Abstract
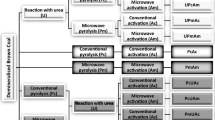
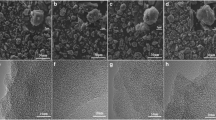
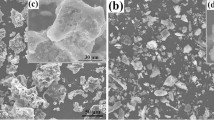
Taking the selection of coal-tar pitch as precursor and KOH as activated agent, the activated carbon electrode material was fabricated for supercapacitor. The surface area and the pore structure of activated carbon were analyzed by Nitro adsorption method. The electrochemical properties of the activated carbons were determined using two-electrode capacitors in 6 mol/L KOH aqueous electrolytes. The influences of activated temperature and mass ratio of KOH to C on the pore structure and electrochemical property of porous activated carbon were investigated in detail. The reasons for the changes of pore structure and electrochemical performance of activated carbon prepared under different conditions were also discussed theoretically. The results indicate that the maximum specific capacitance of 240 F/g can be obtained in alkaline medium, and the surface area, the pore structure and the specific capacitance of activated carbon depend on the treatment methods; the capacitance variation of activated carbon cannot be interpreted only by the change of surface area and pore structure, the lattice order and the electrolyte wetting effect of the activated carbon should also be taken into account.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kotz R, Carlen M. Principle and application of electrochemical capacitors[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 54(15–16): 2483–2498.
Vix-Guterl C, Saadallah S, Jurewicz K, et al. Supercapacitor electrodes from new ordered porous carbon materials obtained by a templating procedure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2004, 108(1–2): 148–155.
Teng H, WANG Sheng-chi. Preparation of porous carbons from phenol-formaldehyde resins with chemical and physical activation[J]. Carbon, 2000, 38(6): 817–824.
Lillo-Rodenas M A, Juan-Juan J, Cazorla-Amorós D, et al. About reaction occurring during chemical activation with hydroxides[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(7): 1365–1369.
Yamashita Y. Carbonization of 3, 5-dimethylphenol-formaldehyde resin with NaOH[J]. Carbon, 1982, 20(1): 41–51.
Lozano-Castelló D, Lillo-Ródenas M L, Cazorla-Amorós D, et al. Preparation of activated carbons from Spanish anthracite I. Activation by KOH[J]. Carbon, 2001, 39(5): 741–749.
Ahmadpour A, DO D D. The preparation of activated carbon from macadamia nutshell by chemical activation [J]. Carbon, 1997, 35(12): 1723–1732.
Molina-Sabio M, Rodríguez-Reinoso F. Role of chemical activation in the development of carbon porosity [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2004, 241(1–3): 15–25.
Raymundo-pinero E, Azais P, Cacciaguerra T, et al. KOH and NaOH activation mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotube with different structural organisation [J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(4): 786–795.
Yamashita J, Hirano T, Shioya M. Development of mesopores during activation poly (vinylidene fluoride)-based carbon[J]. Carbon, 2002, 40(9): 1541–1548.
Portet C, Taberna P L, Simon p, et al. Modification of Al current collector surface by sol-gel deposit for carbon-carbon supercapacitor applications[J]. Electrochemical Acta, 2004, 49(6): 905–912.
Molina-Sabio M, Rodriguez F, Caturla F, et al. porosity in granular carbons actived with phosphoric acid[J]. Carbon, 1995, 33(8): 1105–1113.
QU De-yang. Studies of the activated carbon used in double-layer supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Power Source, 2002, 109(2): 403–411.
Yong-Jung K, Horie Y, Matsuzawa Y, et al. Structure features necessary to obtain a high specific capacitance in electric double layer capacitor[J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(12–13): 2423–2432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2005CB623703) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; project(5JJ30103) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, J., Lai, Yq. et al. Influence of KOH activation techniques on pore structure and electrochemical property of carbon electrode materials. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 13, 360–366 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-006-0049-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-006-0049-x