Abstract
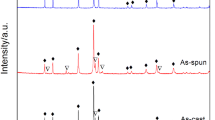
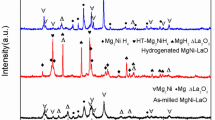
In order to improve the hydriding and dehydriding kinetics of the Mg2Ni-type alloys, Ni in the alloy is substituted by element Co. The nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg2Ni-type Mg2Ni1−xCox (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) alloys were synthesized by melt-spinning technique. The structures of the as-cast and spun alloys were studied with an X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and a high resolution transmission electronic microscope (HRTEM). An investigation on the thermal stability of the as-spun alloys was carried out with a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). The hydrogen absorption and desorption kinetics of the alloys were measured with an automatically controlled Sieverts apparatus. The results demonstrate that the substitution of Co for Ni does not alter the major phase of Mg2Ni but results in the formation of secondary phase MgCo2. No amorphous phase is detected in the as-spun Co-free alloy, but a certain amount of amorphous phase is clearly found in the as-spun Co-containing alloys. The substitution of Co for Ni exerts a slight influence on the hydriding kinetics of the as-spun alloy. However, it dramatically enhances the dehydriding kinetics of the as-cast and spun alloys. As Co content (x) increases from 0 to 0.4, the hydrogen desorption capacity increases from 0.19% to 1.39% (mass fraction) in 20 min for the as-cast alloy, and from 0.89% to 2.18% (mass fraction) for the as-spun alloy (30 m/s).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WOO J H, LEE K S. Electrode characteristics of nanostructured Mg2Ni-type alloys prepared by mechanical alloying [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1999, 146(3): 819–823.
LIU F J, SUDA S. A method for improving the long-term storability of hydriding alloys by air water exposure [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1995, 231: 742–750.
LIU Y N, ZHANG X J. Effect of lanthanum additions on electrode properties of Mg2Ni [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1998, 276: 231–234.
YU Z X, LIU Z Y, WANG E D. Hydrogen storage properties of nanocomposite Mg-Ni-Cu-CrCl3 prepared by mechanical alloying [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2002, 335: 43–48.
JANOT R, DAROK X, ROUGIER A, AYMARD L, NAZRI G A, TARASCON J M. Hydrogen sorption properties for surface treated MgH2 and Mg2Ni alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 404/405/406: 293–296.
KOHNO T, KANDA M. Effect of partial substitution on hydrogen storage properties of Mg2Ni alloy [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144: 2384–2388.
NOHARA S, FUJITA N, ZHANG S G, INOUE H, IWAKURA C. Electrochemical characteristics of a homogeneous amorphous alloy prepared by ball milling Mg2Ni with Ni [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1998, 267: 76–78.
HUANG L J, LIANG G Y, SUN Z B, WU D C. Electrode properties of melt-spun Mg-Ni-Nd amorphous alloys [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 160: 684–687.
TANAKA K, KANDA Y, FURUHASHI M, SAITO K, KURODA K, SAKA H. Improvement of hydrogen storage properties of melt-spun Mg-Ni-RE alloys by nanocrystallization [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 293/294/295: 521–525.
SPASSOV T, KÖSTER U. Thermal stability and hydriding properties of nanocrystalline melt-spun Mg63Ni30Y7 alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1998, 279: 279–286.
YAMAURA S I, KIM H Y, KIMURA H, INOUE A, ARATA Y. Thermal stabilities and discharge capacities of melt-spun Mg-Ni-based amorphous alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 339: 230–235.
INOUE A, MASUMOTO T. Mg-based amorphous alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1993, 173: 1–8.
CHEN H S. Thermodynamic considerations on the formation and stability of metallic glasses [J]. Acta Materialia, 1974, 22(12): 1505–1511.
SPASSOV T, SPLSONA P, SURIÑACH S, BARÓ M D. Optimization of the ball-milling and heat treatment parameters for synthesis of amorphous and nanocrystalline Mg2Ni-based alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2003, 349: 242–254.
ORIMO S, FUJII H. Materials science of Mg-Ni-based new hydrides [J]. Applied Physics A, 2001, 72: 167–186.
SPASSOV T, KÖSTER U. Hydrogenation of amorphous and nanocrystalline Mg-based alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 287: 243–250.
GOO N H, JEONG W T, LEE K S. The hydrogen storage properties of new Mg2Ni alloy [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 87: 118–124.
TAKAHASHI Y, YUKAWA H, MORINAGA M. Alloying effects on the electronic structure of Mg2Ni intermetallic hydride [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1996, 242: 98–107.
KHRUSSANOVA M, GRIGOROVA E, BOBET J L, KHRISTOV M, PESHEV P. Hydrogen sorption properties of the nanocomposites Mg-Mg2Ni1-xCox obtained by mechanical alloying [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 365: 308–313.
KHRUSSANOVA M, MANDZHUKOVA T, GRIGOROVA E, KHRISTOV M, PESHEV P. Hydriding properties of the nano-composite 85wt.%Mg-15wt.%Mg2Ni0.8Co0.2 obtained by ball milling [J]. Journal of Material Science, 2007, 42: 3338–3342.
BOBET J L, CHEVALIER B, DARRIET B. Effect of reactive mechanical grinding on chemical and hydrogen sorption properties of the Mg+10wt.%Co mixture [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 330/331/332: 738–742.
LEE D S, KWON I H, BOBET J L, SONG M Y. Effects on the H2-sorption properties of Mg of Co (with various sizes) and CoO addition by reactive grinding [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 366: 279–288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2006AA05Z132) supported by the National High-tech Research and Development Program of China; Projects(50871050, 50961009) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2010ZD05) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia, China; Project(NJzy08071) supported by the High Education Science Research Program of Inner Mongolia, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yh., Zhao, Dl., Li, Bw. et al. Influence of substituting Ni with Co on hydriding and dehydriding kinetics of melt spun nanocrystalline and amorphous Mg2Ni-type alloys. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 18, 303–309 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-011-0695-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-011-0695-5