Abstract
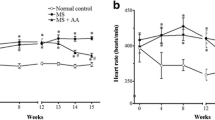
The aim of the present study was to investigate whether a mixture of dietary n−6 and n−3 PUFA could lower blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) of different ages. In addition, we studied how such a treatment could normalize the FA composition of plasma TAG and cholesterol esters (CE), and of red blood cell (RBC) total lipids. SHR (ages 4, 19, and 50 wk) were fed a normal diet (control groups) or a semisynthetic diet containing a mixture of γ-linolenic acid (GLA), EPA, and DHA (experimental groups). Systolic blood pressure was measured at regular intervals. After 11 wk of consuming this diet, plasma TAG and CE were separated by TLC and analyzed for their FA composition. Total FA composition of RBC was also determined. The degree to which blood pressure was elevated was reduced in SHR after 11 wk of diet. The largest decrease was obtained with the oldest animals. In RBC, EPA and DHA contents increased. In plasma TAG and CE, EPA, DHA, and GLA increased whereas arachidonic acid decreased. The n−6 and n−3 unsaturated FA mix slowed the development of hypertension in young SHR and decreased blood pressure in adult and aged SHR. In addition, the present treatment altered the n−3 and n−6 PUFA content of SHR lipids to that seen in normotensive rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CE:
-
cholesterol ester
- DGLA:
-
dihomo-γ-linolenic acid
- GLA:
-
γ-linolenic acid
- RBC:
-
red blood cells
- SHR:
-
spontaneously hypertensive rat
- WKY:
-
Wistar Kyoto rat
References
Lorenz, R., Spengler, U., Fischer, S., Duhm, J., and Weber, P.C. (1983) Platelet Function, Thromboxane Formation and Blood Pressure Control During Supplementation of the Western Diet with Cod Liver Oil, Circulation 67, 504–511.
Morris, M.C., Sacks, F., and Rosner, B. (1993) Does Fish Oil Lower Blood Pressure? A Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials, Circulation 88, 523–533.
Bao, D.Q., Mori, T.A., Burke, V., Puddey, I.B., and Beilin, L.J. (1998) Effects of Dietary Fish and Weight Reduction on Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Overweight Hypertensives, Hypertension 32, 710–717.
Howe, P.R.C., Rogers, P.F., and Lungershausen, Y. (1991) Blood Pressure Reduction by Fish Oil in Adult Rats with Established Hypertension—Dependence on Sodium Intake, Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 44, 113–117.
Yin, K., Chu, Z.M., and Beilin, L.S. (1991) Blood Pressure and Vascular Reactivity Changes in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Fed Fish Oil, Br. J. Pharmacol. 102, 991–997.
Bonaa, K.H., Bjerve, K.S., Straume, B., Gram, I.T., and Thelle, D. (1990) Effect of Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acids on Blood Pressure in Hypertension. A Population-Based Intervention Trial from the Tromsø Study, N. Engl. J. Med. 322, 795–801.
Sasaki, S., Nakamura, K., Uchida, A., Fujita, H., Itoh, H., Nakata, T., Takeda, K., and Nakagawa, M. (1995) Effects of Gamma-Linolenic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids on Blood Pressure in SHR, Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. (Suppl. 1), S306–S307.
Yin, K., Chu, Z.M., and Beilin, L.J. (1990) Effect of Fish Oil Feeding on Blood Pressure and Vascular Reactivity in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 17, 235–239.
Flaten, H., Hostmark, A.T., Kierulf, P., Lystad, E., Trygg, K., Bjerkedal, T., and Osland, A. (1990) Fish-Oil Concentrate: Effects on Variables Related to Cardiovascular Disease, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 300–306.
Wing, L.M., Nestel, P.J., Chalmers, J.P., Rouse, I., West, M.J., Bune, A.J., Tonkin, A.L., and Russell, A.E. (1990) Lack of Effect of Fish Oil Supplementation on Blood Pressure in Treated Hypertensives, J. Hypertens. 8, 339–343.
Cobiac, L., Clifton, P.M., Abbey, M., Belling, G.B., and Nestel, P.J. (1991) Lipid, Lipoprotein, and Hemostatic Effects of Fish vs. Fish-Oil n−3 Fatty Acids in Mildly Hyperlipidemic Males, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 53, 1210–1216.
Narce, M., Frenoux, J.M., Dardel, V., Foucher, C., Germain, S., Delachambre, M.C., and Poisson, J.P. (1997) Fatty Acid Metabolism, Pharmacological Nutrients and Hypertension, Biochimie 79, 135–138.
Hamazaki, T., Urakaze, M., Makuta, M., Ozawa, A., Soda, Y., Tatsumi, H., Yano, S., and Kumagai, A. (1987) Intake of Different Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Containing Lipids and Fatty Acid Pattern of Plasma Lipids in the Rats, Lipids 22, 994–998.
Rao, C.V., Zang, E., and Reddy, B.S. (1993) Effect of High Corn Oil, Olive Oil and Fish Oil on Phospholipid Fatty Acid Composition in Male F344 Rats, Lipids 28, 441–447.
Prisco, D., Filippini, M., Francalanci, I., Paniccia, R., Gensini, G.F., Abbate, R., and Neri Serneri, G.G. (1996) Effect of n−3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake on Phospholipid Fatty Acid Composition in Plasma Erythrocytes, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 63, 925–932.
McLennan, P., Howe, P., Abeywardena, M., Muggli, R., Raederstorff, D., Mano, M., Rayner, T., and Head, R. (1996) The Cardiovascular Protective Role of Docosahexaenoic Acid, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 300, 83–89.
Schoene, N.W., and Fiore, D. (1981) Effect of a Diet Containing Fish Oil on Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, Prog. Lipid Res. 20, 569–570.
Rubin, D., and Laposata, M. (1992) Cellular Interactions Between n−6 and n−3 Fatty Acids: A Mass Analysis of Fatty Acid Elongation/Desaturation, Distribution Among Complex Lipids, and Conversion to Eicosanoids, J. Lipid Res. 33, 1431–1440.
Lands, W.E., Libelt, B., Morris, A., Kramer, N.C., Prewitt, T.E., Bowen, P., Schmeisser, D., Davidson, M.H., and Burns, J.H. (1992) Maintenance of Lower Proportions of (n−6) Eicosanoid Precursors in Phospholipids of Human Plasma in Response to Added Dietary (n−3) Fatty Acids, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1180, 147–162.
Watanabe, Y., Huang, Y.-S., Simmons, V.A., and Horrobin, D.F. (1989) The Effect of Dietary n−6 and n−3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Blood Pressure and Tissue Fatty Acid Composition in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, Lipids 24, 638–644.
Kirtland, S.J. (1988) Prostaglandin E1: A Review, Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 32, 165–174.
Mtabaji, J.P., Manku, M.S., and Horrobin, D.F. (1993) Abnormalities in Dihomo-γ-Linolenic Acid: Release in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension, Am. J. Hypertens. 6, 458–462.
Miettinen, T.A., Naukkarinen, V., Huttunen, J.K., Mattilas, J., and Kumlin, T. (1982) Fatty Acid Composition of Serum Predicts Myocardial Infarction, Br. Med. J. 285, 993–996.
Dyerberg, J., Bang, H.O., and Hjørne, N. (1975) Fatty Acid Composition of the Plasma Lipids in Greenland Eskimos, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 28, 958–966.
Engler, M.M., Engler, M.B., Erickson, S.K., and Paul, S.M. (1992) Dietary Gamma-Linolenic Acid Lowers Blood Pressure and Alters Aortic Reactivity and Cholesterol Metabolism in Hypertension, J. Hypertens. 10, 1197–1204.
Hoffmann, P., Block, H.U., Bietz, J., Taube, C., Forster, W., Wortha, P., Singer, P., Naumann, E., and Heine, H. (1986) Comparative Study of the Blood Pressure Effects of Four Different Vegetable Fats on Young, Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, Lipids 21, 733–737.
St. Louis, C., Lee, R.M.K.W., Rosenfeld, J., and Fargas-Babjak, A. (1992) Antihypertensive Effect of γ-Linolenic Acid in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, Hypertension 19 (2 Supp.), II-111–II-115.
Narce, M., and Poisson, J.-P. (1995) Age-Related Depletion of Linoleic Acid Desaturation in Liver Microsomes from Young Hypertensive Rats, Prostaglandins Leukotr. Essent. Fatty Acids 53, 59–63.
Simon, J.A., Hodgkins, M.L., Browner, W.S., Neuhaus, J.M., Bernert, J.T., and Hulley, S.B. (1995) Serum Fatty Acids and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Am. J. Epidemiol. 142, 469–476.
Bonaa, K.H., and Thelle, D.S. (1991) Association Between Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids in a Population. The Tromsø Study, Circulation 83, 1305–1315.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Sloane-Stanley, G.H. (1957) A Simple Method for Isolation and Purification of Total Lipids from Animal Tissues, J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509.
Slover, H.T., and Lanza, E. (1979) Quantitative Analysis of Food Fatty Acids by Capillary Gas Chromatography, J. Am. Oil Soc. 56, 933–943.
Narce, M., Asdrubal, P., Delachambre, M.-C., Gresti, J., and Poisson, J.-P. (1995) Influence of Spontaneous Hypertension on n−3 Δ6-Desaturase Activity and Fatty Acid Composition of Rat Hepatocytes, Mol. Cell. Biochem. 152, 7–12.
Yosefy, C., Viskoper, J.R., Varon, D., Ilan, I., Pilpel, D., Lugassy, G., Schneider, R., Savyon, N., Adan, Y., and Raz, A. (1996) Repeated Fasting and Refeeding with 20∶5n−3 Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA): A Novel Approach for Rapid Fatty Acid Exchange and Its Effect on Blood Pressure, Plasma Lipids and Hemostasis, J. Hum. Hypertens. 10 (Suppl. 3), S135–S139.
Engler, M.M., Engler, M.B., Goodfriend, T.L., Ball, D.L., Yu, Z., Su, P., and Kroetz, D.L. (1999) Docosahexaenoic Acid Is an Antihypertensive Nutrient That Affects Aldosterone Production in SHR, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 221, 32–38.
Lam, B.J., Marcinkiewicz, E., Quilley, J., Hirai, A., Yoshida, S., Tamura, Y., and Wong, P.Y.K. (1986) Hypotensive Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Its Influence on Eicosanoid Metabolism in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, J. Hypertens. 4 (Suppl.), S453–S455.
Mori, T.A., Bao, D.Q., Burke, V., Puddey, I.A., and Beilin, L.J. (1999) Docosahexaenoic Acid but Not Eicosapentaenoic Acid Lowers Ambulatory Blood Pressure and Heart Rate in Humans, Hypertension 34, 253–260.
Dyeberg, J., and Jorgensen, K.A. (1982) Marine Oils and Thrombogenesis, Prog. Lipid Res. 21, 255–269.
Foucher, C., Narce, M., Nasr, L., Delachambre, M.-C., and Poisson, J.-P. (1997) Liver Microsomal Membrane Fluidity and Microsomal Desaturase Activities in Adult Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, J. Hypertens. 15, 863–869.
Spector, A.A., and Yorek, M.A. (1985) Membrane Lipid Composition and Cellular Function, J. Lipid Res. 26, 1015–1035.
Van den Boom, M.A.P., Groot Wassink, M., Roelofsen, B., De Fouw, N.J., and Op Den Kamp, J.A.F. (1996) The Influence of a Fish-Oil-Enriched Diet on the Phospholipid Fatty Acid Turnover in the Rabbit Red Cell Membrane in vivo, Lipids 31, 285–293.
Russo, C., Olivieri, O., Guarini, P., Pasqualini, R., Azzini, M., and Corrocher, R. (1997) Increased Membrane Ratios of Metabolite to Precursor Fatty Acid in Essential Hypertension, Hypertension 29, 1058–1063.
Christiansen, E.N., Lund, J.S., Rortveit, T., and Rustan, C.R. (1991) Effect of Dietary n−3 and n−6 Fatty Acids on Fatty Acid Desaturation in Rat Liver, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1082, 57–62.
Li, B., Birdwell, C., and Whelan, J. (1994) Antithetic Relationship of Dietary Arachidonic Acid and Eicosapentaenoic Acid on Eicosanoid Production in vivo, J. Lipid Res. 35, 1869–1877.
Leaf, A., and Weber, P.C. (1988) Cardiovascular Effects of n−3 Fatty Acids, N. Engl. J. Med. 318, 549–557.
Zheng, Z.J., Folsom, A.R., Ma, J., Arnett, D.K., McGovern, P.G., and Eckfeldt, J.H. (1999) Plasma Fatty Acid Composition and 6-Year Incidence of Hypertension in Middle-Aged Adults: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study, Am. J. Epidemiol. 150, 492–500.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bellenger-Germain, S., Poisson, J.P. & Narce, M. Antihypertensive effects of a dietary unsaturated FA mixture in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Lipids 37, 561–567 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-002-0933-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-002-0933-z