracted acankoreanogenin A on mice with fulminant hepatitis [J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2011, 10(8): 1018–1023
NHIEM Nguyen-xuan, KIEM Phan-van, MINH Chau-van, TAI Bui-huu, QUANG Tran-hong, SOUNG Kwang-su, KOO Jung-euu, KOH Young-sang, KIM Young-ho. Anti-inflammatory activity on LPS-stimulated dendritic cells of lupine-type triterpenoids from the leaves of Acanthopanax koreanum [J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2011, 34(10): 1593–1598.
ZOU Qin-peng, LIU Xiang-qian, LEE Hyeong-kyu. Lupane-triterpenoids from the methanol extracts of leaves of Acanthopanax gracilistylus W.W.Smith [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 47(6): 120–127. (in Chinese)
WANG Jun, CHEN Jun, YANG Ke-di. Study on the pretreatment of diosgenin in Dioscorea nipponica [J]. Chinese Pharmacy Journal, 2005, 40(9): 660–663. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Qing-an, ZHANG Zhi-qi, YUE Xuan-feng, FAN Xue-Hui, LI Tao, CHEN Shou-fen. Response surface optimization of ultrasound assisted oil extraction from autoclaved almond powder [J]. Food Chemistry, 2009, 116(2): 513–518.
MIR Ali farajzadeh, MORTEZA Bahram, MOHAMMAD Reza vardast, MEHDI Bamorowat. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the analysis of three organophosphorus pesticides in real samples by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection and its optimization by experimental design [J]. Microchim Acta, 2011, 172: 465–470.
NHIEM Nguyen-xuan, KIEM Phan-van, MINH Chau-van, TAI Bui-huu, QUANG Tran-hong, SOUNG Kwang-su, KOO Jung-euu, KOH Young-sang, KIM Young-ho. Anti-inflammatory activity on LPS-stimulated dendritic cells of lupine-type triterpenoids from the leaves of acanthopanax koreanum [J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2011, 34(10): 1593–1598.
BAO Ying-ling, Yan Zong-cheng, Wang Hong-lin. Optimization of bioethanol production during simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in very high-gravity cassava mash [J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2011, 99: 329–339.
ZHONG Xian-feng, HUANG Gui-dong, CHEN Yan, LI Chao-bo, DENG Ze-yuan, MA Xiaojuan. Optimition of extracting stachyose from stachys floridana schuttl. Ex Benth by response surface methodology [J]. Journal of Food Science Technology, 2013, 50(5): 942–949.
ZOU Qin-peng, LIU Xiang-qian, ZHENG Li-sheng, FENG Sheng, DAI Ling. Accumulation dynamic of acankoreagenin in leaves of Acanthopanax gracilistylus [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2012, 43(8): 1550–1552. (in Chinese)
ZHOU Min, ZHU Hong-lin, WANG Kui-wu, WEI Wang-xing, ZHANG Yong. Isolation and X-ray crystal structure of a securinegatype alkaloid from Phyllanthus nururi Linn [J]. Natural Product Research, 2012, 26(8): 762–764.
ZHONG Ming, HUANG Ke-long, ZENG Jian-guo. Determination of contents of (Willd) R. Br. from different eight alkaloids in fruits of Macleaya cordata habitats and antioxidant activities of extracts [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology. 2010, 17: 472–479.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(11JJ2042) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China; Project supported by the “Twelfth Five-Year” Key Discipline of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine-Pharmaceutical Analysis Science, China; Project(11K048) supported by the Innovation Platform and Open Foundation Program of Higher Colleges of Hunan Province, China; Project(K1207010-21) supported by the Changsha City Science and Technology Bureau Key Projects, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, L., Liu, Xq., Xie, X. et al. Characterization of stereostructure by X-ray and technology of extracting in combination hydrolysis in situ of acankoreanogenin from leaves of Acanthopanax gracilistylus W. W. Smith. J. Cent. South Univ. 21, 3063–3070 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2277-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2277-9