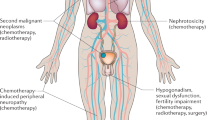
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate neurotoxicity in testicular cancer survivors (TCSs) years after treatment and secondly the influence of neurotoxicity on quality-of-life (QoL).
Methods
We identified 2234 TCSs who completed the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity questionnaire. QoL was evaluated with the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30. Patients were grouped according to treatment strategy: surveillance (N = 1113), infradiaphragmatic radiotherapy (N = 301), cisplatin-etoposide-bleomycin (BEP) (N = 759), and more than one line of treatment (MTOL) (N = 61). Association of treatment modality with long-term neurotoxicity was analyzed with ordinal logistic regression. Secondly, associations between neurotoxicity and QoL were analyzed in BEP-treated patients. Analyses were age-adjusted and repeated with additional adjustment for comorbidity, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Results
After a median follow-up of 18.4 years, treatment with BEP and MTOL was associated with overall increased risk of neurotoxicity (odds ratio 2.4–4.7 depending on treatment intensity, P < 0.001) as well as subscales (peripheral neuropathy, ototoxicity, and dysfunction associated with neuropathy, all P < 0.001). Radiotherapy and surveillance were not associated with neurotoxicity. In patients treated with BEP, neurotoxicity was highly associated with all indicators of worse QoL outcomes (P-trend: 1.5 × 10−17 to 1.1 × 10−28) after almost 20 years of follow-up.
Conclusions
Treatment with BEP was associated with long-term neurotoxicity, which was highly associated with decreased QoL. Strategies to ameliorate or prevent neurotoxicity should be investigated.
Implications for Cancer Survivors
Treatment with chemotherapy for testicular cancer induces long-term neuro- and ototoxicity which may have severe influence on quality-of-life years after treatment cessation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calabrò F, Albers P, Bokemeyer C, Martin C, Einhorn LH, Horwich A, et al. The contemporary role of chemotherapy for advanced testis cancer: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol. 2012;61:1212–21.
Travis LB, Beard C, Allan JM, Dahl AA, Feldman DR, Oldenburg J, et al. Testicular cancer survivorship: research strategies and recommendations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:1114–30.
Fung C, Fossa SD, Williams A, Travis LB. Long-term morbidity of testicular cancer treatment. Urol Clin North Am. 2015;42:393–408.
Chovanec M, Abu Zaid M, Hanna N, El-Kouri N, Einhorn LH, Albany C. Long-term toxicity of cisplatin in germ-cell tumor survivors. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:2670–9.
von Schlippe M, Fowler C, Harland S. Cisplatin neurotoxicity in the treatment of metastatic germ cell tumour: time course and prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:823–6. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.2006.
Glendenning JL, Barbachano Y, Norman AR, Dearnaley DP, Horwich A, Huddart RA. Long-term neurologic and peripheral vascular toxicity after chemotherapy treatment of testicular cancer. Cancer. 2010;116:2322–31.
Brydøy M, Oldenburg J, Klepp O, Bremnes RM, Wentzel-Larsen T, Hauge ER, et al. Observational study of prevalence of long-term Raynaud-like phenomena and neurological side effects in testicular cancer survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:1682–95.
Mykletun A, Dahl AA, Haaland CF, Bremnes R, Dahl O, Klepp O, et al. Side effects and cancer-related stress determine quality of life in long-term survivors of testicular cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3061–8.
Dolan ME, El Charif O, Wheeler HE, Gamazon ER, Ardeshir-Rouhani-fard S, Monahan P, et al. Clinical and genome-wide analysis of cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult-onset cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:5757–68.
Rossen PB, Pedersen AF, Zachariae R, von der Maase H. Health-related quality of life in long-term survivors of testicular cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5993–9.
Dahl AA, Mykletun A, Fosså SD. Quality of life in survivors of testicular cancer. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. 2005;23:193–200.
Gilligan T. Quality of life among testis cancer survivors. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. 2015;33:413–9.
Dahl AA, Haaland CF, Mykletun A, Bremnes R, Dahl O, Klepp O, et al. Study of anxiety disorder and depression in long-term survivors of testicular cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2389–95.
Sprauten M, Haugnes HS, Brydøy M, Kiserud C, Tandstad T, Bjøro T, et al. Chronic fatigue in 812 testicular cancer survivors during long-term follow-up: increasing prevalence and risk factors. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:2133–40.
Kreiberg M, Bandak M, Lauritsen J, Skøtt JW, Johansen NB, Agerbaek M, et al. Cohort profile: the Danish testicular cancer late treatment effects cohort (DaTeCa-LATE). Front Oncol. 2018;8:37. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00037.
Huang HQ, Brady MF, Cella D, Fleming G, Mackey D. Validation and reduction of FACT/GOG-Ntx subscale for platinum/paclitaxel- induced neurologic symptoms: a gynecologic oncology group study. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2007;17:387–93.
Lauritsen J, Kier MGG, Mortensen MS, Bandak M, Gupta R, Holm NV, et al. Germ cell cancer and multiple relapses: toxicity and survival. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3116–23.
Calhoun EA, Welshman EE, Chang CH, Lurain JR, Fishman DA, Hunt TL, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the functional assessment of cancer therapy/gynecologic oncology group - neurotoxicity (fact/GOG-Ntx) questionnaire for patients receiving systemic chemotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2003;13:741–8.
Hershman DL, Weimer LH, Wang A, Kranwinkel G, Brafman L, Fuentes D, et al. Association between patient reported outcomes and quantitative sensory tests for measuring long-term neurotoxicity in breast cancer survivors treated with adjuvant paclitaxel chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;125:767–74.
Driessen CML, de Kleine-Bolt KME, Vingerhoets AJJM, Mols F, Vreugdenhil G. Assessing the impact of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity on the quality of life of cancer patients: the introduction of a new measure. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20:877–81.
Cella D, Huang H, Homesley HD, Montag A, Salani R, De Geest K, et al. Patient-reported peripheral neuropathy of doxorubicin and cisplatin with and without paclitaxel in the treatment of advanced endometrial cancer: results from GOG 184. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;119:538–42.
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:365–76.
Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, Fong A, Burnand B, Luthi J-C, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43:1130–9.
Lynge E, Sandegaard JL, Rebolj M. The Danish National Patient Register. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:30–3.
Daugaard G, Kier MGG, Bandak M, Mortensen MS, Larsson H, Søgaard M, et al. The Danish Testicular Cancer database. Clin Epidemiol. 2016;8:703–7.
Martyn CN, Hughes RAC. Epidemiology of peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;62:310–8.
Clair C, Cohen MJ, Eichler F, Selby KJ, Rigotti NA. The effect of cigarette smoking on diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30:1193–203.
Frisina RD, Wheeler HE, Fossa SD, Kerns SL, Fung C, Sesso HD, et al. Comprehensive audiometric analysis of hearing impairment and tinnitus after cisplatin-based chemotherapy in survivors of adult-onset cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:2712–20.
Sprauten M, Darrah TH, Peterson DR, Campbell ME, Hannigan RE, Cvancarova M, et al. Impact of long-term serum platinum concentrations on neuro- and ototoxicity in cisplatin-treated survivors of testicular cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:300–7.
Juul T, Petersen MA, Holzner B, Laurberg S, Christensen P, Grønvold M. Danish population-based reference data for the EORTC QLQ-C30: associations with gender, age and morbidity. Qual Life Res. 2014;23:2183–93.
Megari K. Quality of life in chronic disease patients. Health Psychol Res. 2013;1:27.
Wilson IB. Clinical understanding and clinical implications of response shift. Soc Sci Med. 1999;48:1577–88.
Capogrosso P, Boeri L, Ferrari M, Ventimiglia E, La Croce G, Capitanio U, et al. Long-term recovery of normal sexual function in testicular cancer survivors. Asian J Androl. 2016;18:85.
Oldenburg J, Fossa SD, Dahl AA. Scale for chemotherapy-induced long-term neurotoxicity (SCIN): psychometrics, validation, and findings in a large sample of testicular cancer survivors. Qual Life Res. 2006;15:791–800.
Postma TJ, Aaronson NK, Heimans JJ, Muller MJ, Hildebrand JG, Delattre JY, et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: the QLQ-CIPN20. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:1135–9.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Danish Cancer Society and Preben and Anna Simonsens foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Patients provided informed consent for participation in this study, and the study was approved by the regional ethical committee (File number, H-2-2012-044), as well as the National Board of Data Protection (File number, 2012-41-0751).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 270 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lauritsen, J., Bandak, M., Kreiberg, M. et al. Long-term neurotoxicity and quality of life in testicular cancer survivors—a nationwide cohort study. J Cancer Surviv 15, 509–517 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-020-00944-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-020-00944-1