Abstract
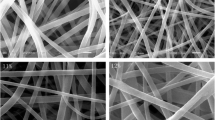
A polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinylidene) fluoride-hexafluoropropylene was prepared by evaporating the solvent of dimethyl formamide, and non-woven fabric was used to reinforce the mechanical strength of polymer electrolyte and maintain a good interfacial property between the polymer electrolyte and electrodes. Polymer lithium batteries were assembled by using LiCoO2 as cathode material and lithium foil as anode material. Scanning electron microscopy, alternating current impedance, linear sweep voltammetry and charge-discharge tests were used to study the properties of polymer membrane and polymer Li-ion batteries. The results show that the technics of preparing polymer electrolyte by directly evaporating solvent is simple. The polymer membrane has rich micro-porous structure on both sides and exhibits 280% uptake of electrolyte solution. The electrochemical stability window of this polymer electrolyte is about 5.5 V, and its ionic conductivity at room temperature reaches 0.151 S/m. The polymer lithium battery displays an initial discharge capacity of 138 mA·h/g and discharge plateau of about 3.9 V at 0.2 current rate. After 30 cycles, its loss of discharge capacity is only 2%. When the battery discharges at 0.5 current rate, the voltage plateau is still 3.7 V. The discharge capacities of 0.5 and 1.0 current rates are 96% and 93% of that of 0.1 current rate, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ZHANG S S, ERVIN M H, XU K, et al. Microporous P(AN-MMA) membrane as a separator of rechargeable lithium battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49(20): 3339–3345.
KIM H S, KUN K S, CHO B W, et al. Electrochemical and physical properties of composites polymer electrolyte of PMMA and PEGDA[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 124(1): 221–224.
KIM K M, KO J M, PARK N G, et al. Characterization of P(VDF-HFP)-based polymer electrolyte filled with rutile TiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2003, 161(1): 121–131.
KIM D W, KIM Y R, PARK J K, et al. Electrical properties of the plasticized polymer electrolytes based on acrylonitrile-methacrylate copolymers[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1998, 106(2): 329–337.
DONG D Y, DAEJON Y. Cycling performances of Li/LiCoO2 cell with polymer-coated separator[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 50(2/3): 323–326.
SONG M K, KIM Y T, CHO J Y, et al. Composed polymer electrolytes reinforced by non-won fabric[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 125(1): 10–16.
XI J Y, TANG X Z. Enhanced lithium ion transference number and ionic conductivity of composite polymer electrolyte doped with organic-inorganic hybrid P123@SBA-15[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2004, 400(1): 68–73.
LIU G, KEINHOUT M, BAKER G. L. Nanoscale lithium ion conducting polyethylene oxide with self-attached insulating layers[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2005, 175(4): 721–724.
WU C G, LU M I, CHUANG H J. PVDF-HFP/P123 hybrid with mesopores: a new matrix for high-conducting, low-leakage porous polymer electrolyte[J]. Polymer 2005, 46(20): 5929–5938.
WANG Z L, TANG Z Y. Characterization of the polymer electrolyte based on the blend of PVDF-HFP and PVP for lithium battery[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 82(1): 16–20.
SONG J Y, WANG Y Y, WANG C C. Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1999, 77(2): 183–197.
KUM K, SONG M, KIM Y T, et al. The effect of mixed salts in gel-coated polymer electrolyte for advanced lithium battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 50(2/3): 285–288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project (2003AA32X010) supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Yj., Chen, Bz. & Yuan, Y. Preparation and electrochemical properties of polymer Li-ion battery reinforced by non-woven fabric. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 14, 47–50 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-007-0010-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-007-0010-7