Abstract
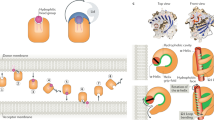
Fatty acids are the main structural and energy sources of the human body. Within the organism, they are presented to cells as fatty acid: albumin complexes. Dissociation from albumin represents the first step of the cellular uptake process, involving membrane proteins with high affinity for fatty acids, e.g., fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD 36) or the membrane fatty acid-binding protein (FABPpm). According to the thus created transmembrane concentration gradient, uncharged fatty acids can flip-flop from the outer leaflet across the phospholipid bilayer. At the cytosolic surface of the plasma membrane, fatty acids can associate with the cytosolic FABP (FABP c ) or with caveolin-1. Caveolins are constituents of caveolae, which are proposed to serve as lipid delivery vehicles for subcellular organelles. It is not known whether protein (FABP c )- and lipid (caveolae)-mediated intracellular trafficking of fatty acids operates in conjunction, or in parallel. Channeling fatty acids to the different metabolic pathways requires activation to acyl-CoA. For this process, the family of fatty acid transport proteins (FATP 1-5/6) might be relevant because they have been shown to possess acyl-CoA synthetase activity. Their variable N-terminal signaling sequences suggest that they might be targeted to specific organelles by anchoring in the phospholipid bilayer of the different subcellular membranes. At the highly conserved cytosolic AMP-binding site of FATP, fatty acids are activated to acyl-CoA for subsequent metabolic disposition by specific organelles. Overall, fatty acid uptake represents a continuous flow involving the following: dissociation from albumin by membrane proteins with high affinity for fatty acids; passive flip-flop across the phospholipid bilayer; binding to FABP c and caveolin-1 at the cytosolic plasma membrane; and intracellular trafficking via FABP c and/or caveolae to sites of metabolic disposition. The uptake process is terminated after activation to acyl-CoA by the members of the FATP family targeted intracellularly to different organelles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACBP:
-
acyl-CoA binding proteins
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- FABP c :
-
cytosolic fatty acid binding protein
- FABPpm :
-
plasma membrane fatty acid binding protein
- FAT:
-
fatty acid translocase
- FATP:
-
fatty acid transport protein
- mAspAT:
-
mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase
- PPAR:
-
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- VLDL:
-
very low density lipoproteins
References
Stremmel, W. (1987) Absorption of Fat and Fat-Soluble Vitamins, in Diabetes Forum Series, Structure and Function of the Small Intestine (Caspary, W.F., ed.), Vol. 1, pp. 175–184, Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam.
Tso, P., and Balint, J.A. (1986) Formation and Transport of Chylomicrons by Enterocytes to the Lymphatics, Am. J. Physiol. 250, G715-G726.
Van der Vusse, G.J., Glatz, J.F.C., Van Nieuwenhoven, F.A., Reneman, R.S., and Bassinthwaighte, J.B. (1998) Transport of Long-Chain Fatty Acids Across the Muscular Endothelium, in Skeletal Muscle Metabolism in Exercise and Diabetes (Richter, E.A., Galbo, H., Kiens, B., and Saltin B., eds.) pp. 181–191, Plenum Press, New York.
Spahr, R., Krutzfeldt, A., Mertens, S., Siegmund, B., and Piper, H.M. (1989) Fatty Acids Are Not an Important Fuel for Coronary Endothelial Cells, Mol. Cell. Biochem. 88, 59–64.
Schnitzer, J.E., Carley, W.W., and Palade, G.E. (1988) Specific Albumin Binding to Microvascular Endothelium in Culture, Am. J. Physiol. 254, H425-H437.
Scow, R.O., and Blanchette-Mackie, E.J. (1991) Transport of Fatty Acids and Monoacylglycerols in White and Brown Adipose Tissues, Brain Res. Bull. 27, 487–491.
Fitscher, B.A., Elsing, C., Riedel, H.D., Gorski, J., and Stremmel, W. (1996) Protein-Mediated Facilitated Uptake Process for Fatty Acids, Bilirubin, and Other Amphipatic Compounds, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 212, 15–23.
Noy, N., and Zakim, D. (1993) Physical Chemical Basis for the Uptake of Organic Compound, by Cells, in Hepatic Transport and Bile Secretion: Physiology and Pathophysiology (Tavaloni, N., and Berk, P.D., eds.), pp. 313–335, Raven Press, New York.
Hamilton, J.A., and Kamp, F. (1999) How Are Fatty Acids Transported in the Membranes? Is It by Proteins or by Free Diffusion Through the Lipids? Diabetes 48, 2255–2269.
Goresky, C.A., Stremmel, W., Rose, P., Guirguis, S., Schwab, A.J., Diede, H.E., and Ibrahim, E. (1994) The Capillary Transport System for Free Fatty Acids in the Heart, Circulation Res. 74, 1015–1026.
Weisiger, R., Gollan, J., and Ockner, R. (1981) Receptor for Albumin on the Liver Cell Surface May Mediate Uptake of Fatty Acids and Other Albumin-Bound Substances, Science 211, 1048–1051.
Stremmel, W., Potter, B.J., and Berk, P.D. (1983) Studies of Albumin Binding to Rat Liver Plasma Membranes: Implications for the Albumin Receptor Hypothesis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 756, 20–27.
Berk, P.D., and Stermmel, W. (1986) Hepatocellular Uptake of Organic Anions, in Progress in Liver Disease (Popper, H., and Schaffner, F., eds.), Vol. 8, pp. 25–144, Grune & Stratton, New York.
Stremmel, W. (1988) Fatty Acid Uptake by Isolated Rat Heart Mycocytes Represents, a Carrier Mediated Transport Process, J. Clin. Invest. 81, 844–852.
Stremmel, W. (1988) Uptake of Fatty Acids by Jejenal Mucosal Cells Is Mediated by a Specific Fatty Acid Binding Membrane Protein, J. Clin. Invest. 82, 2001–2010.
Stremmel, W., Strohmeyer, G., and Berk, P.D. (1986) Hepatocellular Uptake of Oleate Is Energy Dependent, Sodium Linked, and Inhibited by an Antibody to a Hepatocyte Plasma Membrane Fatty Acid Binding Protein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 3584–3588.
Maniscalco, W.M., Stremmel, W., and Heeney, M. (1990) Uptake of Palmitic Acid by Rabbit Alveolar Type II Cells, Am. J. Physiol. 259, 206–212.
Elsing, C., Gorski, J., Boeker, C., and Stremmel, W. (1998) Long-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake by Skeletal Myocytes: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Study, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 54, 744–750.
Schürer, N.Y., Stremmel, W., Grundmann, J.U., Schliep, V., Kleinert, H., Bass, N.M., and Williams, M.L. (1994) Evidence for a Novel Keratinocyte Fatty Uptake Mechanism with Preference for Linoleic Acid: Comparison of Oleic and Linoleic Acid Uptake by Cultured Human Keratinocytes, Fibroblasts and a Human Hepatoma Cell Line, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1211, 51–60.
Trimble, M.E. (1989) Mediated Transport of Long Chain Fatty Acids by Rat Renal Basolateral Membranes, Am. J. Physiol. 257, F539-F546.
Schwieterman, W., Sorrentino, D., Potter, B.J., Rand, J., Kiang, C.-L., Stump, D., and Berk, P.D. (1988) Uptake of Oleate by Isolated Rat Adipocytes Is Mediated by a 40-kD Plasma Membrane Fatty Acid Binding Protein Closely Related to That in Liver and Gut, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 359–363.
Stremmel, W., and Theilmann L. (1986) Selective Inhibition of Long Chain Fatty Acid Uptake in Short-Term Cultured Rat Hepatocytes by an Antibody to the Rat Liver Plasma Membrane Fatty Acid Binding Protein, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 877, 191–197.
Stremmel, W., and Berk, P.D. (1986) Hepatocellular Influx of 14C-Oleate Reflect Membrane Transport Rather Than Intracellular Metabolism or Binding, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 3086–3090.
Stremmel, W., and Gunawan, J. (1998) Indication for a Specific Interaction of Fatty Acids with a Liver Sinusoidal Plasma Membrane Carrier, Eur. J. Med. Res. 3, 71–76.
Sorrentino, D., Stump, D.D., van Ness, K., Simard, A., Schwab, A.J., Zhou, S.L., Goresky, C.A., and Berk, P.D. (1996) Oleate Uptake by Isolated Hepatocytes and the Perfused Rat Liver Is Competitively Inhibited by Palmitate, Am. J. Physiol. 270, G385-G392.
Vyska, K., Stremmel, W., Meyer, W., Notohamiprodio, M.K., Meyer, H., and Körfer, R. (1994) Effects of Temperature and Sodium on Myocardial and Hepatocellular Fatty Acid Uptake, Circ. Res. 74, 1–13.
Stremmel, W. (1988) Translocation of Fatty Acids Across the Basolateral Rat Liver Plasma Membrane Is Driven by an Active, Potential Sensitive, Sodium Dependent Transport System, J. Biol. Chem. 262, 6284–6289.
Elsing, C., Kassner, A., and Stremmel, W. (1996) Effect of Surface and Intracellular pH on Hepatocellular Fatty Acid Uptake, Am. J. Physiol. 271, G1067-G1073.
Storch, J., and Thumser, E.A. (2000) The Fatty Acid Transport Function of Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1486, 28–44.
Glatz, J.F.C., and Storch, J. (2001) Unraveling the Significance of Cellular Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins, Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 12, 267–274.
Spitsberg, V.L., Matitashvili, E., and Gorewit, R.C. (1995) Association and Coexpression of Fatty-Acid-Binding Protein and Glycoprotein CD36 in the Bovine Mammary Gland, Eur. J. Biochem. 230, 872–878.
Glatz, J.F., and Van der Vusse, J. (1996) Cellular Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins: Their Function and Physiological Significance, Prog. Lipid Res. 35, 243–282.
gorski, J., Elsing, C., Bucki, R., Zendzian-Piotrowska, M., and Stremmel, W. (1996) The Plasma Borne Free Fatty Acids Rapidly Enter Hepatocellular Nuclei, Life Sci. 59, 2209–2215.
Trigatti, B.L., Anderson, R.G., and Gerber, G.E. (1999) Identification of Caveolin-1 as a Fatty Acid Binding Protein, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 255, 34–39.
Kurzchalia, T.V., and Parton, R.G. (1999) Membrane Microdomains and Caveolae, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 424–431.
Anderson, R.G.W. (1998) The Caveolae Membrane System, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 199–225.
Pol, A., Luetterforst R., Lindsay, M., Heino, S., Ikonen, E., and Parton, R.G. (2001) A Caveolin Dominant Negative Mutant Associates with Lipid Bodies and Induces Intracellular Cholesterol Imbalance, J. Cell Biol. 152, 1057–1070.
Elsing, C., Winn-Börner, U., and Stremmel, W. (1995) Confocal Analysis of Hepatocellular Long-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake, Am. J. Physiol. 269, G842-G851.
Vance, D.E., and Vance, J. (1996) Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Abumrad, N.A., el-Maghrabi, M.R., Amri, E.Z., Lopez, E., and Grimaldi, P.A. (1993) Cloning of a Rat Adipocyte Membrane Protein Implicated in Binding or Transport of Long-Chain Fatty Acids That Is Induced During Preadipocyte Differentiation. Homology with Human CD 36, J. Biol. Chem. 268, 17665–17668.
Abumrad, N., Coburn, C., and Ibrahimi, A. (1999) Membrane Proteins Implicated in Long-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake by Mammalian Cells: CD36, FATP and FABPpm, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1441, 4–13.
Ibrahimi, A., Sfeir, Z., Magharaie, H., Amri, E.Z., Grimaldi, P., and Abumrad, N.A. (1996) Expression of the CD36 Homolog (FAT) in Fibroblast, Cells: Effects on Fatty Acid Transport, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 2646–2651.
Babitt, J., Trigatti, B., Rigotti, A., Smart, E.J., Anderson, R.G., Xu, S., and Krieger, M. (1997) Murine SR-BI, a High Density Lipoprotein Receptor That Mediates Selective Lipid Uptake, Is N-Glycosylated and Colocalizes with Plasma Membrane Caveolae, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 13242–13249.
Bonen, A., Luiken, J.J., Arumugam, Y., Glatz, J.F., and Tandon, N.N. (2000) Acute Regulation of Fatty Acid Uptake Involves the Cellular Redistribution of Fatty Acid Translocase, J. Biol. Chem. 275, 14501–14508.
Febbraio, M., Abumrad, N.A., Hajjar, D.P., Sharma, K., Cheng, W., Pearce, S.F., and Silverstein, R.L. (1999) A Null Mutation in Murine CD 36 Reveals, an Important Role in Fatty Acid and Lipoprotein Metabolism, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 19055–19062.
Berk, P.D., Wada, H., Horio, Y., Potter, B.J., Sorrentino, D., Zhou, S.L., Isola, L.M., Stump, D., Kiang, C.L., and Thung, S. (1990) Plasma Membrane Fatty Acid-Binding Protein and Mitochondrial Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase of Rat Liver Are Related, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 3484–3488.
Stremmel, W., Strohmeyer, G., Borchard, F., Kochowa, S., and Berk, P.D. (1985) Isolation and Partial Characterization of a Fatty Acid Binding Protein from Rat Liver Plasma Membranes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 4–8.
Zhou, S.L., Stump, D., Isola, L.M., and Berk, P.D. (1994) Constitutive Expression of a Saturable Transport System for Non-Esterified Fatty Acids in Xenopus laevis Oocytes, Biochem. J. 297, 315–319.
Isola, L.M., Zhou, S.-L., Kiang, C.-L., Stump, D.D., Bradbury, M.W., and Berk, P.D. (1995) 3T3 Fibroblasts Transfected with a cDNA for Mitochondrial Asparate Aminotransferase Express Plasma Membrane Fatty Acid-Binding Protein and Saturable Fatty Acid Uptake, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9866–9870.
Schaffer, J.E., and Lodish, H.F. (1994) Expression Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Adipocyte Long Chain Fatty Acid Transport Protein. Cell 79, 427–436.
Hirsch, D., Stahl, A., and Lodish, H.F. (1998) A Family of Fatty Acid Transporters Conserved from Mycobacterium to Man, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8625–8629.
Lewis, S.E., Listenberger, L.L., Ory, D.S., and Schaffer, J.E. (2001) Membrane Topology of the Murine Fatty Acid Transport Protein 1 (FATP1), J. Biol. Chem. 276, 37042–37050.
Stuhlsatz-Krouper, S.M., Bennett, N.E., and Schaffer, J.E. (1998) Substitution of Alanine for Serine 250 in the Murine Fatty Acid Transport Protein Inhibits Long Chain Fatty Acid Transport, J. Biol. Chem. 273, 28642–28650.
Coe, N.R., Smith, A.J., Frohnert, B.I., Watkins, P.A., and Bernlohr, D.A. (1999) The Fatty Acid Transport Protein (FATP1) Is a Very Long Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 36300–36304.
Uchiyama, A., Aoyama, T., Kamijo, K., Uchida, Y., Kondo, N., Orii, T., and Hashimoto, T. (1996) Molecular Cloning of cDNA Encoding Rat Very Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase, J. Biol. Chem. 271, 30360–30365.
Berger, J., Truppe, C., Neumann, H., and Forss-Petter, S. (1998) cDNA Cloning and mRNA Distribution of a Mouse Very Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase, FEBS Lett. 425, 305–309.
Steinberg, S.J., Wang, S.J., Kim, D.G., Mihalik, S.J., and Watkins, P.A. (1999) Human Very-Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase: Cloning, Topography, and Relevance to Branched-Chain Fatty Acid Metabolism, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 615–621.
Steinberg, S.J., Wang, S.J., McGuinness, M.C., and Watkins, P.A. (1999) Human Liver-Specific Very-Long-Chain Acyl-Coenzyme A Synthetase: cDNA Cloning and Characterization of a Second Enzymatically Active Protein, Mol. Genet. Metab. 68, 32–42.
Herrmann, T., Buchkremer, F., Gosch, I., Hall, A.M., Bernlohr, D.A., and Stremmel, W. (2001) Mouse Fatty Acid Transport Protein 4 (FATP 4): Characterization of the Gene and Functional Assessment as a Very Long Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase, Gene 270, 31–40.
Frohnert, B.I., and Bernlohr, D.A. (2000) Regulation of Fatty Acid Transporters in Mammalian Cells, Prog. Lipid Res. 39, 83–107.
Sprong, H., van der Sluijs, P., and van Meer, G. (2001) How Proteins Move Lipids and Lipids Move Proteins, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 504–512.
Stahl, A., Gimeno, R.E., Tartaglia, L.A., and Lodish, H.F. (2001) Fatty Acid Transport Proteins: A Current View of a Growing Family, Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 12, 266–273.
Stahl, A., Hirsch, D.J., Gimeno, R.E., Punreddy, S., Ge, P., Watson, N., Patel, S., Kotler, M., Raimondi, A., Tartaglia, L.A., and Lodish, H.F. (1999) Identification of the Major Intestinal Fatty Acid Transport Protein, Mol. Cell 4, 299–308.
Zucker, S.D. (2001) Kinetic Model of Protein-Mediated Ligand Transport: Influence of Soluble Binding Proteins on the Intermembrane Diffusion of a Fluorescent Fatty Acid, Biochemistry 40, 977–986.
Wu, F., Corsico, B., Flach, C.R., Cistola D.P., Storch, J., and Mendelsohn, R. (2001) Delection of the Helical Motif in the Intestinal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Reduces Its Interactions with Membrane Monolayers: Brewster Angle Microscopy, IR Reflection-Absorption Spectroscopy, and Surface Pressure Studies, Biochemistry 40, 1976–1983.
Smith, E.R., and Storch, J. (1999) The Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Binds to Membranes by Electrostatic Interactions, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 35325–35330.
Davies, J.K., Thumser, A.E., and Wilton, D.C. (1999) Binding of Recombinant Rat Liver Fatty Acid-Binding Protein to Small Anionic Phospholipid Vesicles Results in Ligand Release: A Model for Interfacial Binding and Fatty Acid Targeting, Biochemistry, 38, 16932–16940.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Stremmel, W., Pohl, J., Ring, A. et al. A new concept of cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of long-chain fatty acids. Lipids 36, 981–989 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0809-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0809-2