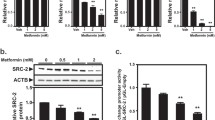
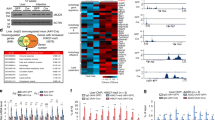
Abstract
The liver X receptor alpha (LXRα), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, has been shown to regulate the expression of the fatty acid synthase (FAS) gene through direct interaction with the FAS promoter. However, its regulation of gene expression is not completely understood. Histone modifications and chromatin remodeling are closely linked to transcriptional activation of genes. In the present study, we examined the effect of LXRα activation or silencing on histone modifications (i.e., acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation) across the FAS gene, with the aim to investigate whether LXRα could regulate its target gene expression at the epigenetic level. The addition of LXR agonist T0901317 or ectopic expression of LXRα stimulated the FAS transcription, which was coupled with increased levels of histones H3 and H4 acetylation and H3 phosphorylation and methylation at the LXR response element (LXRE). LXR ligation or overexpression induced distinct histone modification patterns at the distal region 2,272 bp upstream from the transcription start site (TSS) and TSS of the FAS gene. Moreover, RNA interference-mediated downregulation of LXRα impaired the histone acetylation and methylation but not phosphorylation on the FAS gene. In conclusion, we provide evidence that LXRα ligation-mediated transcriptional activation of the FAS gene is associated with LXRα-dependent histone acetylation and methylation rather than phosphorylation on this target gene.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASC-2:
-
Activating signal cointegrator-2
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- FAS:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- FXR:
-
Farnesoid X-receptor
- LXR:
-
Liver X receptor
- LXRE:
-
LXR response element
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- TSS:
-
Transcription start site
References
Joseph SB, Laffitte BA, Patel PH, Watson MA, Matsukuma KE, Walczak R, Collins JL, Osborne TF, Tontonoz P (2002) Direct and indirect mechanisms for regulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression by liver X receptors. J Biol Chem 277:11019–11025
Laffitte BA, Chao LC, Li J, Walczak R, Hummasti S, Joseph SB, Castrillo A, Wilpitz DC, Mangelsdorf DJ, Collins JL, Saez E, Tontonoz P (2003) Activation of liver X receptor improves glucose tolerance through coordinate regulation of glucose metabolism in liver and adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5419–5424
Lehmann JM, Kliewer SA, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Oliver BB, Su JL, Sundseth SS, Winegar DA, Blanchard DE, Spencer TA, Willson TM (1997) Activation of the nuclear receptor LXR by oxysterols defines a new hormone response pathway. J Biol Chem 272:3137–3140
Korf H, Vander Beken S, Romano M, Steffensen KR, Stijlemans B, Gustafsson JA, Grooten J, Huygen K (2009) Liver X receptors contribute to the protective immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. J Clin Invest 119:1626–1637
Zhao C, Dahlman-Wright K (2010) Liver X receptor in cholesterol metabolism. J Endocrinol 204:233–240
Peet DJ, Turley SD, Ma W, Janowski BA, Lobaccaro JM, Hammer RE, Mangelsdorf DJ (1998) Cholesterol and bile acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Cell 93:693–704
Sul HS, Wang D (1998) Nutritional and hormonal regulation of enzymes in fat synthesis: studies of fatty acid synthase and mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase gene transcription. Annu Rev Nutr 18:331–351
Soncini M, Yet SF, Moon Y, Chun JY, Sul HS (1995) Hormonal and nutritional control of the fatty acid synthase promoter in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 270:30339–30343
Demeure O, Duby C, Desert C, Assaf S, Hazard D, Guillou H, Lagarrigue S (2009) Liver X receptor alpha regulates fatty acid synthase expression in chicken. Poult Sci 88:2628–2635
Mellor J (2006) Dynamic nucleosomes and gene transcription. Trends Genet 22:320–329
Buranapramest M, Chakravarti D (2009)Chromatin remodeling and nuclear receptor signaling. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 87:193–234
Li X, Wong J, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW (2003) Progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors recruit distinct coactivator complexes and promote distinct patterns of local chromatin modification. Mol Cell Biol 23:3763–3773
Ananthanarayanan M, Li S, Balasubramaniyan N, Suchy FJ, Walsh MJ (2004) Ligand-dependent activation of the farnesoid X-receptor directs arginine methylation of histone H3 by CARM1. J Biol Chem 279:54348–54357
Kalaany NY, Mangelsdorf DJ (2006) LXRS and FXR: the yin and yang of cholesterol and fat metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 68:159–191
Stayrook KR, Rogers PM, Savkur RS, Wang Y, Su C, Varga G, Bu X, Wei T, Nagpal S, Liu XS, Burris TP (2008) Regulation of human 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C4) expression by the liver X receptor alpha. Mol Pharmacol 73:607–612
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Tong EH, Guo JJ, Xu SX, Mak K, Chung SK, Chung SS, Huang AL, Ko BC (2009) Inducible nucleosome depletion at OREBP-binding-sites by hypertonic stress. PLoS One 4:e8435
Li G, Reinberg D (2011) Chromatin higher-order structures and gene regulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 21:175–186
Rosenfeld MG, Lunyak VV, Glass CK (2006) Sensors and signals: a coactivator/corepressor/epigenetic code for integrating signal-dependent programs of transcriptional response. Genes Dev 20:1405–1428
Lonard DM, O’malley BW (2007) Nuclear receptor coregulators: judges, juries, and executioners of cellular regulation. Mol Cell 27:691–700
Kim DH, Lee J, Lee B, Lee JW (2009) ASCOM controls farnesoid X receptor transactivation through its associated histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferase activity. Mol Endocrinol 23:1556–1562
Lee S, Lee J, Lee SK, Lee JW (2008) Activating signal cointegrator-2 is an essential adaptor to recruit histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferases MLL3 and MLL4 to the liver X receptors. Mol Endocrinol 22:1312–1319
Kiskinis E, Hallberg M, Christian M, Olofsson M, Dilworth SM, White R, Parker MG (2007) RIP140 directs histone and DNA methylation to silence Ucp1 expression in white adipocytes. EMBO J 26:4831–4840
DiRenzo J, Shang Y, Phelan M, Sif S, Myers M, Kingston R, Brown M (2000) BRG-1 is recruited to estrogen-responsive promoters and cooperates with factors involved in histone acetylation. Mol Cell Biol 20:7541–7549
Boulias K, Talianidis I (2004) Functional role of G9a-induced histone methylation in small heterodimer partner-mediated transcriptional repression. Nucleic Acids Res 32:6096–6103
Chen H, Lin RJ, Xie W, Wilpitz D, Evans RM (1999) Regulation of hormone-induced histone hyperacetylation and gene activation via acetylation of an acetylase. Cell 98:675–686
Grunstein M (1997) Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 389:349–352
Struhl K (1998) Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Genes Dev 12:599–606
Wagner BL, Valledor AF, Shao G, Daige CL, Bischoff ED, Petrowski M, Jepsen K, Baek SH, Heyman RA, Rosenfeld MG, Schulman IG, Glass CK (2003) Promoter-specific roles for liver X receptor/corepressor complexes in the regulation of ABCA1 and SREBP1 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 23:5780–5789
Esteller M (2007) Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Nat Rev Genet 8:286–298
Stewart MD, Li J, Wong J (2005) Relationship between histone H3 lysine 9 methylation, transcription repression, and heterochromatin protein 1 recruitment. Mol Cell Biol 25:2525–2538
Wright JR, Siegel TN, Cross GA (2010) Histone H3 trimethylated at lysine 4 is enriched at probable transcription start sites in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol 172:141–144
Vermeulen M, Mulder KW, Denissov S, Pijnappel WW, van Schaik FM, Varier RA, Baltissen MP, Stunnenberg HG, Mann M, Timmers HT (2007) Selective anchoring of TFIID to nucleosomes by trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 4. Cell 131:58–69
Nowak SJ, Corces VG (2004) Phosphorylation of histone H3: a balancing act between chromosome condensation and transcriptional activation. Trends Genet 20:214–220
Lo WS, Trievel RC, Rojas JR, Duggan L, Hsu JY, Allis CD, Marmorstein R, Berger SL (2000) Phosphorylation of serine 10 in histone H3 is functionally linked in vitro and in vivo to Gcn5-mediated acetylation at lysine 14. Mol Cell 5:917–926
Alberti S, Schuster G, Parini P, Feltkamp D, Diczfalusy U, Rudling M, Angelin B, Björkhem I, Pettersson S, Gustafsson JA (2001) Hepatic cholesterol metabolism and resistance to dietary cholesterol in LXRbeta-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 107:565–573
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (30871160).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Wu, J., Yang, M. et al. Involvement of Liver X Receptor Alpha in Histone Modifications Across the Target Fatty Acid Synthase Gene. Lipids 47, 249–257 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-011-3635-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-011-3635-0