Abstract
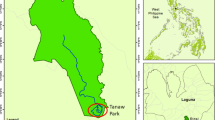
The nature heritages are the precious legacy of nature with outstanding scientific and aesthetic value. They are quite different from other common ecotourism areas, because of its original and unique system, sensitive and vulnerable landscape, and peripheral cultural features. Therefore, the tourism development in the nature heritage sites should be on the premise of ecological security. The evaluation index system of tourism ecological security in nature heritage sites was constructed in this article by AHP and Delphi methods, including nature ecological security, landscape visual security and local culture ecological security, and the security thresholds of indices were also established. In the indices’ weights of the evaluation model, the nature ecological security ranked the highest, followed by tourist landscape visual security and culture ecological security, which reflected the influence degree of the limited factor to tourism ecological security. Then, this paper carried out an empirical study of Kanas of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China, which has the potential to be the World Nature Heritage. On the basis of the data attained from survey and observation on the spot, as well as questionnaire answered by tourists and local communities, the ecological security status in Kanas was evaluated. The result showed that the status of Kanas tourism ecological security was better, but there had some limiting factors. Lastly, effective measures were put forward to ensure its ecological security.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao Xinxiang, 2006. Ecological security evaluation of tourism destination based on ecological footprint analyses—A case of Kaifeng City. China Population, Resources and Environment, 16(2): 70–75. (in Chinese)
Cao Xinxiang, Chen Taizheng, Wang Weihong, 2006. Ecological security evaluation of tourism destination—A case of Kaifeng City. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(2): 149–152. (in Chinese)
Cheng Daopin, He Ping, Zhang Heping, 2004. Establishment and valuation of the index system for the sample area of national ecotourism. Journal of Central South Forestry University, 24(2): 28–33. (in Chinese)
Costanza R, d’Arge R, de Groot R et al., 1997. The value of the world’s ecosystem service and natural capital. Nature, 387(15): 253–260. DOI: 10.1038/387253a0
Dong Xuewang, 2003. Ecological security evaluation of tourist destinations—A case of Wudalianchi National Park. Natural Science Journal of Harbin Normal University, 19(6): 100–105. (in Chinese)
Dong Xuewang, 2004. Ecological security evaluation of Jingpohu National Park. Territory & Natural Resources Study, 2: 74–76. (in Chinese)
Gong Zixian, 2006. Research on Ecotourism Development in Emei World Nature Heritage. Chengdu: Chengdu Engineering University. (in Chinese)
Lee D N B, Snepenger D J, 1992. An ecotourism assessment of Tortuguero, Costa Rica. Annals of Tourism Research, 19: 367–370. DOI: 10.1016/0160-7383(92)90092-4
Liu Yang, Lv Yihe, Chen Liding et al., 2005. The impact assessment of ecotourism in nature reserves: Progress and implications. Journal of Natural Resources, 20(5): 771–779. (in Chinese)
Lu Xiaoli, Wu Chunyou, Xiao Guirong, 2006. Fuzzy synthetic evaluation on resident’s perceptions of tourism impacts—Case of Jiuzhaigou National Park, Sichuan Province, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 16(1): 87–95. DOI: 10.1007/s11769-00-6-0028-z
Ministry of Forestry of P. R. China, 1995. Standard for Forest Parks Design (LY/T5132-95). http://www.chinafpark.net/flfg/more.aspx?id=80. (in Chinese)
National Tourism Administration of P. R. China, 2003. Division and Evaluation on the Quality of Tourism Scenic Areas (GB/T17775-2003). http://www.cnta.gov.cn/html/2008-6/2008-6-27-20-31-36-5.html. (in Chinese)
Ross S, Wall G, 1999a. Ecotourism: Towards congruence between theory and practice. Tourism Management, 20: 123–132. DOI:10.1016/S0261-5177(98)00098-3
Ross S, Wall G, 1999b. Evaluating ecotourism: The case of North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Tourism Management, 20: 673–682. DOI:10.1016/S0261-5177(99)00040-0
SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration of P. R. China), 1994. Evaluation Index System of Environmental Impact of Resources Development in Mountain Scenic Area (HJ/T6-94). http://www.sepa.gov.cn/image20010518/5608.pdf. (in Chinese)
SEPA, 1996a. Ambient Air Quality Standard (GB 3095-1996). http://www.mep.gov.cn/image20010518/5298.pdf. (in Chinese)
SEPA, 1996b. Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB 8978-1996). http://www.sepa.gov.cn/tech/hjbz/bzwb/shjbh/swrwpfbz/199801/W020061027521858212955.pdf. (in Chinese)
SEPA, 1998. Acceptance Criteria of National Ecological Demonstration Zones. http://www.sepa.gov.cn/image20010518/6300.pdf. (in Chinese)
SEPA, 2002. Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002). http://www.sepa.gov.cn/tech/hjbz/bzwb/shjbh/shjzlbz/200206/W020061027509896672057.pdf. (in Chinese)
SEPA, 2003. Construction Index of Ecological County, Municipality and Province (Trial Implementation). http://www.zhb.gov.cn/image20010518/6304.pdf. (in Chinese)
Simon F J G, Narangajavana Y, Marques D P, 2004. Carrying capacity in the tourism industry: A case study of Hengistbury Head. Tourism Management, 25: 275–283. DOI: 10.1016/S0261-5177(03)00089-X
Sun Yujun, Wang Rusong, 2000. Environment capacity of ecotourism resort. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 11(4): 564–566. (in Chinese)
Wang Liangjian, 2001. On the indicator system of sustainable development of tourism and the evaluating method. Tourism Tribune, 16(1): 67–70. (in Chinese)
Yang Zhaoping, Zhang Xiaolei, 2000. Study on eco-tourism and sustainable development in nature reserve—A case of Khanas Nature Reserve. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 20(5): 450–454. (in Chinese)
Yu Kongjian, 1996. Security patterns and surface model in landscape planning. Landscape and Urban Planning, 36(5): 1–17. DOI:10.1016/S0169-2046(96)00331-3
Yu Kongjian, 1999. Landscape ecological security patterns in biological conservation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19(1): 8–15. (in Chinese)
Zhang Zheng, Zhang Jianwen, Li Yinnian et al., 1999. Indicators for wetland ecological assessment. Rural Environment Protection, 18(6): 283–285. (in Chinese)
Zheng Yunwen, Xue Dayuan, Zhang Gengsheng, 1994. A study on evaluation criteria for effective management of natural reserves in China. Rural Eco-environment, 10(3): 22–25. (in Chinese)
Zhou Nianxing, Lin Zhenshan, Huang Zhenfang et al., 2008. Tourist ecological footprint and eco-efficiency on Nanji Archipelago. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 28(4): 571–578. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40671057), Knowledge Innovation Programs of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX3-SW-355)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Yang, Z., Di, F. et al. Evaluation on tourism ecological security in nature heritage sites —Case of Kanas nature reserve of Xinjiang, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 19, 265–273 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-009-0265-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-009-0265-z