Abstract
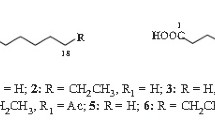
The present work characterizes novel FA in the royal jelly of honeybees (Apis mellifera). TLC analysis showed that the chloroform/methanol extract obtained from royal jelly consists mainly of FA. The FABMS spectrum of this extract gave several ion peaks due to compounds with higher M.W. than those of the FA so far reported. The methanol extract was found to contain unknown phospholipids. By means of reversed-phase HPLC with various solvent systems, 13 compounds were obtained in pure state. Their structures including absolute configurations were determined by chemical, NMR, and MS spectral analysis. Six compounds were identified as novel mono- or diesters of 10-hydroxy-2E-decenoic acid in which the hydroxyl group was esterified by another FA unit, and one was hydroxy-2E-decenoic acid 10-phosphate. In addition, we demonstrated that 9-hydroxy-2E-decenoic acid exists as a mixture of optical isomers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HDA:
-
hydroxy-2E-decenoic acid
- HMBC:
-
2-D heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation
- MTPA:
-
2-methoxy-2-trifluoromethylphenylacetate
References
Tamura, T., Fuji, A., and Kubota, N. (1987) Anti-tumor Effects of Royal Jelly (RJ), Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 89, 73–80 (in Japanese).
Sauerwald, N., Polster, J., Bengsch, E., Niessen, L., and Vogel, R.F. (1998) Combined Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Water-soluble Fraction of Royal Jelly, Adv. Food Sci. 20, 46–52.
Kamakura, M., Mitani, N., Fukuda, T., and Fukushima, M. (2001) Anti-fatigue Effect of Fresh Royal Jelly in Mice, J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 47, 394–401.
Tokunaga, K., Yoshida, C., Suzuki, K., Maruyama, H., Futamura, Y., Araki, Y., and Mishima, S. (2004) Antihypertensive Effect of Peptides from Royal Jelly in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27, 189–192.
Takenaka, T. (1982) Chemical Composition of Royal Jelly, Honeybee Sci. 3, 69–74.
Svoboda, J.A., Herbert, E.W., Jr., Thompson, M.J., and Feldlaufer, M.F. (1986) Selective Sterol Transfer in the Honey Bee: Its Significance and Relationship to Other Hymenoptera, Lipids 21, 97–101.
Lercker, G., Capella, P., Conte, L.S., Ruini, F., and Giordani, G. (1981) Components of Royal Jelly: I. Identification of the Organic Acids, Lipids 16, 912–919.
Antinelli, J.-F., Davico, R., Rognone, C., Faucon, J.-P., and Lizzani-Cuvelier, L. (2002) Application of Solid/Liquid Extraction for the Gravimetric Determination of Lipids in Royal Jelly, J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 2227–2230.
Barker, S.A., Foster, A.B., Lamb, D.C., and Hodgson, N. (1959) Identification of 10-Hydroxy-Δ2-Decenoic Acid in Royal Jelly, Nature 183, 996–997.
Butenandt, A., and Rembold, H. (1957) Über den Weiselzellenfuttersaft der Honigbiene I. Isolierung, Konstitutionsermittlung und Vorkommen der 10-Hydroxy-Δ2-decensäure, Z. Physiol. Chem. 308, 284–289.
Brown, W.H., and Freure, R.J. (1959) Some Carboxylic Acids Present in Royal Jelly, Can. J. Chem. 37, 2042–2046.
Townsend, G.F., Morgan, J.F., and Hazlett, B. (1959) Activity of 10-Hydroxydecenoic Acid from Royal Jelly Against Experimental Leukaemia and Ascitic Tumours, Nature 183, 1270–1271.
Pollet, S., Bottex-Gauthier, C., Li, M., Potier, P., Favier, A., and Vidal, D. (2002) Insight into Some of the Signaling Pathways Triggered by a Lipid Immunomodulator, Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 24, 527–546.
Koya-Miyata, S., Okamoto, I., Ushio, S., Iwaki, K., Ikeda, M., and Kurimoto, M. (2004) Identification of a Collagen Production-promoting Factor from an Extract of Royal Jelly and Its Possible Mechanism, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 68, 767–773.
Dittmer, J.C., and Lester, R.L. (1964) Specific Spray for the Detection of Phospholipids on Thin-layer Chromatograms, J. Lipid Res. 5, 126–127.
Kusumi, T., Ohtani, I., Inoue, Y., and Kakisawa, H. (1988) Absolute Configurations of Cytotoxic Marine Cembranolides: Consideration of Mosher’s Method, Tetrahedron Lett. 29, 4731–4734.
Ono, M., Yamada, F., Noda, N., Kawasaki, T., and Miyahara, K. (1993) Determination by Mosher’s Method of the Absolute Configurations of Mono- and Dihydroxyfatty Acids Originated from Resin Glycosides, Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 41, 1023–1026.
Breitmaier, E., and Voelter, W. (1987) Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy, 3rd edn., pp. 250–254, VCH Verlagsgeselschaft, Weinheim.
Robinson, S.R. (1960) The Biological Activity and Synthesis of Royal Jelly Acid, Croat. Chem. Acta 32, 119–122.
Pain, J., Barbier, M., Bogdanovsky, D., and Lederer, E. (1962) Some Carboxylic Acids Present in Royal Jelly, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 6, 233–241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, N., Umebayashi, K., Nakatani, T. et al. Isolation and characterization of some hydroxy fatty and phosphoric acid esters of 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid from the royal jelly of honeybees (Apis mellifera). Lipids 40, 833–838 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-005-1445-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-005-1445-6