Abstract
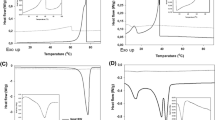
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), optical microscopy, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to examine the thermal behavior, crystal structure, and crystal morphology of rice bran wax (RBX) in bulk and oil–wax mixtures, and to compare them with those of carnauba wax (CRX) and candellila wax (CLX). The RBX employed in the present study was separated from rice bran oil by winterization, filtration, refinement, bleaching, and deodorization. The RBX crystals melted in the bulk state at 77–79 °C with ΔH melting = 190.5 J/g, which is quite large compared with CLX (129 J/g) and CRX (137.6 J/g). XRD data of the RBX crystals revealed O⊥ subcell packing and a long spacing value of 6.9 nm. Thin long needle-shaped crystals were observed in the mixtures of RBX and liquid oils [olive oil and salad oil (canola:soy bean oil = 50:50)]; therefore, the dispersion of RBX crystals in these liquid oils was much finer than that of CRX and CLX crystals. Organogels formed when the mixture of every plant wax and liquid oil was melted at elevated temperature and cooled to ambient temperature. However, the mixture of RBX and olive oil at a concentration ratio of 1:99 wt.% formed an organogel at 20 °C, whereas the lowest concentration necessary for CRX to form an organogel in olive oil was 4 wt.% and that for CLX was 2 wt.%. Observation of the rate of gel formation using DSC and viscosity measurements indicated that the gel structure formed soon after RBX crystallized, whereas a time delay was observed between the organogel formation and wax crystallization of CRX and CLX. These results demonstrate RBX’s good organogel-forming properties, mostly because of its fine dispersion of long needle like crystals in liquid oil phases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terech P, Weiss RG (1997) Low molecular mass gelators of organic liquids and the properties of their gels. Chem Rev 97:3133–3159
Abdallah DJ, Weiss RG (2000) Organogels and low molecular mass organic gelators. Adv Mater 12:1237–1247
Abdallah DJ, Sirchio SA, Weiss RG (2000) Hexatriacontane organogels. The first determination of the conformation and molecular packing of a low-molecular-mass organogelator in its gelled state. Langmuir 16:7558–7561
Pernetti M, van Malssen K, Kalnin D, Flöter E (2007) Structuring of edible oil with lecithin and sorbitan tri-stearate. Food Hydrocoll 21:855–861
Toro-Vazquez JF, Morales-Rueda JA, Dibildox-Alvarado E, Charó-Alonso M, Alonzo-Macias M, González-Chávez MM (2007) Thermal and textural properties of organogels developed by candelilla wax in safflower oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 84:989–1000
Xiao Huang, Weiss RG (2007) Molecular organogels of the sodium salt of (R)-12-hydroxystearic acid and their templated syntheses of inorganic oxides. Tetrahedron 63:7375–7385
Pernetti M, van Malssen KF, Flöter E, Bot A (2007) Structuring of edible oils by alternatives to crystalline fat. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 12:221–231
Bot A, Veldhuizen YSJ, den Adel R, Roijers EC (2009) Non-TAG structuring of edible oils and emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 23:1184–1189
Vintiloiu A, Leroux JC (2008) Organogels and their use in drug delivery—a review. J Control Release 125:179–192
Bot A, Agterof WGM (2006) Structuring of edible oils by mixtures of γ-oryzanol with β-sitosterol or related phytosterols. J Am Oil Chem Soc 83:513–521
Bot A, Adel R, Roigers EC (2008) Fibrils of γ-oryzanol + β-sitosterol in edible oil organogels. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85:1127–1134
Daniel J, Rajasekaran R (2003) Organogelation of plant oils and hydrocarbons by long-chain saturated FA, fatty alcohols, wax esters, and dicarboxylic acids. J Am Oil Chem Soc 80:417–421
Gandolfo FG, Bot A, Flöter E (2004) Structuring of edible oils by long-chain FA, fatty alcohols and their mixtures. J Am Oil Chem Soc 81:1–6
Schaink HM, van Malssen KF, Morgado-Alves S, Kalnin D, van der Linden (2007) Crystal network for edible oil organogels: possibilities and limitations of fatty acid and fatty alcohol systems. Food Res Intern 40:1185–1193
Tamura T, Ichikawa M (1997) Effect of lecithin on organogel formation of 12-hydroxystearic acid. J Am Oil Chem Soc 74:491–495
Rogers MA, Wright AJ, Marangoni AG (2008) Crystalline stability of self-assembled fibrillar networks of 12-hydroxystearic acid in edible oils. Food Res Intern 41:1026–1034
Rogers MA, Marangoni AG (2008) Non-isothermal nucleation and crystallization of 12-hydroxystearic acid in vegetable oils. Cryst Growth Des 8:4596–4601
Rogers MA, Wright AJ, Marangoni AG (2009) Nanostructuring fiber morphology and solvent inclusions in 12-hydroxystearic acid/canola oil organogels. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 14:33–42
Wright AJ, Marangoni AG (2006) Formation, structure, and rheological properties of ricinoelaidic acid–vegetable oil organogels. J Am Oil Chem Soc 83:497–503
Wright AJ, Marangoni AG (2007) Time, temperature, and concentration dependance of ricinoelaidic acid–canola oil organogelation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 84:3–9
Murdan S, Gregoriadis G, Florence AT (1999) Novel sorbitan monostearate organogels. J Pharm Sci 88:608–614
Rogers MA (2009) Novel structuring strategies for unsaturated fats—meeting the zero-trans, zero-saturated fat challenge: a review. Food Res Intern 42:747–753
Small DM (ed) (1986) Handbook of lipid research 4. The physical chemistry of lipids from alkanes to phopholipids. Plenum, New York
Akoh CC, Min BD (eds) (2002) Food lipids chemistry, nutrition & biotechnology, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Martini S, Añón MC (2003) Crystallization of sunflower oil waxes. J Am Oil Chem Soc 80:525–532
Vali SR, Yi-Hsu Ju, Kaimal TNB, Yaw-Terang Chern (2005) A process for the preparation of food-grade rice bran wax and the determination of its composition. J Am Oil Chem Soc 82:57–64
Ghosh M, Bandyopadhyay S (2005) Studies on the crystal growth of rice bran wax in a hexane medium. J Am Oil Chem Soc 82:229–231
Morales-Rueda JA, Dibilox-Alvarado E, Charó-Alonso M, Weiss RG, Toro-Vazquez JF (2009) Thermo-mechanical properties of candelilla wax and dotriacontane organogels in safflower oil. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 111:207–215
MD Idea Exporting Division. Uses and application rice bran wax, from octacosanol to phytosterol. http://www.mdidea.com/products/proper/proper059.html Accessed November 2008
Global Agritech Inc., (2009) Stabilization of long chain polyunsaturated oils. US Patent (PTC/US2008/071178)
Letcher CS (1983) Waxes. Kirk–Othmer encyclopedia on chemical technology, 3rd edn. vol 24, Wiley, New York, pp 466–81
Tulloch AP (1973) Comparison of some commercial waxes by gas liquid chromatography. J Am Oil Chem Soc 50:367–371
Tada A, Masuda A, Sugimoto N, Yamagata K, Yamazaki T, Tanamoto K (2007) Analysis of constituents of ester type gum bases used as natural food additives. Food Hyg 48:179–185
Cyber Lipid Center Waxes and other esters. http://www.cyberlipid.org/wax/wax0001.htm#2 Accessed July 2009
Sato K, Goto M, Yano J, Honda K, Kodali DR, Small DM (2001) Atomic resolution structure analysis of β′ polymorph crystals of triacylglycerol: 1, 2-dipalmitoyl-3-myristoyl-sn-glycerol. J Lipid Res 42:338–345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Dassanayake, L.S.K., Kodali, D.R., Ueno, S. et al. Physical Properties of Rice Bran Wax in Bulk and Organogels. J Am Oil Chem Soc 86, 1163–1173 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-009-1464-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-009-1464-6