Abstract
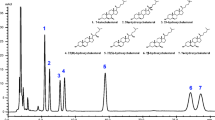
CLA, defined as one or more octadecadienoic acids (18∶2) with conjugated double bonds, has been reported to be active in a number of bological systems. GC and silver ion HPLC (Ag+-HPLC) have been the primary techniques for identifying specific CLA isomers in both foods and biological extracts. Recently, GC relative retention times were reported for all c,c, c/t (c,t and t,c), and t,t CLA FAME from the 6,8- to the 13,15-positions in octadecadienoic acid (18∶2). Presented here is the relative retention order of the same CLA FAME using Ag+-HPLC with two different elution systems. The first elution system, consisting of 0.1% acetonitrile/0.5% diethyl ether (DE)/hexane, has been used previously to monitor CLA composition in foods. Also presented here is the retention order of CLA FAME using 2% acetic acid/hexane elution solvent, which has advantages of more stable retention volumes and a complementary elution order of CLA FAME isomers. The data are reported using retention volumes (RV) adjusted for toluene, an estimator for dead volume, and relative to c9,t11-18∶2. Measurement of relative RV in the analysis of 88 samples of cow plasma, milk, and rumen fluids using Ag+-HPLC is also presented here. The % CV ranged from 1.04 to 1.62 for t,t isomers and from 0 to 0.48 for c/t isomers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DE:
-
diethyl ether
- MeCN:
-
acetonitrile
- RRV:
-
relative retention volume
- RV:
-
retention volume
References
Sehat, N., Kramer, J.K.G., Mossoba, M.M., Roach, J.A.G., Yurawecz, M.P., Eulitz, K., and Ku, Y. (1998) Identification of Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) Isomers in Cheese by Gas Chromatography, Silver Ion High Performance Liquid Chromatography, and Mass Spectral Reconstructed Ion Profiles: Comparison of Chromatographic Elution Sequences, Lipids 33, 963–971.
Yurawecz, M.P., and Morehouse, K.M. (2001) Silver-Ion HPLC of Conjugated Linoleic Acid Isomers, Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 103, 609–613.
Yurawecz, M.P., Roach, J.A.G., Sehat, N., Mossoba, M.M., Kramer, J.K.G., Fritsche, J., and Steinhart, H. (1998) A New Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) Isomer, 7-trans,9-cis-Octadecadienoic Acid, in Cow Milk, Cheese, Beef, and Human Milk and Adipose Tissue, Lipids 33, 803–809.
Delmonte, P., Roach, J.A.G., Mossoba, M.M., Losi, G., and Yurawecz, M.P. (2004) Synthesis, Isolation, and GC Analysis of All the 6,8- to 13,15-cis/trans Conjugated Linoleic Acid Isomers, Lipids 39, 185–191.
Corl, B., Baumgard, L.H., Griinari, J.M., Delmonte, P., Morehouse, K.M., Yurawecz, M.P., and Bauman, D.E. (2002) Trans-7,cis-9 CLA Is Synthesized Endogenously by Δ9-Desaturase in Dairy Cows, Lipids 37, 681–688.
Pollard, M.R., Gunstone, F.D., James, A.T., and Morris, L.J. (1980) Desaturation of Positional and Geometric Isomers of Monoenoic Fatty Acids by Microsomal Preparations from Rat Liver, Lipids 15, 306–314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Delmonte, P., Kataoka, A., Corl, B.A. et al. Relative retention order of all isomers of cis/trans conjugated linoleic acid FAME from the 6,8- to 13,15-positions using silver ion HPLC with two elution systems. Lipids 40, 509–514 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-005-1411-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-005-1411-3