Abstract
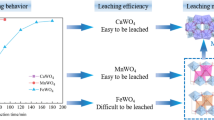
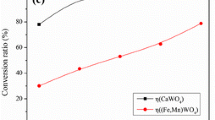
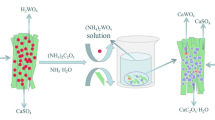
Scheelite and scheelite-wolframite mixed concentrates with different grades were decomposed by caustic soda digestion, and the effects of caustic soda (NaOH) dosage, the ratio of water to ore and the stirring rate on tungsten recovery were studied. The results show that under the conditions that the ratio of water to ore is 0.8, stirring rate is 500 r · min−1 and the heating time is 2.0 h at 160 °C, the recovery of tungsten reaches 98% for scheelite (w(WO3) is 65.04%) and wolframite containing high proportion of calcium (w(WO3) is 65.58%, w(Ca) is 7.53%), when caustic soda dosage is 2.2 and 2.0 times of theoretical value, respectively; the recovery of tungsten can be more than 98%, 98% and 96% respectively for low-grade scheelite-wolframite mixed concentrate with 55.78%, 45.32% and 25.21% WO3, when caustic soda dosage is 2.6, 3.2 and 5.5 times of theoretical value, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LI Hong-gui, SUN Pei-mei, LI Yun-jiao, et al. Facing challenge of industry, improving our tungsten hydrometallurgy technique to emulate the top countries[J]. China Tungsten Industry, 2001, 16(5–6): 49–51. (in Chinese)
LI Hong-gui. Rare Metals Metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 1990. (in Chinese)
LI Hong-gui, LIU Mao-sheng, SI Ze-jin, et al. Caustic Decomposition of Scheelite Concentrate and Scheelite-Wolframite Mixed Concentrate: Technique and Equipment[P]. China, 003508, 1985-04-01. (in Chinese)
LI Hong-gui, LIU Mao-sheng, DAI Chao-jia, et al. Research on new technique of tungsten caustic decomposition[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 1987, (1–2): 1–3. (in Chinese)
LI Yun-jiao, SUN Pei-mei, LIU Mao-sheng, et al. Mechanical activated caustic decomposition to scheelite concentrate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1995, 5(3):27–29. (in Chinese)
LIU Mao-sheng, SUN Pei-mei, LI yun-jiao, et al. Mechanical activated caustic decomposition of tungsten concentrate with a high content of calcium[A]. CHEN Jian-yong, YANG Song-qing, Deng Zuo-qing. ICHM ’92[C]. Changsha: International Academic Publishers, 1992.
LI Hong-gui. Foundation and New Technique of Tungsten Caustic Decomposition[M]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology Publisher, 1997: 1–10. (in Chinese)
SUN Pei-mei, LI Yun-jiao, LI Hong-gui, et al. Thermodynamics of scheelite caustic decomposition [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1993, 3(2): 37–43. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Pm., Li, Hg., Li, Yj. et al. Decomposing scheelite and scheelite-wolframite mixed concentrate by caustic soda digestion. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 10, 297–300 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-003-0027-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-003-0027-5
Key words
- scheelite concentrate
- wolframite with high proportion of calcium
- low-grade scheelite-wolframite mixed concentrate
- caustic soda digestion